package com.mine;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectableChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class SelectorDemo {
public static int PORT_NUMBER = 1234;
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
new SelectorDemo().go(argv);
}
public void go(String[] argv) throws Exception {
int port = PORT_NUMBER;
if (argv.length > 0) {
// Override default listen port
port = Integer.parseInt(argv[0]);
}
System.out.println("Listening on port " + port); // Allocate an unbound server socket channel
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 新建一个通道
ServerSocket serverSocket = serverChannel.socket(); // 从通道获得一个socket连接
Selector selector = Selector.open(); // 新建一个选择器
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port)); // 把socket连接绑定到一个端口上
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 设置通道为非阻塞模式,只有非阻塞模式才能使用nio带来的好处,socket通道能设置为非阻塞的,文件通道不能设置为非阻塞的
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //把这个通道注册到一个选择器上,感兴趣的操作时OP_ACCEPT,等待连接
while (true) {// 从选择器中循环选择已经准备好的选择器键,键就是保持通道跟选择器的对应关系
int n = selector.select(); //从选择器中获得已经准备好的选择器键的个数
if (n == 0) {
continue; // nothing to do
}// Get an iterator over the set of selected keys
Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); // 遍历所有已经准备好的选择器键
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) it.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()) { //如果该键是等待连接的状态
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); //从改键中获取已经准备连接好的server socket通道
SocketChannel channel = server.accept(); //从server socket通道获得本次socket连接
registerChannel(selector, channel, SelectionKey.OP_READ); //把该连接注册为可读的操作状态
sayHello(channel);//往该socket连接发送数据
}// Is there data to read on this channel?
if (key.isReadable()) { //下次当该链接为可读的时候
readDataFromSocket(key);//接收该socket链接的数据,并显示
}// Remove key from selected set; it's been handled
it.remove();//删除本次已经执行过的准备好的键,下次再执行selector.select(),仍然能选出所有已经准备好的键
}
}
}
protected void registerChannel(Selector selector, SelectableChannel channel, int ops) throws Exception {
if (channel == null) {
return;
}
channel.configureBlocking(false); //设置通道为非阻塞模式
channel.register(selector, ops);//把该连接注册为可读的操作状态
}
private ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
protected void readDataFromSocket(SelectionKey key) throws Exception {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
int count;
buffer.clear();
while ((count = socketChannel.read(buffer)) > 0) { //从通道里面独处数据
buffer.flip(); //标准该通道的数据是可读的
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(buffer);//往通道里面写数据
}
buffer.clear();
if (count < 0) {
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
private void sayHello(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
buffer.clear();
buffer.put("Hi there!\r\n".getBytes());
buffer.flip();
channel.write(buffer);
}
}
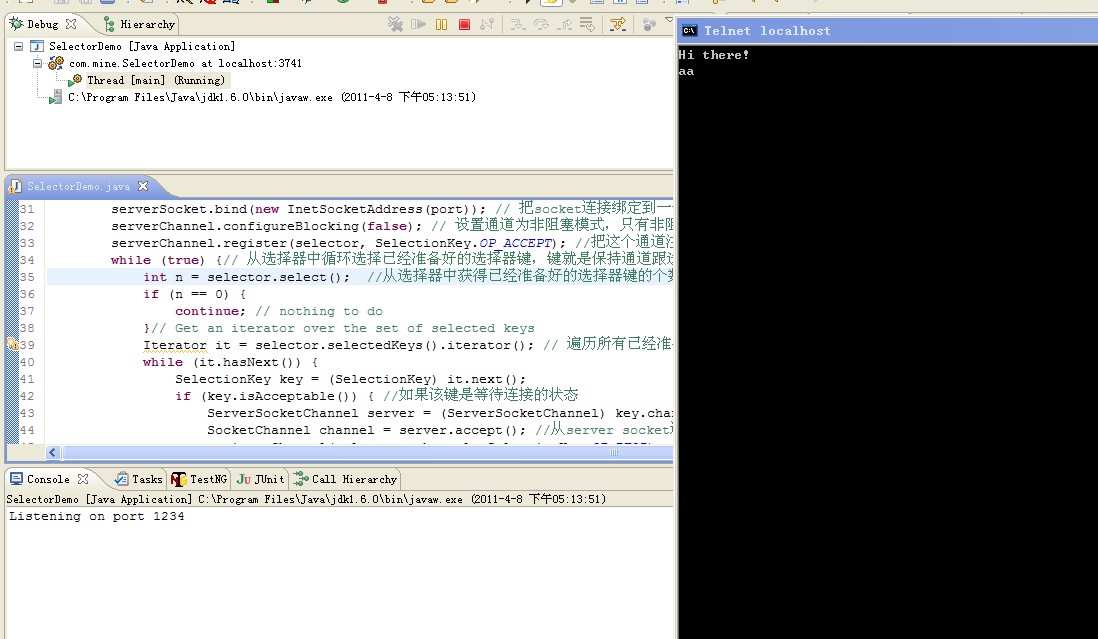
执行该程序,用telnet登陆本机的1234端口,你输入一个字符,程序把接收到的字符发送出去。





















 1394
1394











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








