前言:
本文的代码是 LearnOpenGL 中对应代码,这里提供学习,大家喜欢的可去官方网站去看看:
https://learnopengl-cn.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/![]() https://learnopengl-cn.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/本章简单讲解GLSL 中的简单使用,详细知识点请查阅对应书籍
https://learnopengl-cn.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/本章简单讲解GLSL 中的简单使用,详细知识点请查阅对应书籍
GLSL:
着色器是使用一种叫GLSL的类C语言写成的。 GLSL是为图形计算量身定制的, 它包含针对向
量和矩阵操作的有用特性。
比如我们顶点着色器写成:
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 position; // 位置变量的属性为0
out vec4 vertexColor; // 为片段着色器指定一个颜色输出
void main()
{
gl_Position = vec4(position, 1.0); // 把一个vec3作为vec4的构造器的参数
vertexColor = vec4(0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f); // 把输出颜色设置为暗红色
}这里我们看到有layout out ,其实我们常用的就是 in out 、layout、uniform这几个,下面我给你们讲下基本情况,大家也就了解了。
in 与 out
在shader.vs 文件下:
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 position;
out vec4 vertexColor;
void main()
{
gl_Position = vec4(position.x, position.y, position.z, 1.0);
vertexColor = vec4(0.5f,0.0f,0.0f,1.0f);
}
在shader.fs 文件下:
#version 330 core
out vec4 color;
in vec4 vertexColor;
void main()
{
color = vertexColor;//RGBA
}
我们可以看到里面都有个变量vertexColor,在顶点着色器中输出,然后在片段着色器接受,然后在给颜色。
输出结果:
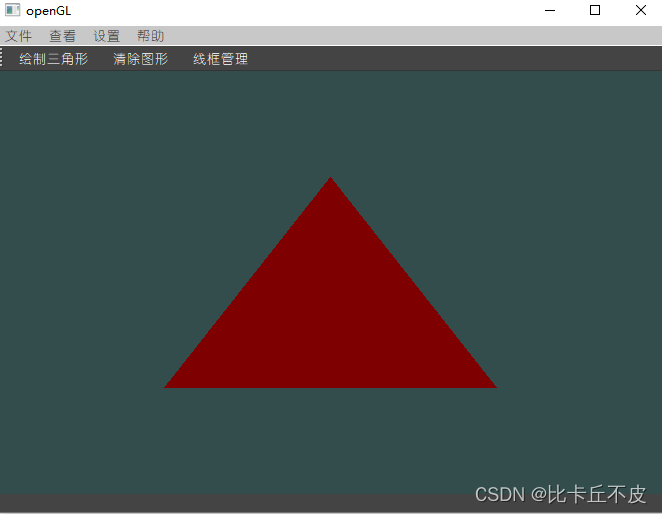
如何理解in 与 out 呢:
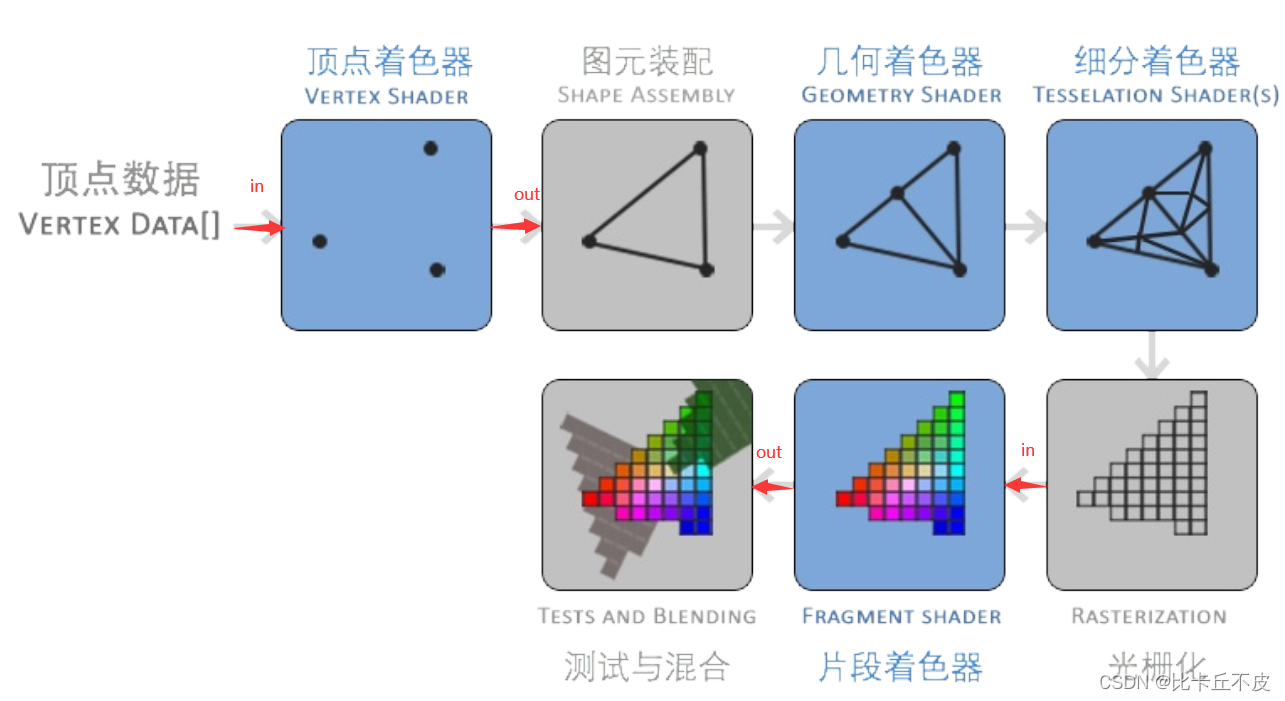
如图,in 就是给这个着色器的值,out 就是送出去的值。这下,你懂了吧。
全部代码:
#ifndef BKQOPENGLW_H
#define BKQOPENGLW_H
#include <QOpenGLWidget>
#include <QOpenGLFunctions_3_3_Core>
#include <QOpenGLShaderProgram>
class BKQOpenglW : public QOpenGLWidget, QOpenGLFunctions_3_3_Core
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
enum Shape{None,Rect,circle,Triangle};
explicit BKQOpenglW(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
~BKQOpenglW();
void drawShapes(Shape shape);
void setWireFrame(bool b);
protected:
virtual void initializeGL();
virtual void resizeGL(int w, int h);
virtual void paintGL();
signals:
public slots:
private:
unsigned int VBO, VAO;
Shape m_Shape;
QOpenGLShaderProgram shaderProgram;
};
#endif // BKQOPENGLW_H
cpp
#include "bkqopenglw.h"
#include<iostream>
const float vertices[] = {
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // left
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // right
0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f // top
};
//顶点着色器
const char *vertexShaderSource = "#version 330 core\n"
"layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;\n"
"void main()\n"
"{\n"
" gl_Position = vec4(aPos.x, aPos.y, aPos.z, 1.0);\n"
"}\0";
//片段着色器
const char *fragmentShaderSource = "#version 330 core\n"
"out vec4 FragColor;\n"
"void main()\n"
"{\n"
" FragColor = vec4(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.2f, 1.0f);\n"
"}\n\0";
BKQOpenglW::BKQOpenglW(QWidget *parent) : QOpenGLWidget(parent)
{
}
BKQOpenglW::~BKQOpenglW()
{
makeCurrent();
glDeleteVertexArrays(1,&VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1,&VBO);
doneCurrent();
}
void BKQOpenglW::drawShapes(BKQOpenglW::Shape shape)
{
m_Shape = shape;
update();
}
void BKQOpenglW::setWireFrame(bool b)
{
makeCurrent();
if(b)
{
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE);
}
else {
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_FILL);
}
update();
doneCurrent();
}
void BKQOpenglW::initializeGL()
{
initializeOpenGLFunctions();
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
// bind the Vertex Array Object first, then bind and set vertex buffer(s), and then configure vertex attributes(s).
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(float), nullptr);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// note that this is allowed, the call to glVertexAttribPointer registered VBO as the vertex attribute's bound vertex buffer object so afterwards we can safely unbind
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
// You can unbind the VAO afterwards so other VAO calls won't accidentally modify this VAO, but this rarely happens. Modifying other
// VAOs requires a call to glBindVertexArray anyways so we generally don't unbind VAOs (nor VBOs) when it's not directly necessary.
glBindVertexArray(0);
// shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceCode(QOpenGLShader::Vertex,vertexShaderSource);
// shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceCode(QOpenGLShader::Fragment,fragmentShaderSource);
shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceFile(QOpenGLShader::Vertex,":/shader/shader.vs");
shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceFile(QOpenGLShader::Fragment,":/shader/shader.fs");
shaderProgram.link();
//链接着色器
}
void BKQOpenglW::resizeGL(int w, int h)
{
glViewport(0,0,w,h);
}
void BKQOpenglW::paintGL()
{
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
shaderProgram.bind();
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
switch (m_Shape) {
case Triangle:
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES,0,3);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
layout
我们先看基本标识:
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 position;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aColor;
out vec3 outColor;
void main()
{
gl_Position = vec4(position.x, position.y, position.z, 1.0);
outColor = aColor;
}
#version 330 core
out vec4 color;
in vec3 outColor;
void main()
{
color = vec4(outColor,1.0f);//RGBA
}
这里有location = 0,1.这里就是对应变量的编号。比如我想把顶点写成
float vertices[] = {
// positions // colors
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // bottom right
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // bottom left
0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f // top
};前边是位置,后面是颜色值,那我们要告诉gpu改如何操作,于是下面代码你就懂了:
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// color attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);第一参数就是对应的location,然后最后一个是偏移量。这下你懂了吧。
int nPos = shaderProgram.attributeLocation("position");
glVertexAttribPointer(nPos, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float), nullptr);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(nPos);我们使用qt中找到对应的pos值也是可以的 。
输出结果:
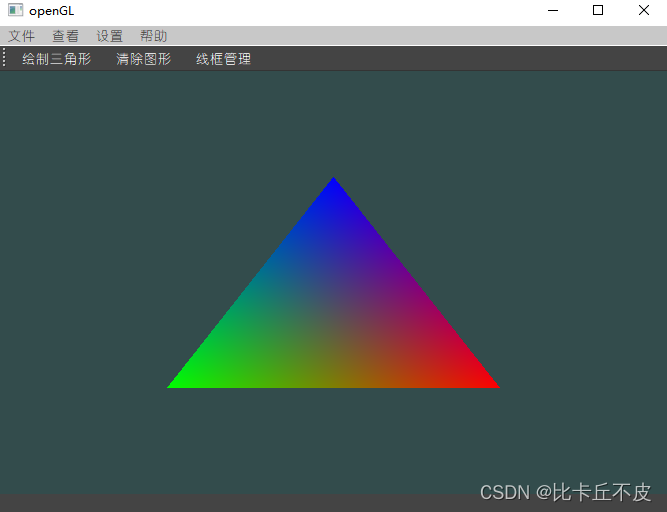
cpp代码:
#include "bkqopenglw.h"
#include<iostream>
float vertices[] = {
// positions // colors
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // bottom right
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // bottom left
0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f // top
};
BKQOpenglW::BKQOpenglW(QWidget *parent) : QOpenGLWidget(parent)
{
}
BKQOpenglW::~BKQOpenglW()
{
makeCurrent();
glDeleteVertexArrays(1,&VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1,&VBO);
doneCurrent();
}
void BKQOpenglW::drawShapes(BKQOpenglW::Shape shape)
{
m_Shape = shape;
update();
}
void BKQOpenglW::setWireFrame(bool b)
{
makeCurrent();
if(b)
{
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE);
}
else {
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_FILL);
}
update();
doneCurrent();
}
void BKQOpenglW::initializeGL()
{
initializeOpenGLFunctions();
// shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceCode(QOpenGLShader::Vertex,vertexShaderSource);
// shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceCode(QOpenGLShader::Fragment,fragmentShaderSource);
shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceFile(QOpenGLShader::Vertex,":/shader/shader.vs");
shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceFile(QOpenGLShader::Fragment,":/shader/shader.fs");
shaderProgram.link();
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
// bind the Vertex Array Object first, then bind and set vertex buffer(s), and then configure vertex attributes(s).
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
int nPos = shaderProgram.attributeLocation("position");
glVertexAttribPointer(nPos, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float), nullptr);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(nPos);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
// note that this is allowed, the call to glVertexAttribPointer registered VBO as the vertex attribute's bound vertex buffer object so afterwards we can safely unbind
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
// You can unbind the VAO afterwards so other VAO calls won't accidentally modify this VAO, but this rarely happens. Modifying other
// VAOs requires a call to glBindVertexArray anyways so we generally don't unbind VAOs (nor VBOs) when it's not directly necessary.
glBindVertexArray(0);
//链接着色器
}
void BKQOpenglW::resizeGL(int w, int h)
{
glViewport(0,0,w,h);
}
void BKQOpenglW::paintGL()
{
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
shaderProgram.bind();
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
switch (m_Shape) {
case Triangle:
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES,0,3);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
uniform
uniform是另一种从CPU应用向GPU着色器发送数据的方式, 但uniform和顶点属性有点不
同。 首先, uniform是全局的(Global)。 这里全局的意思是uniform变量必须在所有着色器程序
对象中都是独一无二的, 它可以在着色器程序的任何着色器任何阶段使用。 第二, 无论你把
uniform值设置成什么, uniform会一直保存它们的数据, 直到它们被重置或更新。
我们先看基本标识:
#version 330 core
out vec4 color;
uniform vec4 vertexColor;
void main()
{
color = vertexColor;//RGBA
}#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 position;
void main()
{
gl_Position = vec4(position.x, position.y, position.z, 1.0);
}
然后我们在代码中写到:
shaderProgram.bind();
shaderProgram.setUniformValue("vertexColor",0.5f,0.0f,0.0f,1.0f);这个是qt提供的类使用的方法,原生方式:
/*
opengl 基本写法
shaderProgram 为glCreateProgram() 返回值 这里可以调用这个shaderProgram.programId() 可以利用
int vertexColorLocation = glGetUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "vertexColor");
glUniform4f(vertexColorLocation, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
*/
GLuint id = shaderProgram.programId();
int vertexColorLocation = glGetUniformLocation(id, "vertexColor");
glUniform4f(vertexColorLocation, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);这里的id 就是你glCreateProgram()返回的值,原生态你要创建的链接器id
然后修改对应的数据:
输出结果:
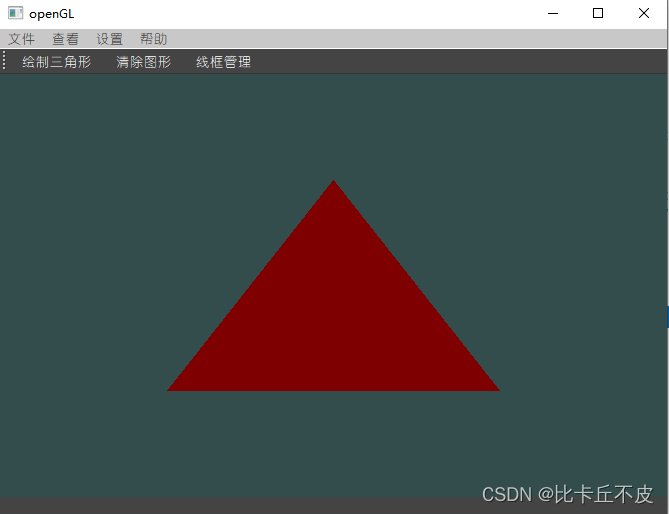
全部代码:
#include "bkqopenglw.h"
#include<iostream>
const float vertices[] = {
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // left
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // right
0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f // top
};
BKQOpenglW::BKQOpenglW(QWidget *parent) : QOpenGLWidget(parent)
{
}
BKQOpenglW::~BKQOpenglW()
{
makeCurrent();
glDeleteVertexArrays(1,&VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1,&VBO);
doneCurrent();
}
void BKQOpenglW::drawShapes(BKQOpenglW::Shape shape)
{
m_Shape = shape;
update();
}
void BKQOpenglW::setWireFrame(bool b)
{
makeCurrent();
if(b)
{
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE);
}
else {
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_FILL);
}
update();
doneCurrent();
}
void BKQOpenglW::initializeGL()
{
initializeOpenGLFunctions();
// shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceCode(QOpenGLShader::Vertex,vertexShaderSource);
// shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceCode(QOpenGLShader::Fragment,fragmentShaderSource);
shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceFile(QOpenGLShader::Vertex,":/shader/shader.vs");
shaderProgram.addShaderFromSourceFile(QOpenGLShader::Fragment,":/shader/shader.fs");
shaderProgram.link();
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
// bind the Vertex Array Object first, then bind and set vertex buffer(s), and then configure vertex attributes(s).
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(float), nullptr);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// note that this is allowed, the call to glVertexAttribPointer registered VBO as the vertex attribute's bound vertex buffer object so afterwards we can safely unbind
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
// You can unbind the VAO afterwards so other VAO calls won't accidentally modify this VAO, but this rarely happens. Modifying other
// VAOs requires a call to glBindVertexArray anyways so we generally don't unbind VAOs (nor VBOs) when it's not directly necessary.
glBindVertexArray(0);
/*
opengl 基本写法
shaderProgram 为glCreateProgram() 返回值 这里可以调用这个shaderProgram.programId() 可以利用
int vertexColorLocation = glGetUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "vertexColor");
glUniform4f(vertexColorLocation, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
*/
shaderProgram.bind();
shaderProgram.setUniformValue("vertexColor",0.5f,0.0f,0.0f,1.0f);
// GLuint id = shaderProgram.programId();
// int vertexColorLocation = glGetUniformLocation(id, "vertexColor");
// glUniform4f(vertexColorLocation, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
//链接着色器
}
void BKQOpenglW::resizeGL(int w, int h)
{
glViewport(0,0,w,h);
}
void BKQOpenglW::paintGL()
{
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
shaderProgram.bind();
//shaderProgram 写法
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
switch (m_Shape) {
case Triangle:
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES,0,3);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
写在后面的话:
喜欢我博客的小伙伴们,也同时想在qt上学习opengl的伙伴,可以关注与点赞博客,让我们共同进步吧。






















 1043
1043











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








