目录
注解声明为@interface(注:这与interface接口没有任何关系)
1.声明注解
注解声明为@interface(注:这与interface接口没有任何关系)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
}
内部定义成员通常用value表示
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value();
}
使用
@MyAnnotation(value = "Hello")
public int add(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
可以指定成员的默认值,使用default定义
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value() default "Hello";
} 介绍
- 如果自定义注解没有成员,表明是一个标识;如果注解有成员,在使用注解时必须指定成员的值。
- 定义新的注解类型使用@interface
- 自定义注解自动继承java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口
- 注解的成员变量类型可以是8中基本数据类型、String类型、Class类型、Enum类型、Annotation类型或以上类型的数组。
- 自定义注解必须配上注解的信息处理流程(使用反射)才有意义
2.JDK中的元注解
元注解用于修饰其他Annotation的定义,它是对现有的注解进行解释说明的注解。
4个元注解:@Retention、@Target、@Documented、@Inherited
@Retention:
表示需要在什么级别保存该注释信息,用于描述注解的生命周期。
进入@Retention注解源码看到它只有一个RetentionPolicy类型的成员。
到,他是一个枚举类型,包括三个值(SOURCE、CLASS、RUNTIME)。
- RetentionPolicy.SOURCE:在源文件中有效,编译器直接丢弃这种策略的注释。
- RetentionPolicy.CLASS:在class文件中有效,当运行java程序时,JVM不会保留注释。
- RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:在运行时有效,当运行java程序时,JVM会保留注释。程序可以通过反射获取该注释。
@Target:
用于描述注解的适用范围(即可以用在什么地方)
进入@Target注解源码看到它只有一个ElementType数组类型的成员。
public enum ElementType {
TYPE,
FIELD,
METHOD,
PARAMETER,
CONSTRUCTOR,
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
PACKAGE,
TYPE_PARAMETER,
TYPE_USE
}
@Documented:
说明该注解将被包含在javadoc中
@Inherited:
说明子类可以继承父类中的该注解
3.JDK8中注解的新特性
可重复注解
如果我们需要定义重复注解,就必须给它定义容器类,还要使用 @Repeatable 注解修饰。
@Repeatable(MyAnnotations.class)
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value() default "hello";
}
/**
* 容器类
*/
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotations {
RepetitionAnnotation[] value();
}
测试重复定义注解
public class AnnotationTest {
/**
* @Description 获取指定两个数之和
* @param a
* @param b
* @return 两数之和
*/
@MyAnnotation(value = "Hello")
@MyAnnotation(value = "你好")
public int add(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
}
类型注解
- 向 @Target 中添加两种类型 TYPE_PARAMETER和TYPE_USE
4.使用注解
@Target(value= {ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Documented
@Retention(value= RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@interface myAnnotation{
String name() default "9999";
}
@myAnnotation(name="sssss")
static class as9{
@myAnnotation(name="ss9")
public void ss(){
}
public void cc() throws NoSuchMethodException {
as9.class.getAnnotation(myAnnotation.class).name();
}
}
@myAnnotation()
static class as6{
}
@Test
public void t17() throws Exception {
System.out.println(as9.class.getAnnotation(myAnnotation.class).name());//sssss
System.out.println(as6.class.getAnnotation(myAnnotation.class).name());//sssss
System.out.println(
as9.class.getMethod("ss",null).getAnnotation(myAnnotation.class).name()
);//获取方法上的注解值
}
5.示例-反射获取注解
先定义一个注解:
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyField {
String description();
int length();
}
通过反射获取注解
public class MyFieldTest {
//使用我们的自定义注解
@MyField(description = "用户名", length = 12)
private String username;
@Test
public void testMyField(){
// 获取类模板
Class c = MyFieldTest.class;
// 获取所有字段
for(Field f : c.getDeclaredFields()){
// 判断这个字段是否有MyField注解
if(f.isAnnotationPresent(MyField.class)){
MyField annotation = f.getAnnotation(MyField.class);
System.out.println("字段:[" + f.getName() + "], 描述:[" + annotation.description() + "], 长度:[" + annotation.length() +"]");
}
}
}
}
6.示例使用场景
- 自定义注解+拦截器 实现登录校验
- 自定义注解+AOP 实现日志打印
7.通过反射获取类中所有加了注解的方法、变量-示例
@Target(value= {ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.FIELD})
@Documented
@Retention(value= RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@interface myAnnotation{
String name() default "9999";
}
@myAnnotation(name="sssss")
static class as9{
@myAnnotation(name="ss9")
public void ss(){
}
@myAnnotation(name="ss92")
public void ss2(){
}
@myAnnotation(name="ss929")
private String cc;
}
@myAnnotation()
static class as6{
}
@Test
public void t17() throws Exception {
System.out.println(as9.class.getAnnotation(myAnnotation.class).name());//sssss
System.out.println(as6.class.getAnnotation(myAnnotation.class).name());//sssss
System.out.println(
as9.class.getMethod("ss",null).getAnnotation(myAnnotation.class).name()
);
Class c = as9.class;
for (Field f:c.getDeclaredFields()){//反射获取所有字段
if(f.isAnnotationPresent(myAnnotation.class)){
myAnnotation my = f.getAnnotation(myAnnotation.class);
System.out.println("字段:[" + f.getName() + "], 值:[" + my.name() + "]");
}
}
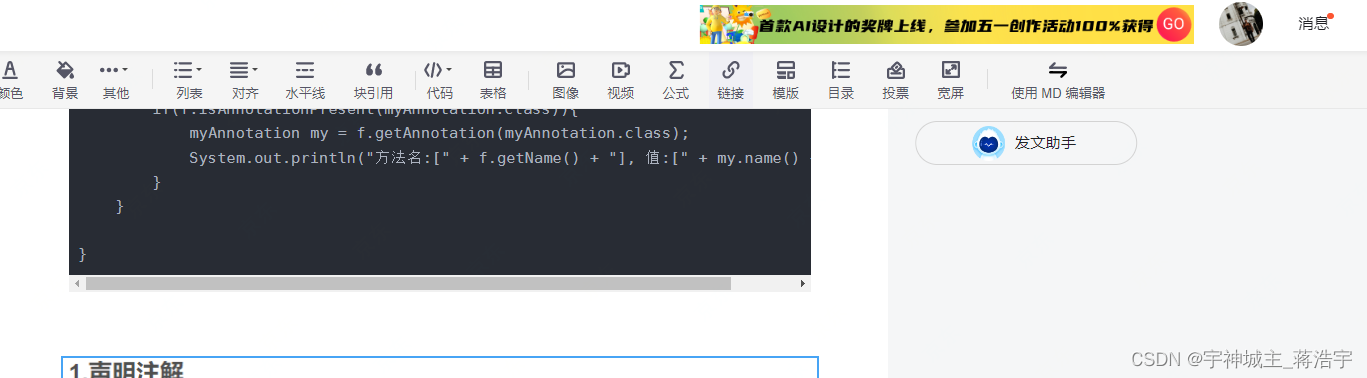
for (Method f:c.getDeclaredMethods()){//获取所有方法
if(f.isAnnotationPresent(myAnnotation.class)){
myAnnotation my = f.getAnnotation(myAnnotation.class);
System.out.println("方法名:[" + f.getName() + "], 值:[" + my.name() + "]");
}
}
}


ok
持续更新






















 689
689











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








