vuex:专为vue.js开发的状态管理模式,主要包含以下几个部分:state,view,actions

其主要应用场景就是多个组件使用同一个变量时,兄弟组件无法传参,父子组件传参拷贝时原本的模式脆弱,通常会导致无法维护的代码。因此就把组件的共享状态抽离出来,以全局单例模式管理。(为解决每个组件中需要注入vuex,通过store选项,把store实例注入到所有子组件中,子组件可以通过this.$store获取)
vuex的应用核心是store,包含应用中大部分的状态。
state:管理变量,即状态,vuex,单一状态树,用一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态,唯一数据源。
由于 Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的,从 store 实例中读取状态最简单的方法就是在计算属性中返回某个状态:
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
},
},mapState 辅助函数
当一个组件需要获取多个状态时候,将这些状态都声明为计算属性会有些重复和冗余。为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用 mapState 辅助函数帮助我们生成计算属性,可以少敲几次键盘:
computed:{
...mapState([
'count',
'b'
]),
}console.log("count:",this.count);
console.log('b:',this.b);运行结果如下:
![]()
Getter:有时候我们需要从 store 中的 state 中派生出一些状态,例如对列表进行过滤并计数,如果有多个组件需要用到此属性,我们要么复制这个函数,或者抽取到一个共享函数然后在多处导入它——无论哪种方式都不是很理想,此时定义一个getter,如state,可以共享。(根据依赖被缓存,当依赖值发生改变,重新计算)
Getter接受state作为其第一个参数
state: {
todos:[
{id:1,text:'....',done:true},
{id:2,text:'....',done:false},
],
},
getters: {
doneTodos:state => {
return state.todos.filter(todo=>todo.done);
},
todoLength:(state,getters)=> {
return getters.doneTodos.length;
},
}通过属性访问:
Getter 会暴露为 store.getters 对象,你可以以属性的形式访问这些值:
console.log('doneTodos',this.$store.getters.doneTodos);打印结果:

通过方法访问:
也可以通过让getter返回一个函数,来实现给getter传参,对store里的数组进行查询时非常有用:
state: {
todos:[
{id:1,text:'....',done:true},
{id:2,text:'....',done:false},
],
},
getters: {
getTodoById:(state) => (id)=> {
return state.todos.find(todo=>todo.id===id);
}
}console.log("通过方法访问store",this.$store.getters.getTodoById(2));打印结果如下:
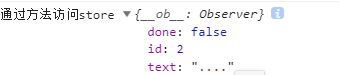
mapGetters同mapState一样,简便写法,用于getters。
Mutation:更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation
state: {
count: 1,
},
mutations: {
increment:state => state.count++,
},this.$store.commit('increment');
console.log("count++:",this.count);打印结果如下:
![]()
提交载荷(Payload):可以向 store.commit 传入额外的参数,即 mutation 的 载荷(payload)
state: {
count: 1,
},
mutations: {
increment:(state,n) => state.count += n,
},this.$store.commit('increment',5);
console.log("count++:",this.count);打印结果如下:
![]()
对象风格的提交方式:提交 mutation 的另一种方式是直接使用包含 type 属性的对象
state: {
count: 1,
},
mutations: {
increment:(state,payload) => state.count += payload.amount,
},this.$store.commit({
type:'increment',
amount:10
});
console.log("count++:",this.count);打印结果如下:
![]()
Action
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
-
Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
-
Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
Action 函数接受一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的 context 对象,因此可以调用 context.commit 提交一个 mutation,或者通过 context.state 和 context.getters 来获取 state 和 getters。
actions: {
incrementAsync ({ commit }) {
//actions用于异步操作
setTimeout(() => {
commit('increment2');
},1000);
}
}this.$store.dispatch('incrementAsync');Actions 支持同样的载荷方式和对象方式进行分发:
// 以载荷形式分发
store.dispatch('incrementAsync', {
amount: 10
})
// 以对象形式分发
store.dispatch({
type: 'incrementAsync',
amount: 10
})
在组件中分发 Action
在组件中使用 this.$store.dispatch('xxx') 分发 action,或者使用 mapActions 辅助函数将组件的 methods 映射为 store.dispatch 调用
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
}组合 Action
Action 通常是异步的,那么如何知道 action 什么时候结束呢?更重要的是,我们如何才能组合多个 action,以处理更加复杂的异步流程?
首先,你需要明白 store.dispatch 可以处理被触发的 action 的处理函数返回的 Promise,并且 store.dispatch 仍旧返回 Promise:
actions: {
actionA ({ commit }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('someMutation')
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
}
}store.dispatch('actionA').then(() => {
// ...
})在另外一个 action 中也可以:
actions: {
// ...
actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) {
return dispatch('actionA').then(() => {
commit('someOtherMutation')
})
}
}最后,如果我们利用 async / await,我们可以如下组合 action:
// 假设 getData() 和 getOtherData() 返回的是 Promise
actions: {
async actionA ({ commit }) {
commit('gotData', await getData())
},
async actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) {
await dispatch('actionA') // 等待 actionA 完成
commit('gotOtherData', await getOtherData())
}
}一个 store.dispatch 在不同模块中可以触发多个 action 函数。在这种情况下,只有当所有触发函数完成后,返回的 Promise 才会执行。
Module
Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
模块的局部状态
对于模块内部的 mutation 和 getter,接收的第一个参数是模块的局部状态对象。
const moduleA = {
state: { count: 0 },
mutations: {
increment (state) {
// 这里的 `state` 对象是模块的局部状态
state.count++
}
},
getters: {
doubleCount (state) {
return state.count * 2
}
}
}同样,对于模块内部的 action,局部状态通过 context.state 暴露出来,根节点状态则为 context.rootState:
const moduleA = {
// ...
actions: {
incrementIfOddOnRootSum ({ state, commit, rootState }) {
if ((state.count + rootState.count) % 2 === 1) {
commit('increment')
}
}
}
}对于模块内部的 getter,根节点状态会作为第三个参数暴露出来:
const moduleA = {
// ...
getters: {
sumWithRootCount (state, getters, rootState) {
return state.count + rootState.count
}
}
}命名空间
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
account: {
namespaced: true,
// 模块内容(module assets)
state: { ... }, // 模块内的状态已经是嵌套的了,使用 `namespaced` 属性不会对其产生影响
getters: {
isAdmin () { ... } // -> getters['account/isAdmin']
},
actions: {
login () { ... } // -> dispatch('account/login')
},
mutations: {
login () { ... } // -> commit('account/login')
},
// 嵌套模块
modules: {
// 继承父模块的命名空间
myPage: {
state: { ... },
getters: {
profile () { ... } // -> getters['account/profile']
}
},
// 进一步嵌套命名空间
posts: {
namespaced: true,
state: { ... },
getters: {
popular () { ... } // -> getters['account/posts/popular']
}
}
}
}
}
})启用了命名空间的 getter 和 action 会收到局部化的 getter,dispatch 和 commit。换言之,你在使用模块内容(module assets)时不需要在同一模块内额外添加空间名前缀。更改 namespaced 属性后不需要修改模块内的代码。
在带命名空间的模块内访问全局内容(Global Assets)
如果你希望使用全局 state 和 getter,rootState 和 rootGetter 会作为第三和第四参数传入 getter,也会通过 context 对象的属性传入 action。
若需要在全局命名空间内分发 action 或提交 mutation,将 { root: true } 作为第三参数传给 dispatch 或 commit 即可。
modules: {
foo: {
namespaced: true,
getters: {
// 在这个模块的 getter 中,`getters` 被局部化了
// 你可以使用 getter 的第四个参数来调用 `rootGetters`
someGetter (state, getters, rootState, rootGetters) {
getters.someOtherGetter // -> 'foo/someOtherGetter'
rootGetters.someOtherGetter // -> 'someOtherGetter'
},
someOtherGetter: state => { ... }
},
actions: {
// 在这个模块中, dispatch 和 commit 也被局部化了
// 他们可以接受 `root` 属性以访问根 dispatch 或 commit
someAction ({ dispatch, commit, getters, rootGetters }) {
getters.someGetter // -> 'foo/someGetter'
rootGetters.someGetter // -> 'someGetter'
dispatch('someOtherAction') // -> 'foo/someOtherAction'
dispatch('someOtherAction', null, { root: true }) // -> 'someOtherAction'
commit('someMutation') // -> 'foo/someMutation'
commit('someMutation', null, { root: true }) // -> 'someMutation'
},
someOtherAction (ctx, payload) { ... }
}
}
}在带命名空间的模块注册全局 action
若需要在带命名空间的模块注册全局 action,你可添加 root: true,并将这个 action 的定义放在函数 handler 中。
{
actions: {
someOtherAction ({dispatch}) {
dispatch('someAction')
}
},
modules: {
foo: {
namespaced: true,
actions: {
someAction: {
root: true,
handler (namespacedContext, payload) { ... } // -> 'someAction'
}
}
}
}
}带命名空间的绑定函数
当使用 mapState, mapGetters, mapActions 和 mapMutations 这些函数来绑定带命名空间的模块时,写起来可能比较繁琐:
computed: {
...mapState({
a: state => state.some.nested.module.a,
b: state => state.some.nested.module.b
})
},
methods: {
...mapActions([
'some/nested/module/foo', // -> this['some/nested/module/foo']()
'some/nested/module/bar' // -> this['some/nested/module/bar']()
])
}对于这种情况,你可以将模块的空间名称字符串作为第一个参数传递给上述函数,这样所有绑定都会自动将该模块作为上下文。于是上面的例子可以简化为:
computed: {
...mapState('some/nested/module', {
a: state => state.a,
b: state => state.b
})
},
methods: {
...mapActions('some/nested/module', [
'foo', // -> this.foo()
'bar' // -> this.bar()
])
}而且,你可以通过使用 createNamespacedHelpers 创建基于某个命名空间辅助函数。它返回一个对象,对象里有新的绑定在给定命名空间值上的组件绑定辅助函数:
import { createNamespacedHelpers } from 'vuex'
const { mapState, mapActions } = createNamespacedHelpers('some/nested/module')
export default {
computed: {
// 在 `some/nested/module` 中查找
...mapState({
a: state => state.a,
b: state => state.b
})
},
methods: {
// 在 `some/nested/module` 中查找
...mapActions([
'foo',
'bar'
])
}
}基本上就是这些了,在我之前的用法中,Action与Module很少用到,这两部分的代码也很少写,就用了官网的例子,vuex终于被我写完了,不知道在我的计划中拖了几周了,真是。






















 6103
6103











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








