文章目录
一、json文件简介
1、json文件
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation, JS 对象简谱) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。它基于 ECMAScript (欧洲计算机协会制定的js规范)的一个子集,采用完全独立于编程语言的文本格式来存储和表示数据。简洁和清晰的层次结构使得 JSON 成为理想的数据交换语言。 易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成,并有效地提升网络传输效率。
2、json与其他存储数据方式比较
为什么要用json文件呢?
我们最常使用的存储数据的方式有很多,比如利用txt文件存,利用xml存,利用word存,利用Excel存,如果我们要求比较高,还可以使用数据库存。
相对于txt,word来说,json格式更加明确,获取重要信息非常方便。
相对于xml来说,json格式更加简洁,存储同样的文件,花费的内存更小。
相对于Excel来说,json更适合存储字符类文件。Excel相当于比较简单的数据库了。
相对于数据库来说,json更加方便,数据库我们还需要做一些设置,安装一些软件。json可以直接使用。
二、C++操作json文件
1、jsoncpp 库下载
大家可以自己上网下载jsoncpp 库,也可以加群:326866692下载;
群二维码
2、C++从字符串中读取json
json样式比较多,这里分享两种,一种比较直接简单的,一种稍微有些复杂的。
1.简单json样式
我们定义一个字符串来保存如下json数据:
{
"name" : "shuiyixin",
"age" : "21",
"sex" : "man"
}
读取代码如下:
void readStrJson()
{
//字符串
const char* str =
"{\"name\":\"shuiyixin\",\"age\":\"21\",\"sex\":\"man\"}";
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
//从字符串中读取数据
if (reader.parse(str, root))
{
string name = root["name"].asString();
int age = root["nomen"].asInt();
string sex = root["sex"].asString();
cout << name + "," << age << "," << sex << endl;
}
}
2.复杂json样式
所谓复杂,就是说,json里面分好几层,上面那个简单的只有一层,json数据如下:
{
"name":"shuiyixin",
"major":[
{
"AI":"MachineLearning"
},
{
"AI":"DeepLearning"
},
{
"AI":"ComputerVision"
}]
}
读取代码如下:
void readStrProJson()
{
string strValue = "{\"name\":\"shuiyixin\",\"major\":[{\"AI\":\"MachineLearning\"},{\"AI\":\"DeepLearning\"},{\"AI\":\"ComputerVision\"}]}";
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value value;
if (reader.parse(strValue, value))
{
string out = value["name"].asString();
cout << out << endl;
const Json::Value arrayObj = value["major"];
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < arrayObj.size(); i++)
{
out = arrayObj[i]["AI"].asString();
cout << out<<endl;
}
}
}
3、C++从文件中读取json
从字符串中读取json文件只是为了让大家能够了解json文件,我们最终还是要从文件中读取的。
这个读取的json文件,大家可以通过下面的写json文件自己创建一个。
以下面这个json文件为例:
{
"age" : 21,
"friends" : {
"friend_age" : 21,
"friend_name" : "ZhaoWuxian",
"friend_sex" : "man"
},
"hobby" : [ "sing", "run", "Tai Chi" ],
"name" : "shuiyixin",
"sex" : "man"
}
读取代码如下:
void readFileJson()
{
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
//从文件中读取,保证当前文件有demo.json文件
ifstream in("demo.json", ios::binary);
if (!in.is_open())
{
cout << "Error opening file\n";
return;
}
if (reader.parse(in, root))
{
//读取根节点信息
string name = root["name"].asString();
int age = root["age"].asInt();
string sex = root["sex"].asString();
cout << "My name is " << name << endl;
cout << "I'm " << age << " years old" << endl;
cout << "I'm a " << sex << endl;
//读取子节点信息
string friend_name = root["friends"]["friend_name"].asString();
int friend_age = root["friends"]["friend_age"].asInt();
string friend_sex = root["friends"]["friend_sex"].asString();
cout << "My friend's name is " << friend_name << endl;
cout << "My friend's sex is "<<friend_sex << endl;
cout << "My friend is " << friend_age << " years old" << endl;
//读取数组信息
cout << "Here's my hobby:" << endl;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < root["hobby"].size(); i++)
{
string ach = root["hobby"][i].asString();
cout << ach << '\t';
}
cout << endl;
cout << "Reading Complete!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "parse error\n" << endl;
}
in.close();
}
4、C++写入json文件
除了读,我们经常还会写入json文件,json文件如下:
{
"age" : 21,
"friends" : {
"friend_age" : 21,
"friend_name" : "ZhaoWuxian",
"friend_sex" : "man"
},
"hobby" : [ "sing", "run", "Tai Chi" ],
"name" : "shuiyixin",
"sex" : "man"
}
写入代码如下:
void writeFileJson()
{
//根节点
Json::Value root;
//根节点属性
root["name"] = Json::Value("shuiyixin");
root["age"] = Json::Value(21);
root["sex"] = Json::Value("man");
//子节点
Json::Value friends;
//子节点属性
friends["friend_name"] = Json::Value("ZhaoWuxian");
friends["friend_age"] = Json::Value(21);
friends["friend_sex"] = Json::Value("man");
//子节点挂到根节点上
root["friends"] = Json::Value(friends);
//数组形式
root["hobby"].append("sing");
root["hobby"].append("run");
root["hobby"].append("Tai Chi");
//直接输出
//cout << "FastWriter:" << endl;
//Json::FastWriter fw;
//cout << fw.write(root) << endl << endl;
//缩进输出
cout << "StyledWriter:" << endl;
Json::StyledWriter sw;
cout << sw.write(root) << endl << endl;
//输出到文件
ofstream os;
os.open("demo.json", std::ios::out | std::ios::app);
if (!os.is_open())
cout << "error:can not find or create the file which named \" demo.json\"." << endl;
os << sw.write(root);
os.close();
}
要注意的是:
1.如果要写入的文件不存在,会自动创建该文件;
2.如果文件存在,写入过程不会覆盖文件中原有数据,而是将新数据写在原有数据后面。
5、主函数
所有的功能模块都写好啦,剩下就是主函数啦:
#include <string>
#include <json.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
void readStrJson(); //从字符串中读取JSON
void readStrProJson(); //从字符串中读取JSON(内容复杂些)
void readFileJson(); //从文件中读取JSON
void writeFileJson(); //将信息保存为JSON格式
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
writeFileJson(); //写入json
readFileJson(); //从文件中读取JSON
cout << "\n\n";
readStrJson(); //从字符串中读json
cout << "\n\n";
readStrProJson();//从字符串中读取JSON(内容复杂些)
system("pause");
return 0;
}
附:jsoncpp库配置
jsoncpp库配置与opencv配置原理相同,大家可以看一下下面的教程:
opencv配置(win10+VS2015+OpenCV3.1.0)
不过jsoncpp库的内容比较少,配置没有opencv那么麻烦:
1、解压并转移
首先将库解压,将下面的两个文件夹复制到你创建的项目下面
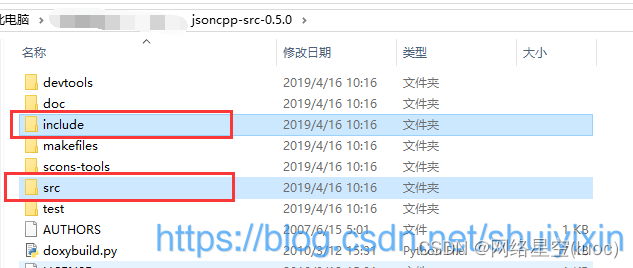
将库解压
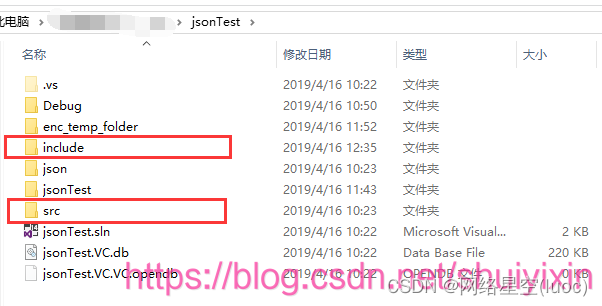
将两个文件夹复制到自己创建的项目中
2、配置属性
点击调试,并点击项目属性
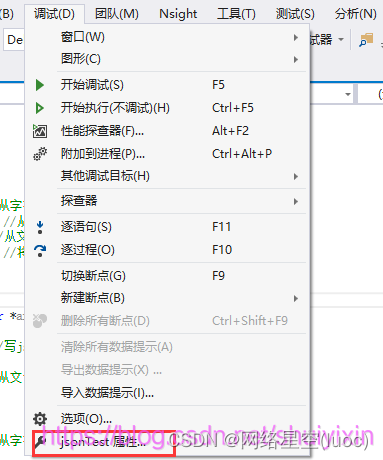
点击调试->项目属性
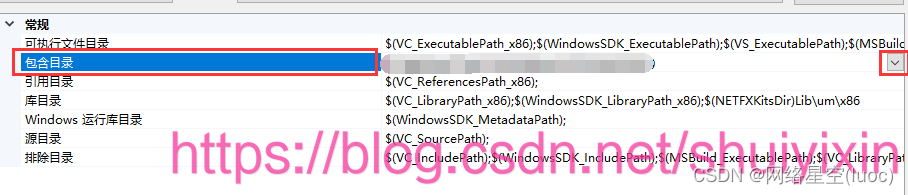
选择VC++目录中的包含目录,点击修改
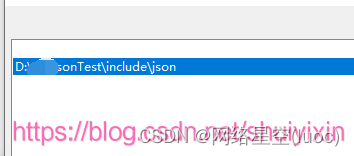
将includ文件夹下的json文件路径复制到这里,并保存
3、配置项目
将src文件夹下的lib_json文件夹下的cpp文件,添加到源文件中:
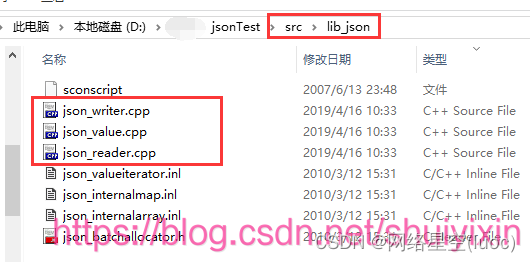
找到src文件夹->lib_json文件夹->所有cpp文件,并复制

添加到源文件中
然后就可以使用啦。
#include <string>
#include "json/json.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
void readStrJson(); //从字符串中读取JSON
void readStrProJson(); //从字符串中读取JSON(内容复杂些)
void readFileJson(); //从文件中读取JSON
void writeFileJson(); //将信息保存为JSON格式
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
writeFileJson(); //写入json
readFileJson(); //从文件中读取JSON
cout << "\n\n";
readStrJson(); //从字符串中读json
cout << "\n\n";
readStrProJson();//从字符串中读取JSON(内容复杂些)
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void readStrJson()
{
//字符串
const char* str =
"{\"name\":\"shuiyixin\",\"age\":\"21\",\"sex\":\"man\"}";
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
//从字符串中读取数据
if (reader.parse(str, root))
{
string name = root["name"].asString();
int age = root["nomen"].asInt();
string sex = root["sex"].asString();
cout << name + "," << age << "," << sex << endl;
}
}
void readStrProJson()
{
string strValue = "{\"name\":\"shuiyixin\",\"major\":[{\"AI\":\"MachineLearning\"},{\"AI\":\"DeepLearning\"},{\"AI\":\"ComputerVision\"}]}";
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value value;
if (reader.parse(strValue, value))
{
string out = value["name"].asString();
cout << out << endl;
const Json::Value arrayObj = value["major"];
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < arrayObj.size(); i++)
{
out = arrayObj[i]["AI"].asString();
cout << out << endl;
}
}
}
void readFileJson()
{
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
//从文件中读取,保证当前文件有demo.json文件
ifstream in("demo.json", ios::binary);
if (!in.is_open())
{
cout << "Error opening file\n";
return;
}
if (reader.parse(in, root))
{
//读取根节点信息
string name = root["name"].asString();
int age = root["age"].asInt();
string sex = root["sex"].asString();
cout << "My name is " << name << endl;
cout << "I'm " << age << " years old" << endl;
cout << "I'm a " << sex << endl;
//读取子节点信息
string friend_name = root["friends"]["friend_name"].asString();
int friend_age = root["friends"]["friend_age"].asInt();
string friend_sex = root["friends"]["friend_sex"].asString();
cout << "My friend's name is " << friend_name << endl;
cout << "My friend's sex is " << friend_sex << endl;
cout << "My friend is " << friend_age << " years old" << endl;
//读取数组信息
cout << "Here's my hobby:" << endl;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < root["hobby"].size(); i++)
{
string ach = root["hobby"][i].asString();
cout << ach << '\t';
}
cout << endl;
cout << "Reading Complete!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "parse error\n" << endl;
}
in.close();
}
void writeFileJson()
{
//根节点
Json::Value root;
//根节点属性
root["name"] = Json::Value("shuiyixin");
root["age"] = Json::Value(21);
root["sex"] = Json::Value("man");
//子节点
Json::Value friends;
//子节点属性
friends["friend_name"] = Json::Value("ZhaoWuxian");
friends["friend_age"] = Json::Value(21);
friends["friend_sex"] = Json::Value("man");
//子节点挂到根节点上
root["friends"] = Json::Value(friends);
//数组形式
root["hobby"].append("sing");
root["hobby"].append("run");
root["hobby"].append("Tai Chi");
//直接输出
//cout << "FastWriter:" << endl;
//Json::FastWriter fw;
//cout << fw.write(root) << endl << endl;
//缩进输出
cout << "StyledWriter:" << endl;
Json::StyledWriter sw;
cout << sw.write(root) << endl << endl;
//输出到文件
ofstream os;
os.open("demo.json", std::ios::out | std::ios::app);
if (!os.is_open())
cout << "error:can not find or create the file which named \" demo.json\"." << endl;
os << sw.write(root);
os.close();
}























 3115
3115











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










