E. Counting Arrays
time limit per test
3 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
You are given two positive integer numbers x and y. An array F is called an y-factorization of x iff the following conditions are met:
- There are y elements in F, and all of them are integer numbers;
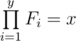 .
.
You have to count the number of pairwise distinct arrays that are y-factorizations of x. Two arrays A and B are considered different iff there exists at least one index i (1 ≤ i ≤ y) such that Ai ≠ Bi. Since the answer can be very large, print it modulo 109 + 7.
Input
The first line contains one integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the number of testcases to solve.
Then q lines follow, each containing two integers xi and yi (1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 106). Each of these lines represents a testcase.
Output
Print q integers. i-th integer has to be equal to the number of yi-factorizations of xi modulo 109 + 7.
Example
input
Copy
2
6 3
4 2
output
Copy
36
6
Note
In the second testcase of the example there are six y-factorizations:
- { - 4, - 1};
- { - 2, - 2};
- { - 1, - 4};
- {1, 4};
- {2, 2};
- {4, 1}.
题意:给出x,y;求y个数的乘积为x的情况有多少;
先把x分解质因子,分解成x=p1^c1*p2^c2*......pn^cn;
然后在处理,求把ci个质因子平均分为y分的方法数ai(即相同的球,放在不同的盒子,允许空盒);
然后可以发现y个数乘积为正,前y-1个数的符号可以任意,取决于最后一个数的正负;
所以结果数为 a1*a2*......an*2^(y-1)(ai为ci个质因子分配的方法数)
如果不懂放球问题,可以先看这个博客:https://blog.csdn.net/my_sunshine26/article/details/77385809
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <list>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
const int p = 1e9+7;
const int maxn = 1e6+100;
//虽然y的最大值是1e6,但是算组合数的时候上界是y+ans-1,所以要开大一点,不然会爆栈
int a[maxn];
ll b[maxn],c[maxn];
int x,y;
void get_prime(){//打印素数表
int i,j;
for(i = 2;i < maxn;i++)
if(!a[i]){
for(j = i*2;j < maxn;j+=i){
a[j] = 1;
}
}
}
void jie(){
int i,j;
b[0] = c[0] = 1;
for(i = 1;i < maxn;i++){
b[i] = (b[i-1]%p*i)%p;//打阶乘的表,不打表循环算组合数会超时,
c[i] = (c[i-1]%p*2)%p;//打2的幂的表,不打表直接用位运算在取模会爆数据类型,
}
}
ll quick_mod(ll a ,ll b){//快速幂
if(b==0) return 1;
ll res = quick_mod(a*a%p,b/2);
if(b%2)
res = res*a%p;
return res;
}
ll C(int n,int m){//组合数
ll ans=b[n];
ans = ((ans%p*quick_mod(b[m],p-2)%p)%p*quick_mod(b[n-m],p-2)%p)%p;
//必须打阶乘表,否则超时
return ans;
}
ll solve(){//计算质因子的数量并直接计算分k份的值
ll sum=1;
int i;
for(i = 2;i <=sqrt(x);i++)//从2到根号x循环(包含),否则从2循环到x会超时;
if(!a[i] && x%i==0){//找质因子
int ans = 1; x /=i;
while(x%i==0){
ans++;
x /= i;
}
sum = (sum%p*C(ans+y-1,y-1)%p)%p;
/*
把ans个i分成y份,允许有0个i,类似于把n个相同的球,放在m个不同的盒子里,允许有空盒;
类似于把(n+m)个相同的球,放在m个不同的盒子里,不允许有空盒,先在每个盒子里放上一个球,在把n个相同的球,放在m个不同的盒子里,允许有空盒;
把n个相同的球,放在m个不同的盒子里,不允许有空盒,可以用隔板法,n-1个位置可以放隔板,要放m-1个隔板,所以有C(n-1,m-1)种,则允许有空盒为C(n-1+m,m-1)(相当于先从每个空盒里拿一个球出来,所以有n+m-1个球,然后不允许有空盒);
*/
}
if(x>1) sum = (sum%p*y%p)%p;
/*
找x的质因子的时候,从2到根号x(包含)找,并且除以质因子,找完以后剩下的如果不是1的话,一定是一个质数
*/
return sum;
}
int main()
{
get_prime();
jie();
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> x >> y;
cout << (solve()%p*c[y-1]%p)%p << endl;
//考虑正负号,当y为奇数或偶数时,正负号分配都是:2^y/2即2^(y-1)种.所以结果要在乘以2^(y-1)
}
return 0;
}





















 6874
6874











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








