方式一:
主函数指针初始化,子函数对指针值进行赋值
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void sonFunc(int *c)
{
*c = 100;
printf("The value of the C is :%d\n",*c);
printf("The address of the C is :0x%x\n",c);
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int *b;
printf("The address of the A is : 0x%x\n", &a);
printf("The address of the B is : 0x%x\n", b);
/* 指针初始化 */
b = &a;
printf("The value of the B is : %d\n", *b);
printf("The address of the B is : 0x%x\n", b);
/* 传递int型指针b */
sonFunc(b);
printf("The value of the B is : %d\n", *b);
return 0;
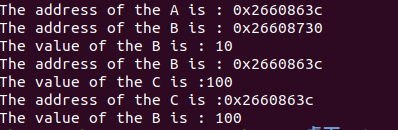
}结果:指针b初始化之后的地址,与传入到子函数中的地址保持一致。
方式二:
主函数定义整型变量,传递整型变量地址,子函数对*(&a)进行赋值;
子函数 sonFunb()中,地址的赋值(局部生效),在回到主函数后实效。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void sonFunc(int *c)
{
*c = 100;
printf("The value of the C is :%d\n",*c);
printf("The address of the C is :0x%x\n",c);
}
void sonFunb(int *b)
{
int d = 111;
printf("The address of the B is : 0x%x\n", b);
printf("The address of the D is :0x%x\n",&d);
/* 子函数中地址赋值,不改变主函数中变量a的地址 */
b = &d;
printf("The address of the B is :0x%x\n",b);
printf("The value of the B is :%d\n",*b);
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
printf("The address of the A is : 0x%x\n", &a);
/* 传递int型变量a的地址 */
sonFunb(&a);
printf("The address of the A is : 0x%x\n", &a);
printf("The value of the A is : %d\n", a);
/* 传递int型变量a的地址 */
sonFunc(&a);
printf("The address of the A is : 0x%x\n", &a);
printf("The value of the A is : %d\n", a);
return 0;
}结果:

函数指针传参的问题,归根结底还是传参地址的问题,一些细节体现在上述给出的代码中了。






















 3854
3854











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








