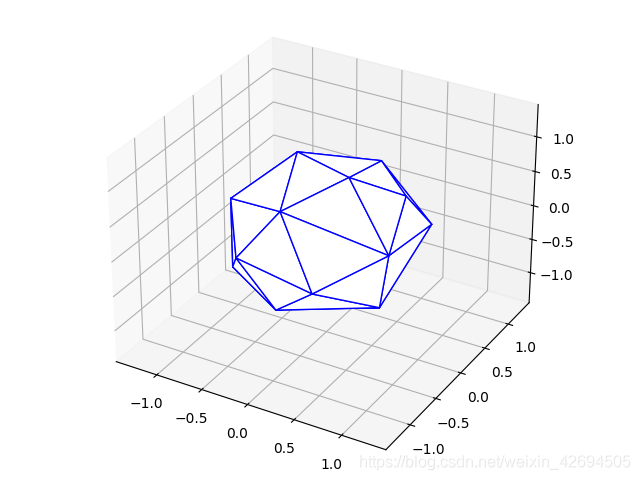
实现效果如下图所示:
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "bowyer_watson.h"
#include <sstream>
#include <fstream>
#include <chrono>
#include <armadillo>
using namespace std;
//function to provide a first-order test of whether BowyerWatson::Triangle::contains() works correctly
void test()
{
typedef BowyerWatson::Triangle Triangle;
//create initial polyhedron
arma::dvec3 u({ 0,0,1 });
arma::dvec3 e({ 1,0,0 });
arma::dvec3 n({ 0,1,0 });
arma::dvec3 w({ -1,0,0 });
arma::dvec3 s({ 0,-1,0 });
arma::dvec3 d({ 0,0,-1 });
Triangle* uen = new Triangle(u, e, n, 0);
Triangle* unw = new Triangle(u, n, w, 0);
Triangle* uws = new Triangle(u, w, s, 0);
Triangle* use = new Triangle(u, s, e, 0);
Triangle* des = new Triangle(d, e, s, 0);
Triangle* dsw = new Triangle(d, s, w, 0);
Triangle* dwn = new Triangle(d, w, n, 0);
Triangle* dne = new Triangle(d, n, e, 0);
uen->neighbors[0] = dne; uen->neighbors[1] = unw; uen->neighbors[2] = use;
unw->neighbors[0] = dwn; unw->neighbors[1] = uws; unw->neighbors[2] = uen;
uws->neighbors[0] = dsw; uws->neighbors[1] = use; uws->neighbors[2] = unw;
use->neighbors[0] = des; use->neighbors[1] = uen; use->neighbors[2] = uws;
des->neighbors[0] = use; des->neighbors[1] = dsw; des->neighbors[2] = dne;
dsw->neighbors[0] = uws; dsw->neighbors[1] = dwn; dsw->neighbors[2] = des;
dwn->neighbors[0] = unw; dwn->neighbors[1] = dne; dwn->neighbors[2] = dsw;
dne->neighbors[0] = uen; dne->neighbors[1] = des; dne->neighbors[2] = dwn;
Triangle* tris[8] = { uen, unw, use, uws, dne, dwn, des, dsw };
//test point containment
cout << "Should be ones:" << endl;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
arma::dvec3 to_test(
{
1.0f * (tris[i]->vertices[0][0] + tris[i]->vertices[1][0] + tris[i]->vertices[2][0]) / 3.0f,
1.0f * (tris[i]->vertices[0][1] + tris[i]->vertices[1][1] + tris[i]->vertices[2][1]) / 3.0f,
1.0f * (tris[i]->vertices[0][2] + tris[i]->vertices[1][2] + tris[i]->vertices[2][2]) / 3.0f
}
);
cout << (tris[i]->contains(to_test) ? '1' : '0');
}
cout << "\nShould be zeroes:" << endl;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
arma::dvec3 to_test(
{
-1.0f * (tris[i]->vertices[0][0] + tris[i]->vertices[1][0] + tris[i]->vertices[2][0]) / 3.0f,
-1.0f * (tris[i]->vertices[0][1] + tris[i]->vertices[1][1] + tris[i]->vertices[2][1]) / 3.0f,
-1.0f * (tris[i]->vertices[0][2] + tris[i]->vertices[1][2] + tris[i]->vertices[2][2]) / 3.0f
}
);
cout << (tris[i]->contains(to_test) ? '1' : '0');
}
for (unsigned int j = 1; j < 8; ++j)
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
arma::dvec3 to_test(
{
1.0f * (tris[i]->vertices[0][0] + tris[i]->vertices[1][0] + tris[i]->vertices[2][0]) / 3.0f,
1.0f * (tris[i]->vertices[0][1] + tris[i]->vertices[1][1] + tris[i]->vertices[2][1]) / 3.0f,
1.0f * (tris[i]->vertices[0][2] + tris[i]->vertices[1][2] + tris[i]->vertices[2][2]) / 3.0f
}
);
cout << (tris[(i + j) % 8]->contains(to_test) ? '1' : '0');
}
cout << endl;
}
//arguments: (pointcount = 1000, relaxations = 5, filename = bwoutput.py, seed = 666)
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
unsigned int pointcount = 20;
unsigned int relaxations = 5;
std::string output_filename("bwoutput.py");
unsigned int seed = 666;
istringstream ss;
bool input_erroneous(false);
bool display_help(false);
switch (argc)
{
case(5):
ss.clear();
ss.str(argv[4]);
if (!(ss >> seed))
{
cout << "Received invalid input \"" << argv[4] << "\" as argument 4; this should be an integer specifying the seed to use for the random number generator. Use argument \"--help\" to see help menu." << endl;
input_erroneous = true;
}
case(4):
output_filename = argv[3];
if (output_filename.substr(output_filename.length() - 3) != ".py")
output_filename += ".py";
case(3):
ss.clear();
ss.str(argv[2]);
if (!(ss >> relaxations))
{
cout << "Received invalid input \"" << argv[2] << "\" as argument 2; this should be a nonnegative integer specifying the number of times to perform modified Lloyd relaxation. Use argument \"--help\" to see help menu." << endl;
input_erroneous = true;
}
case(2):
if (strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0 || strcmp(argv[1], "-help") == 0 || strcmp(argv[1], "help") == 0 || strcmp(argv[1], "\"--help\"") == 0)
{
display_help = true;
input_erroneous = true;
break;
}
ss.clear();
ss.str(argv[1]);
if (!(ss >> pointcount) || pointcount == 0)
{
cout << "Received invalid input \"" << argv[1] << "\" as argument 1; this should be a positive integer specifying the number of points to generate. Use argument \"--help\" to see help menu." << endl;
input_erroneous = true;
}
case(1):
break;
default:
display_help = true; //the OS provides argv[0], so this line should never be reached
input_erroneous = true;
}
if (display_help)
{
cout << "\tBowyer-Watson Algorithm: Generates random points on the unit sphere, constructs a triangulation thereof, and creates a python file for viewing the resuling mesh.\n";
cout << "\tTo view this menu, pass \"--help\" as the first argument.\n";
cout << "\tArguments expected, in order, and their defaults:\n";
cout << "\t\tpointcount = 1000: a positive integer specifying the number of points to generate.\n";
cout << "\t\trelaxations = 5: a nonnegative integer specifying the number of times to relax the points (modified Lloyd relaxation).\n";
cout << "\t\tfilename = bwoutput.py: the filename for the output python file. If it does not end in \".py\", that extension will be appended to it.\n";
cout << "\t\tseed = 666: a nonnegative integer specifying the seed to be used for the random number generator used in generating points.";
cout << endl;
}
if (input_erroneous)
return(0);
srand(seed);
chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point starttime;
chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point endtime;
chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point meshendtime;
BowyerWatson bw;
cout << "\tBeginning spherical Bowyer-Watson test with " << pointcount << " points & " << relaxations << " iterations of the relaxation algorithm..." << endl;
starttime = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
std::vector<std::pair<arma::dvec3, unsigned int> > point_vector;
bw.generate_points(pointcount, point_vector);
BowyerWatson::Triangle* results = bw.perform(bw.create_initial_triangles(point_vector));
for (unsigned int relaxations_performed = 0; relaxations_performed < relaxations; ++relaxations_performed)
{
bw.relax_points(results, point_vector);
results = bw.perform(bw.create_initial_triangles(point_vector));
}
endtime = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
cout << "\tRunning time: " << chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(endtime - starttime).count() << " milliseconds." << endl;
cout << "\tCompleted calculations. Transforming to mesh..." << endl;
BowyerWatson::Mesh mesh = bw.get_mesh(results, true);
meshendtime = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
cout << "\tMesh running time: " << chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(meshendtime - endtime).count() << " milliseconds." << endl;
cout << "\tw00t, you got a mesh! Writing to file..." << endl;
///
ofstream file;
file.open(output_filename);
file << "from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D\n";
file << "from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Poly3DCollection\n";
file << "import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n";
file << "fig = plt.figure()\n";
file << "ax = Axes3D(fig)\n";
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < mesh.triangles.size(); i += 3)
{
file << "ax.add_collection3d(Poly3DCollection([list(zip([" <<
mesh.vertices[mesh.triangles[i]] << "," << mesh.vertices[mesh.triangles[i + 1]] << "," << mesh.vertices[mesh.triangles[i + 2]]
<< "],[" <<
mesh.vertices[mesh.triangles[i] + 1] << "," << mesh.vertices[mesh.triangles[i + 1] + 1] << "," << mesh.vertices[mesh.triangles[i + 2] + 1]
<< "],[" <<
mesh.vertices[mesh.triangles[i] + 2] << "," << mesh.vertices[mesh.triangles[i + 1] + 2] << "," << mesh.vertices[mesh.triangles[i + 2] + 2]
<< "]))], facecolors='w', edgecolors='b'))\n";
}
file << "ax.set_xlim(-1.4, 1.4)\n";
file << "ax.set_ylim(-1.4, 1.4)\n";
file << "ax.set_zlim(-1.4, 1.4)\n";
file << "plt.show()\n";
file.close();
///
cout << "\tBowyer-Watson test complete! Wrote to: " << output_filename << endl;
return(0);
}


























 413
413

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










