Netty服务端启动代码:
public final class EchoServer {
static final int PORT = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("port", "8007"));
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Configure the server.
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
final EchoServerHandler serverHandler = new EchoServerHandler();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
//p.addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO));
p.addLast(serverHandler);
}
});
// Start the server.
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(PORT).sync();
// Wait until the server socket is closed.
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// Shut down all event loops to terminate all threads.
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
1.Channel的创建
通过Bootstrap.bind(PORT)调用AbstractBootstrap.doBind(),doBind()调用initAndRegister()。
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = this.channelFactory().newChannel();
try {
this.init(channel);
} catch (Throwable var3) {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
return (new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE)).setFailure(var3);
}
ChannelFuture regFuture = this.group().register(channel);
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
channel.close();
} else {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}
return regFuture;
}
从该方法可以看出,channel的创建是依赖channelFactory().newChannel()创建的,channelFactory()是获取AbstractBootstrap类的成员变量channelFactory,这个成员变量是在服务器段的Bootstarp.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)的时候进行设置的,而channelFactory().newChannel()则是该方法通过反射获取该类的实例变量。
public T newChannel() {
try {
return (Channel)this.clazz.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable var2) {
throw new ChannelException("Unable to create Channel from class " + this.clazz, var2);
}
}
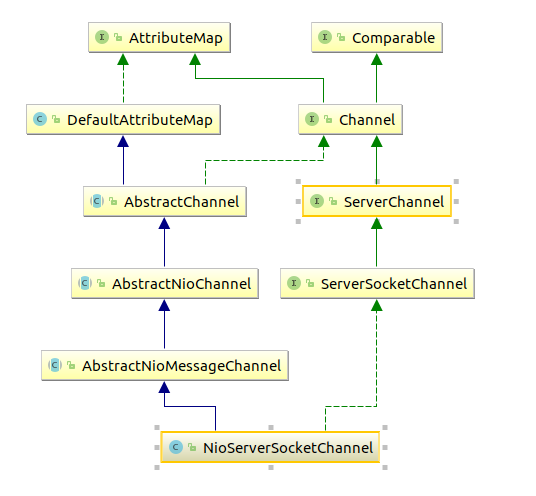
通过反射调用的是NioServerSocketChannel的默认构造函数。NioServerSocketChannel的类关系如下:
public NioServerSocketChannel() {
this(newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER));
}
NioServerSocketChannel通过newSocket创建java nio中的channel,newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER)通过SelectorProvider.provider().openServerSocketChannel()打开一个ServerSocketChannel,这里的ServerSocketChannel是Java nio中的channel,在linux下,我们可以理解为JVM会调用linux操作系统的socket()函数创建了一个socket。这个地方要注意区别它跟前面NioServerSocketChannel实例的关系,他们都是一个socket channel,但是是两个不同的东西,一个是java nio中的,另外一个是经过netty包装过后的。newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER)返回的channel更多的是与操作系统socket相关联的一个东西,后面代码中经常遇到的通过javaChannel()返回的channel就是它,所以我们要进行底层的socket操作时,就是通过它。
然后再调用NioServerSocketChannel的另一个构造函数,调用父类的构造函数,并构造一个配置类NioServerSocketChannelConfig。
通过层层调用父类的构造函数,设置channel需要监听的事件为OP_ACCEPT,调用ch.configureBlocking(false),将channel设置为非阻塞的,并且调用AbstractChannel的构造函数,设置了channel的成员变量parent,unsafe和pipeline。
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
this.unsafe = this.newUnsafe();
this.pipeline = new DefaultChannelPipeline(this);
}
public NioServerSocketChannel(java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel channel) {
super((Channel)null, channel, 16);
this.config = new NioServerSocketChannel.NioServerSocketChannelConfig(this, this.javaChannel().socket());
}
这里的javaChannel()获取的是AbstractNioChannel的SelectableChannel,也就是之前创建java nio中的channel。

2.Channel的初始化
channel的初始化是在initAndRegister中方法中的this.init(channel)完成的,调用了AbstractBootstrap中的init。
void init(Channel channel) throws Exception {
Map, Object> options = this.options();
synchronized(options) {
channel.config().setOptions(options);
}
Map, Object> attrs = this.attrs();
synchronized(attrs) {
Iterator i$ = attrs.entrySet().iterator();
while(true) {
if (!i$.hasNext()) {
break;
}
Entry, Object> e = (Entry)i$.next();
AttributeKey key = (AttributeKey)e.getKey();
channel.attr(key).set(e.getValue());
}
}
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
if (this.handler() != null) {
p.addLast(new ChannelHandler[]{this.handler()});
}
final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = this.childGroup;
final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = this.childHandler;
Map var9 = this.childOptions;
final Entry[] currentChildOptions;
synchronized(this.childOptions) {
currentChildOptions = (Entry[])this.childOptions.entrySet().toArray(newOptionArray(this.childOptions.size()));
}
var9 = this.childAttrs;
final Entry[] currentChildAttrs;
synchronized(this.childAttrs) {
currentChildAttrs = (Entry[])this.childAttrs.entrySet().toArray(newAttrArray(this.childAttrs.size()));
}
p.addLast(new ChannelHandler[]{new ChannelInitializer() {
public void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelHandler[]{new ServerBootstrap.ServerBootstrapAcceptor(currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs)});
}
}});
}
初始化主要作用:
将引导类配置的option设置到上一步创建与Channel绑定的Configure类中
设置attrs
将使用引导类handler()设置的handler添加到pipeline上面
配置channelOption,channelOption是为了childChannel进行服务的
将连接器ServerBootstrapAcceptor添加到pipeline上面
连接器其实也是一种ChannelHandler,在服务器启动完成时候,NioServerSocketChannel的pipeline的结构如下:
Head[I/O] ServerBootstrapAcceptor[IN] Tail[IN]
这里的连接处理器,作用就是处理客户端的连接。其逻辑比较简单:在服务器启动时调用childHandler方法设置了ServerBootstrap的子Channel的处理器,此时会将childChannelHandler添加到子Channel中(NioSocketChannel会在连接过程中创建);设置子Channel的配置和属性;最后将子Channel注册到子线程池组中。经过这个连接处理器的时候子channel已经被创建好了。
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
final Channel child = (Channel)msg;
child.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelHandler[]{this.childHandler});
Entry[] arr$ = this.childOptions;
int len$ = arr$.length;
int i$;
Entry e;
for(i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) {
e = arr$[i$];
try {
if (!child.config().setOption((ChannelOption)e.getKey(), e.getValue())) {
ServerBootstrap.logger.warn("Unknown channel option: " + e);
}
} catch (Throwable var10) {
ServerBootstrap.logger.warn("Failed to set a channel option: " + child, var10);
}
}
arr$ = this.childAttrs;
len$ = arr$.length;
for(i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) {
e = arr$[i$];
child.attr((AttributeKey)e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
try {
this.childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
ServerBootstrap.ServerBootstrapAcceptor.forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable var9) {
forceClose(child, var9);
}
}
3.Channel的注册
ChannelFuture regFuture = this.group().register(channel);
最终调用的是AbstractChannel的register方法,将一个channel和一个eventloop进行绑定。channel和eventloop是多对一的关系,多个channel可以注册到一个eventloop上面。
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (eventLoop == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("eventLoop");
} else if (AbstractChannel.this.isRegistered()) {
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("registered to an event loop already"));
} else if (!AbstractChannel.this.isCompatible(eventLoop)) {
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("incompatible event loop type: " + eventLoop.getClass().getName()));
} else {
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
this.register0(promise);
} else {
try {
eventLoop.execute(new OneTimeTask() {
public void run() {
AbstractUnsafe.this.register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable var4) {
AbstractChannel.logger.warn("Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}", AbstractChannel.this, var4);
this.closeForcibly();
AbstractChannel.this.closeFuture.setClosed();
this.safeSetFailure(promise, var4);
}
}
}
}
从代码可知,如果当前线程是eventloop的线程,则直接执行register0(promise),但知道现在为止,我们的代码一直在main()函数的线程中执行,所以执行的分支是eventLoop.execute(..);
继续调用会调用SingleThreadEventExecutor的executor(task)函数。
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
} else {
boolean inEventLoop = this.inEventLoop();
if (inEventLoop) {
this.addTask(task);
} else {
this.startThread();
this.addTask(task);
if (this.isShutdown() && this.removeTask(task)) {
reject();
}
}
if (!this.addTaskWakesUp && this.wakesUpForTask(task)) {
this.wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
}
因为当前线程不是eventloop线程,所以使用startThread()创建eventloop线程,eventloop线程创建并启动后,通过调用addTask()将task任务添加到taskqueue中。
通过register0(promise)将channel进行注册。
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !this.ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
boolean firstRegistration = this.neverRegistered;
AbstractChannel.this.doRegister();
this.neverRegistered = false;
AbstractChannel.this.registered = true;
this.safeSetSuccess(promise);
AbstractChannel.this.pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
if (firstRegistration && AbstractChannel.this.isActive()) {
AbstractChannel.this.pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
} catch (Throwable var3) {
this.closeForcibly();
AbstractChannel.this.closeFuture.setClosed();
this.safeSetFailure(promise, var3);
}
}
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
while(true) {
try {
this.selectionKey = this.javaChannel().register(this.eventLoop().selector, 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException var3) {
if (selected) {
throw var3;
}
this.eventLoop().selectNow();
selected = true;
}
}
}
可以看出最终还是通过javaChannel()注册到一个selector上面。在注册完了之后,会将channel注册完毕的事件通知到pipeline上。
AbstractChannel.this.pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
4.端口绑定
端口绑定是通过doBind中的doBind0()实现的。
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
private static void doBind0(final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
if (regFuture.isSuccess()) {
channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());
}
}
});
}
Channel的bind函数调用链如下:
// AbstractChannel
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
return pipeline.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
// DefaultChannelPipeline
public final ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
// 因为bind是一个outbound事件,从pipeline链尾tailContext开始执行
return tail.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
// tail context的父类AbstractChannelHandlerContext
public ChannelFuture bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (localAddress == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("localAddress");
}
if (isNotValidPromise(promise, false)) {
// cancelled
return promise;
}
// 应用程序没有添加outbound的情况下,找到的next context是head context
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound();
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);
} else {
safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);
}
}, promise, null);
}
return promise;
}
// head context的父类AbstractChannelHandlerContext
private void invokeBind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
((ChannelOutboundHandler) handler()).bind(this, localAddress, promise);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyOutboundHandlerException(t, promise);
}
} else {
bind(localAddress, promise);
}
}
// 还在head context的父类AbstractChannelHandlerContext
public void bind(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise)
throws Exception {
// 通过unsafe调用bind了,意味着会调用JVM的功能,操作底层的一些函数了
unsafe.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
// AbstractUnsafe
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
assertEventLoop();
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
// See: https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/576
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(config().getOption(ChannelOption.SO_BROADCAST)) &&
localAddress instanceof InetSocketAddress &&
!((InetSocketAddress) localAddress).getAddress().isAnyLocalAddress() &&
!PlatformDependent.isWindows() && !PlatformDependent.maybeSuperUser()) {
// Warn a user about the fact that a non-root user can't receive a
// broadcast packet on *nix if the socket is bound on non-wildcard address.
logger.warn(
"A non-root user can't receive a broadcast packet if the socket " +
"is not bound to a wildcard address; binding to a non-wildcard " +
"address (" + localAddress + ") anyway as requested.");
}
boolean wasActive = isActive();
try {
// 做实际的bind工作
doBind(localAddress);
} catch (Throwable t) {
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
closeIfClosed();
return;
}
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
});
}
safeSetSuccess(promise);
}
// NioServerSocketChannel
protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {
// 最终通过JVM调用server socket的bind、listen等函数,启动服务端
javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
} else {
javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
}
}
当端口绑定完成之后,会调用fireChannelActive()方法,通知端口已经绑定完成。并且会给当前的channel注册accept事件。
public ChannelPipeline fireChannelActive() {
this.head.fireChannelActive();
if (this.channel.config().isAutoRead()) {
this.channel.read();
}
return this;
}
fireChannelActive()调用channel的read(),由于read是outbound方法,最终会调用NioServerSocketChannel的unsafe的beginRead,在里面注册Accept事件。
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
if (!this.inputShutdown) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (selectionKey.isValid()) {
this.readPending = true;
int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & this.readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | this.readInterestOp);
}
}
}
}





















 2431
2431











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








