目录
1️⃣Set系列集合概述

Set系列集合特点:无序,不重复,无索引
💡Set集合实现类的特点:
① HashSet:无序,不重复,无索引
package com.study.d1_set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class SetDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//HsahSet LinkedHashSet TreeSet
//LinkedHashSet有序
//HsahSet 无序不可重复 无索引
Set<String> sets = new HashSet<>();
sets.add("mysql");
sets.add("mysql");
sets.add("java");
sets.add("java");
sets.add("html");
sets.add("html");
sets.add("springboot");
sets.add("springboot");
System.out.println(sets);
}
}

②LinkedHashSet:有序,不重复,无索引
package com.study.d1_set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class SetDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//LinkedHashSet有序 不重复 无索引
Set<String> sets = new LinkedHashSet<>();
sets.add("mysql");
sets.add("mysql");
sets.add("java");
sets.add("java");
sets.add("html");
sets.add("html");
sets.add("springboot");
sets.add("springboot");
System.out.println(sets);
}
}
③TreeSet:排序,不重复,无索引
package com.study.d1_set;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
观察TreeSet对于有值特性的数据如何排序
学会对自定义类型的数据进行排序
*/
public class SetDemo5TreSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> stes = new TreeSet<>(); //不重复 无序 可排序
stes.add(23);
stes.add(12);
stes.add(27);
stes.add(20);
System.out.println(stes);
Set<String> stes1 = new TreeSet<>();
stes1.add("python");
stes1.add("About");
stes1.add("c++");
stes1.add("java");
stes1.add("about");
stes1.add("哇哈哈");
System.out.println(stes1);
System.out.println("---------------");
//方式二 集合人自带比较器对象制定规则
//优先就近原则
Set<Apple5> apple5s = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Apple5>() {
@Override
public int compare(Apple5 o1, Apple5 o2) {
//升序 return o1.getWeight() - o2.getWeight();
// return o2.getWeight() - o1.getWeight(); //降序
//浮点型建议使用Double.compare
return Double.compare(o2.getPrice() ,o1.getPrice());
}
});
apple5s.add(new Apple5("红富士","红色",9.9,500));
apple5s.add(new Apple5("青苹果","绿色",15.9,300));
apple5s.add(new Apple5("绿苹果","青色",29.9,400));
apple5s.add(new Apple5("黄苹果","黄色",9.8,500));
System.out.println(apple5s);
}
}

排序方法有两种:
方式一:在类中自定义比较规则
/**
方式一 类自定义比较规则
* @param o
* @return
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Apple5 o) {
//按照重量进行比较
// return this.weight - o.weight ; 会去掉重量相等的元素
return this.weight - o.weight >= 0 ? 1 : -1; //会保留重量相等的元素
}方式二:集合自带比较器对象进行排序(推荐使用此方法)
//方式二 集合人自带比较器对象制定规则
//优先就近原则
Set<Apple5> apple5s = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Apple5>() {
@Override
public int compare(Apple5 o1, Apple5 o2) {
//升序 return o1.getWeight() - o2.getWeight();
// return o2.getWeight() - o1.getWeight(); //降序
//浮点型建议使用Double.compare
return Double.compare(o2.getPrice() ,o1.getPrice());
}
});TreeSet默认排序规则:
⬛对于数值型:Intrger Double默认从大到小
⬛对于字符串类型:默认按照首字母的编号升序
⬛对于自定义类型:需要自己制定规则
✨Set集合去重复小案例

package com.study.d1_set;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private char sex;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, char sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public char getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(char sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex=" + sex +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return age == student.age && sex == student.sex && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age, sex);
}
}
public class SetDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Set集合去重复的原因是先计算哈希值 再判断equals
Set<Student> sets = new HashSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("张三",22,'男');
Student s2 = new Student("张三",22,'男');
Student s3 = new Student("李四",22,'男');
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());
System.out.println(s2.hashCode());
sets.add(s1);
sets.add(s2);
sets.add(s3);
System.out.println(sets);
}
}
2️⃣Collection体系的特点,使用场景总结

3️⃣可变参数
可变参数
⬛可变参数用在形参中可以接收多个数据
⬛可变参数的格式:数据类型...参数名称
public class MethonDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
sum(); //可以不传参数
sum(10);//可以传一个参数
sum(10,20 ,30); //可以传多个
sum(new int[]{10,20,30}); //可以传一个数组
}
public static void sum(int...nums){
System.out.println("元素个数" + nums.length);
System.out.println("元素内容" + Arrays.toString(nums));
}
}
4️⃣集合工具类Collections
作用:Collections并不属于集合,是用来操作集合的工具类
🔔Collections常用API
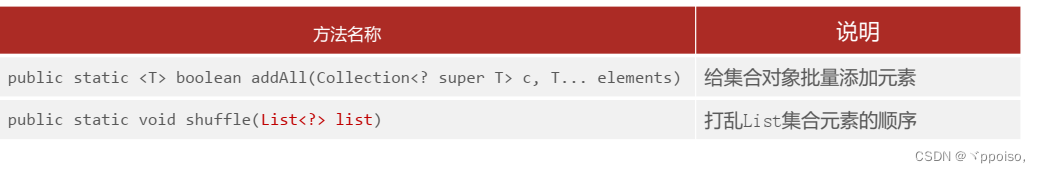
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
// names.add("张无忌");
// names.add("金毛狮王");
// names.add("白眉鹰王");
// names.add("赵敏");
//一次添加多个元素 addAll
Collections.addAll(names,"张无忌","金毛狮王","白眉鹰王","赵敏");//打乱List集合数据 shuffle
Collections.shuffle(names);🔔Collections排序相关API

排序一
//List将集合元素按照默认规则排序(排值特性的元素) sort
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); //shift+f6 可以实现同步改
Collections.addAll(list,10,22,3,54,32);
System.out.println(list);
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);排序二
package com.study.d3_collections;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class CollectionsDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Apple5> apple5s = new ArrayList<>(); //可重复
apple5s.add(new Apple5("红富士","红色",9.9,500));
apple5s.add(new Apple5("青苹果","绿色",15.9,300));
apple5s.add(new Apple5("绿苹果","青色",29.9,400));
apple5s.add(new Apple5("黄苹果","黄色",9.8,500));
System.out.println(apple5s);
//方式一 在类中重写compare方法
Collections.sort(apple5s);
System.out.println(apple5s);
System.out.println("----------------");
//List集合会保留重复 (List集合本身就是可重复的) TreeList不会保留
//方式二 sort自带比较器对象
// Collections.sort(apple5s, new Comparator<Apple5>() {
// @Override
// public int compare(Apple5 o1, Apple5 o2) {
// return Double.compare(o1.getPrice() ,o2.getPrice());
// }
// });
Collections.sort(apple5s, ( o1, o2)-> Double.compare(o1.getPrice() ,o2.getPrice()));
System.out.println(apple5s);
}
}
注意🔔🔔🔔🔔🔔🔔🔔在类中重写排序方法
/**
方式一 类自定义比较规则
* @param o
* @return
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Apple5 o) {
//按照重量进行比较
return this.weight - o.weight ;// 会去掉重量相等的元素
// return this.weight - o.weight >= 0 ? 1 : -1; //会保留重量相等的元素
}
}5️⃣Collection体系综合案例:斗地主
package com.study.d4_doudizhu;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class GameDemo {
/**
1定义一个静态数组集合存储54张牌
* @param args
*/
public static List<Card> allCard = new ArrayList<>();
/**
2 做牌 定义静态代码块
* @param args
*/
static {
//3 点数
String[] sizes = {"3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10","J","Q","K","A","2"};
//4花色
String[] colors = {"♣","♥","♠","♦"};
//5组合
int index = 0; //记录牌的大小
for (String size : sizes) {
index++;
for (String color : colors) {
//6封装成牌对象
Card c = new Card(size,color,index);
//7添加
allCard.add(c);
}
}
//8存大小王
Card c1 = new Card("","🃏",++index);
Card c2 = new Card("","🃏",++index);
Collections.addAll(allCard,c1,c2);
System.out.println("新牌 "+ allCard);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//9洗牌
Collections.shuffle(allCard);
System.out.println("洗牌后" + allCard);
//10发牌(定义三个玩家,每个玩家的牌也是一个容器)
List<Card> a1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> a2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> a3 = new ArrayList<>();
//11发牌
for (int i = 0; i < allCard.size() - 3; i++) {
Card c = allCard.get(i);
if (i %3 == 0){
a1.add(c);
}else if(i%3== 1){
a2.add(c);
}else if(i %3 == 2){
a3.add(c);
}
}
//12拿到底牌,把最后三张牌截取为一个集合
List<Card> lastcard = allCard.subList(allCard.size() - 3,allCard.size());
//13给玩家的牌排序,从大到小
sortCard(a1);
sortCard(a2);
sortCard(a3);
//14输出玩家的牌
System.out.println("a1" +a1);
System.out.println("a2" +a2);
System.out.println("a3" +a3);
System.out.println("三张底牌" + lastcard);
}
private static void sortCard(List<Card> cards) {
Collections.sort(cards, new Comparator<Card>() {
@Override
public int compare(Card o1, Card o2) {
return o2.getIndex() - o1.getIndex();
}
});
}
}

谁能赢??
6️⃣Map集合体系
Map集合的概述和作用
①是一种双列集合,每个元素包含两个数据
②每个元素的格式:key =value; {key1= value1,key2 = value2.....}
③也被称为“键值对集合”
/**
目标:认识Map体系,按照键无序,不重复,无索引,值不做要求
*/
public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
maps.put("鸿星尔克",3);
maps.put("java",3);
maps.put("java",100);
maps.put("枸杞",100);
System.out.println(maps);
}
}Map集合体系特点

Map集合的键无序,不重复,无索引的;Map集合的值不做要求,可以重复。
Map后面重复的键所对应的值会覆盖前面键的值
Map集合的键值对都可以为null
Map集合实现类的特点:

Map常用API

package com.study.d6_mapapi;
import java.util.*;
/**
熟悉Map常用API
*/
public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1HashMap 无序 不重复 无索引
Map<String,Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
maps.put("ipone",10);
maps.put("哇哇",20);
maps.put("ipone",100);
maps.put("huawei",100);
maps.put("生活用品",10);
maps.put("手表",10);
System.out.println(maps);
//2清空集合
// maps.clear();
// System.out.println(maps);
//3判断是否为空
System.out.println(maps.isEmpty());
//4根据键值取值
Integer key = maps.get("huawei");
System.out.println(key);
//5根据键值删除整个元素,返回删除元素的值
System.out.println(maps.remove("ipone"));
System.out.println(maps);
//6判断是否包含某个键 包含返回true
System.out.println(maps.containsKey("pone"));
System.out.println(maps.containsKey("huawei"));
//7是否包含某个值
System.out.println(maps.containsValue(100));
System.out.println(maps.containsValue(1));
//8获取全部键的集合 Public set<k> KeySet()
Set<String> strings = maps.keySet(); //ctrl + alt +v自动生成
System.out.println(strings);
//9获取全部值的集合 Collection<v> values()
Collection<Integer> values = maps.values();
System.out.println(values);
//10集合的大小
System.out.println(maps.size());
//11合并其他Map集合 拓展
System.out.println("------------");
Map<String,Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();
map1.put("java1",1);
map1.put("java2",100);
Map<String,Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();
map2.put("java2",11);
map2.put("java3",100);
map1.putAll(map2);
System.out.println(map1);
System.out.println(map2);
}
}
Map集合的遍历方式

public class MapDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
maps.put("ipone",10);
maps.put("哇哇",20);
maps.put("ipone",100);
maps.put("huawei",100);
maps.put("生活用品",10);
maps.put("手表",10);
System.out.println(maps);
//{huawei=100, 手表=10, ipone=100, 生活用品=10, 哇哇=20}
//1键找值
//先取出所有的键
Set<String> keys = maps.keySet();
for (String key : keys) {
int value = maps.get(key); //根据键取值
System.out.println(key + "--->" + value);
}
}
}

public class MapDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
maps.put("ipone",10);
maps.put("哇哇",20);
maps.put("ipone",100);
maps.put("huawei",100);
maps.put("生活用品",10);
maps.put("手表",10);
System.out.println(maps);
//{huawei=100, 手表=10, ipone=100, 生活用品=10, 哇哇=20}
/**
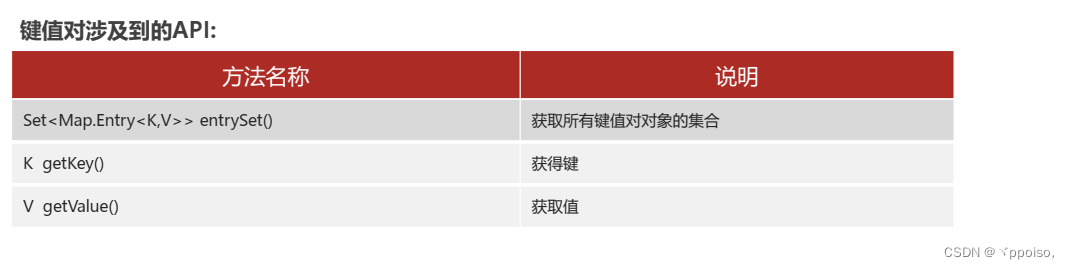
使用foreach便利map集合 发现map集合元素是没有直接类型的,所以不可以使用
可以把map集合转化为Set集合,调用Map集合的方法 entryset把MAP集合转化为set集合
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entries = [(huawei=100), (手表=10), ipone=100, 生活用品=10, 哇哇=20]
entry
此时可以使用foreach便利
*/
//键值对
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = maps.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries){
String key = entry.getKey();
int value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "--->" + value);
}
}
}
ublic class MapDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
maps.put("ipone",10);
maps.put("哇哇",20);
maps.put("ipone",100);
maps.put("huawei",100);
maps.put("生活用品",10);
maps.put("手表",10);
System.out.println(maps);
//{huawei=100, 手表=10, ipone=100, 生活用品=10, 哇哇=20}
// maps.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, Integer>() {
// @Override
// public void accept(String key, Integer value) {
// System.out.println(key + "--->" + value);
// }
// });
maps.forEach(( key, value) ->{
System.out.println(key + "--->" + value);
});
}
}
Map小案例

package com.study.d8_mapTest;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
public class MapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1把80个学生的数据拿过来
String[] select = {"A","B","C","D"};
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Random rs = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) {
sb.append(select[rs.nextInt(select.length)]);
}
System.out.println(sb);
//2定义Map集合记录最终统计的及如果
Map<Character,Integer> infos = new HashMap<>();
//3遍历80个学生的数据
for (int i = 0; i < sb.length(); i++) {
//提取当前选择景点字符
char ch = sb.charAt(i);
//判断集合中是否存在该字符
if (infos.containsKey(ch)){
infos.put(ch,infos.get(ch) + 1);
}else {
//第一次出现
infos.put(ch ,1);
}
}
//4输出集合
System.out.println(infos);
}
}
Map集合实现类TreeMap
public class TreeMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer,String> map1 = new TreeMap<>();
map1.put(11,"哇哈哈");
map1.put(1,"雪碧");
map1.put(10,"可乐");
System.out.println(map1);
//TreeMap自带排序 不重复 无索引
Map<Apple5,String> map2 = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Apple5>() {
@Override
public int compare(Apple5 o1, Apple5 o2) {
return Double.compare(o1.getPrice() , o2.getPrice());
}
});
}
}7️⃣集合嵌套
package com.study.d8_mapTest;
import java.util.*;
public class Map_anli {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用一个Map集合存储
Map<String, List<String>> data = new HashMap<>();
//2把学生选择的数据存进去 直接存了模拟集合嵌套
List<String> select = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(select,"A","C");
data.put("哇哈哈",select);
List<String> select1 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(select1,"B","C");
data.put("哇哈哈1",select1);
List<String> select2 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(select2,"A","C","D");
data.put("哇哈哈2",select2);
System.out.println(data);
//3统计每个景点的选择人数
Map<String,Integer> infos = new HashMap<>();
//提取所有人景点的选择信息
Collection<List<String>> values = data.values(); //提取的是键后面的数据
//values =[[B, C], [A, C, D], [A, C]]
System.out.println(values);
for (List<String> value : values) {
for (String s : value) {
if (infos.containsKey(s)){
infos.put(s,infos.get(s) + 1);
}else {
infos.put(s,1);
}
}
}
System.out.println(infos);
}
}






















 2495
2495











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








