模式动机
一般有两种方式可以实现给一个类或对象增加行为:
继承机制,使用继承机制是给现有类添加功能的一种有效途径,通过继承一个现有类可以使得子类在拥有自身方法的同时还拥有父类的方法。但是这种方法是静态的,用户不能控制增加行为的方式和时机。
关联机制,即将一个类的对象嵌入另一个对象中,由另一个对象来决定是否调用嵌入对象的行为以便扩展自己的行为,我们称这个嵌入的对象为装饰器(Decorator)。
装饰模式以对客户透明的方式动态地给一个对象附加上更多的责任,换言之,客户端并不会觉得对象在装饰前和装饰后有什么不同。装饰模式可以在不需要创造更多子类的情况下,将对象的功能加以扩展。这就是装饰模式的模式动机。
模式结构
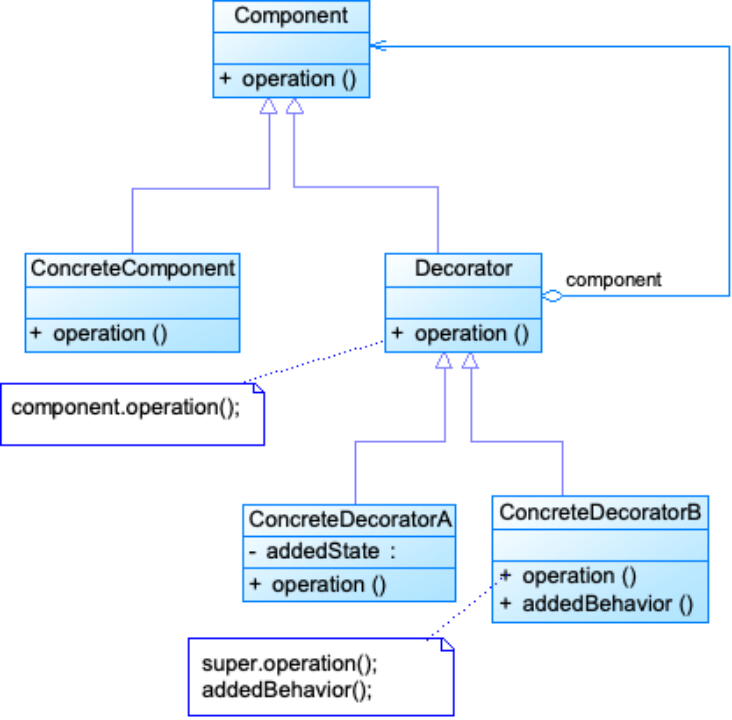
装饰模式包含如下角色:
Component: 抽象构件
ConcreteComponent: 具体构件
Decorator: 抽象装饰类
ConcreteDecorator: 具体装饰类
模式分析
与继承关系相比,关联关系的主要优势在于不会破坏类的封装性,而且继承是一种耦合度较大的静态关系,无法在程序运行时动态扩展。在软件开发阶段,关联关系虽然不会比继承关系减少编码量,但是到了软件维护阶段,由于关联关系使系统具有较好的松耦合性,因此使得系统更加容易维护。当然,关联关系的缺点是比继承关系要创建更多的对象。
使用装饰模式来实现扩展比继承更加灵活,它以对客户透明的方式动态地给一个对象附加更多的责任。装饰模式可以在不需要创造更多子类的情况下,将对象的功能加以扩展。
装饰模式实例与解析
实例一:多重加密系统
某系统提供了一个数据加密功能,可以对字符串进行加密。最简单的加密算法通过对字母进行移位来实现,同时还提供了稍复杂的逆向输出加密,还提供了更为高级的求模加密。用户先使用最简单的加密算法对字符串进行加密,如果觉得还不够可以对加密之后的结果使用其他加密算法进行二次加密,当然也可以进行第三次加密。现使用装饰模式设计该多重加密系统。
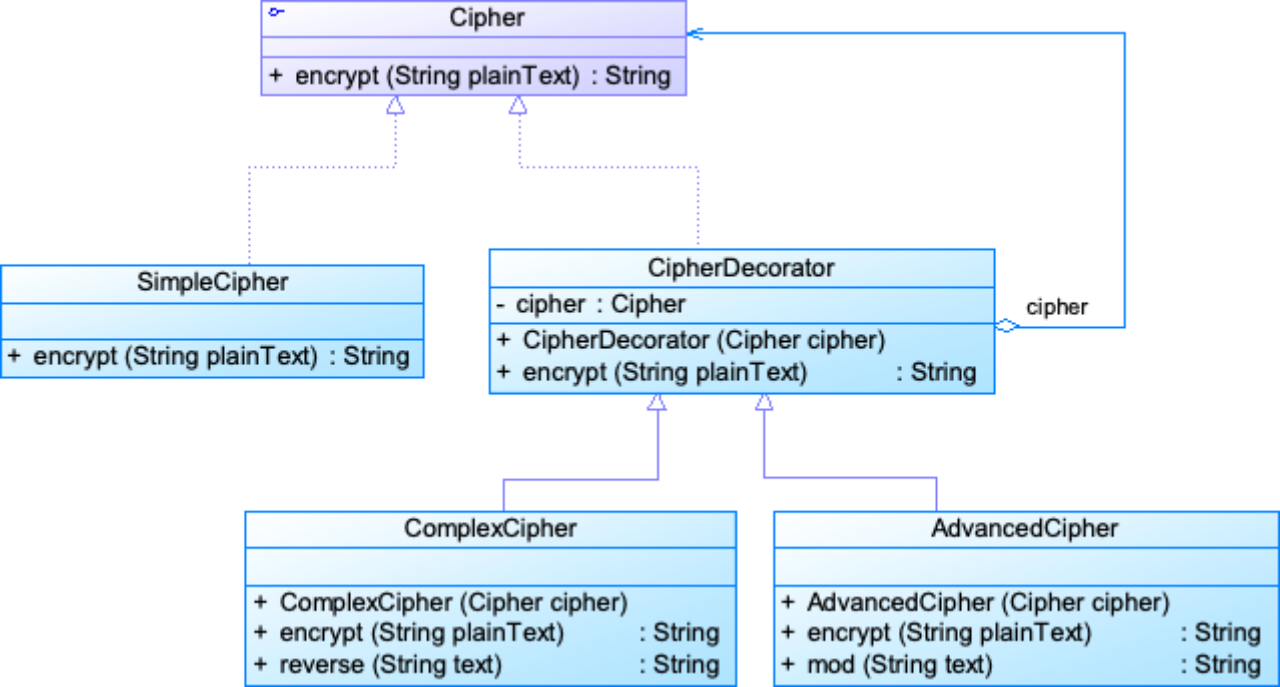
public interface Cipher
{
public String encrypt(String plainText);
}
public final class SimpleCipher implements Cipher {
public String encrypt(String plainText) {
String str = "";
for (int i = 0; i < plainText.length(); i++) {
char c = plainText.charAt(i);
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') {
c += 6;
if (c > 'z') c -= 26;
if (c < 'a') c += 26;
}
if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') {
c += 6;
if (c > 'Z') c -= 26;
if (c < 'A') c += 26;
}
str += c;
}
return str;
}
}
public class CipherDecorator implements Cipher {
private Cipher cipher;
public CipherDecorator(Cipher cipher) {
this.cipher = cipher;
}
public String encrypt(String plainText) {
return cipher.encrypt(plainText);
}
}
public class ComplexCipher extends CipherDecorator {
public ComplexCipher(Cipher cipher) {
super(cipher);
}
public String encrypt(String plainText) {
String result = super.encrypt(plainText);
result = this.reverse(result);
return result;
}
public String reverse(String text) {
String str = "";
for (int i = text.length(); i > 0; i--) {
str += text.substring(i - 1, i);
}
return str;
}
}
public class AdvancedCipher extends CipherDecorator {
public AdvancedCipher(Cipher cipher) {
super(cipher);
}
public String encrypt(String plainText) {
String result = super.encrypt(plainText);
result = mod(result);
return result;
}
public String mod(String text) {
String str = "";
for (int i = 0; i < text.length(); i++) {
String c = String.valueOf(text.charAt(i) % 6);
str += c;
}
return str;
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String password = "sunnyLiu";
String cpassword;
Cipher sc, ac, cc;
sc = new SimpleCipher();
cpassword = sc.encrypt(password);
System.out.println(cpassword);
System.out.println("---------------------");
cc = new ComplexCipher(sc);
cpassword = cc.encrypt(password);
System.out.println(cpassword);
System.out.println("---------------------");
ac = new AdvancedCipher(cc);
cpassword = ac.encrypt(password);
System.out.println(cpassword);
System.out.println("---------------------");
}
}
实例二:经典举例咖啡店模式
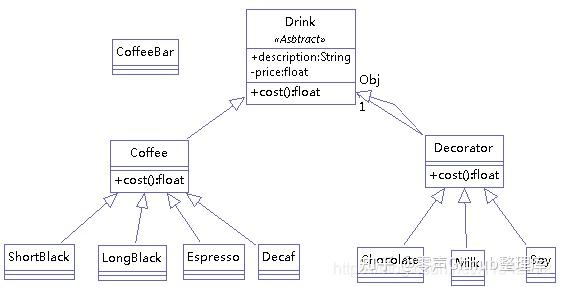
(咖啡馆订单项目:1)、咖啡种类:Espresso、ShortBlack、LongBlack、Decaf2)、调料(装饰者):Milk、Soy、Chocolate),类图如上
被装饰的对象和装饰者都继承自同一个超类
public abstract class Drink {
public String description="";
private float price=0f;;
public void setDescription(String description)
{
this.description=description;
}
public String getDescription()
{
return description+"-"+this.getPrice();
}
public float getPrice()
{
return price;
}
public void setPrice(float price)
{
this.price=price;
}
public abstract float cost();
}
被装饰的对象,不用去改造。原来怎么样写,现在还是怎么写。
public class Coffee extends Drink {
@Override
public float cost() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.getPrice();
}
}
装饰者不仅要考虑自身,还要考虑被它修饰的对象,它是在被修饰的对象上继续添加修饰。例如,咖啡里面加牛奶,再加巧克力。加糖后价格为coffee+milk。再加牛奶价格为coffee+milk+chocolate。
public class Decorator extends Drink {
private Drink Obj;
public Decorator(Drink Obj) {
this.Obj = Obj;
};
@Override
public float cost() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.getPrice() + Obj.cost();
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return super.description + "-" + super.getPrice() + "&&" + Obj.getDescription();
}
}
装饰者实例化(加牛奶)。这里面要对被修饰的对象进行实例化。
public class Milk extends Decorator {
public Milk(Drink Obj) {
super(Obj);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
super.setDescription("Milk");
super.setPrice(2.0f);
}
}
coffee店:初始化一个被修饰对象,修饰者实例需要对被修改者实例化,才能对具体的被修饰者进行修饰。
public class CoffeeBar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Drink order;
order = new Decaf();
System.out.println("order1 price:" + order.cost());
System.out.println("order1 desc:" + order.getDescription());
System.out.println("****************");
order = new LongBlack();
order = new Milk(order);
order = new Chocolate(order);
order = new Chocolate(order);
System.out.println("order2 price:" + order.cost());
System.out.println("order2 desc:" + order.getDescription());
}
}






















 641
641











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










