netty理论部分(一)
缓冲区
ByteBuf
Netty 根据 reference-counting(引用计数)来确定何时可以释放 ByteBuf 或 ByteBufHolder 和其他相关资源
Netty 缓冲 API 提供了几个优势:
- 可以自定义缓冲类型
- 通过一个内置的复合缓冲类型实现零拷贝
- 扩展性好,比如 StringBuilder
- 不需要调用 flip() 来切换读/写模式
- 读取和写入索引分开
- 方法链
- 引用计数
- Pooling(池)
索引
分为读写索引,read和write都会改变,readindex要小于writeindex。
类型
分为普通缓存区与直接缓冲区(direct buff)。正常的io过程分为2个阶段,第二个阶段就是就绪数据处理。正常的数据都会从内核态拷贝到用户态,这也是正常的缓冲区。而实际上我们jvm使用的是虚拟地址,如果直接使用native方法,将该虚拟地址直接映射到规定的内核地址,那么该内核地址将和对用户态和核心态都可以见,那就可以少一个地址传递过程,也就是所谓的direct buff。
与NIO 的缓冲区联系
NIO缓冲区和这里的缓冲区是有区别的,NIO缓冲区就3个控制,location,limit,capity。通过前面2个变量交替,也就是flip来决定读还是写。netty在外层封装了一层,write会将内容写到ByteBuf,然后flush的时候会将内容刷到nio的ByteBuffer 里面。所有内容只有在flush的时候才可以是可见的。而netty的ByteBuf或者DirectBuf都是2个,一个readindex和writeindx。这部分内容在handler在详细解释.
channel
如果对什么是channel不懂得,可以先去看看上一篇文章java nio.
public interface Channel extends AttributeMap, ChannelOutboundInvoker, Comparable<Channel> {
ChannelId id();
EventLoop eventLoop();
Channel parent();
ChannelConfig config();
boolean isOpen();
boolean isRegistered();
boolean isActive();
ChannelMetadata metadata();
SocketAddress localAddress();
SocketAddress remoteAddress();
ChannelFuture closeFuture();
boolean isWritable();
long bytesBeforeUnwritable();
long bytesBeforeWritable();
Channel.Unsafe unsafe();
ChannelPipeline pipeline();
ByteBufAllocator alloc();
Channel read();
Channel flush();
}
-
第一个比较重要的方法是
eventLoop,Channel需要注册到EventLoop的多路复用器上,用于处理IO事件,通过eventLoop方法可以获取到Channel注册的EventLoop。EventLoop本质上就是处理网络读写事件的Reactor线程。在Netty中,它不仅仅用来处理网络事件,也可以用来执行定时任务和用户自定义NioTask等任务。 -
第二个比较常用的方法是
metadata方法,熟悉TCP协议的同学可能知道,当创建Socket的时候需要指定TCP参数,例如接收和发送的TCP缓冲区大小,TCP的超时时间,是否重用地址等等。在Netty中,每个Channel对应一个物理连接,每个连接都有自己的TCP参数配置。所以,Channel会聚合一个ChannelMetadata用来对TCP参数提供元数据描述信息,通过metadata方法就可以获取当前Channel的TCP参数配置。 -
第三个方法是
parent,对于服务端Channel而言,它的父Channel为空,对于客户端Channel,它的父Channel就是创建它的ServerSocketChannel。 -
第四个方法是用户获取Channel标识的
id,它返回ChannelId对象,ChannelId是Channel的唯一标识,它的可能生成策略如下:
(1) 机器的MAC地址(EUI-48或者EUI-64)等可以代表全局唯一的信息。
(2) 当前进程的ID。
(3) 当前系统时间的毫秒——System.currentTimeMillis
(4) 当前系统时间的纳秒——System.nanoTime
(5) 32位的随机整型数
(6) 32位自增的序列数 -
channel config,里面都是设置的option等. -
ChannelFuture也就是future类的东西,netty中都是异步io,或者说执行都是新的线程,想要放回结果就需要查看状态.ChannelFuture有两种状态:未完成(uncompleted)和完成(completed).可以设置监听.
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
ChannelFuture future = ctx.channel().close();
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) {
// Perform post-closure operation
// ...
}
});
}
public abstract class AbstractChannel extends DefaultAttributeMap implements Channel {
派生图
AbstractNioChannel
public abstract class AbstractNioChannel extends AbstractChannel {
private static final InternalLogger logger = InternalLoggerFactory.getInstance(AbstractNioChannel.class);
private static final ClosedChannelException DO_CLOSE_CLOSED_CHANNEL_EXCEPTION = (ClosedChannelException)ThrowableUtil.unknownStackTrace(new ClosedChannelException(), AbstractNioChannel.class, "doClose()");
private final SelectableChannel ch;
protected final int readInterestOp;
volatile SelectionKey selectionKey;
boolean readPending;
private final Runnable clearReadPendingRunnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
AbstractNioChannel.this.clearReadPending0();
}
};
private ChannelPromise connectPromise;
private ScheduledFuture<?> connectTimeoutFuture;
private SocketAddress requestedRemoteAddress;
protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent);
this.ch = ch;
this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp;
try {
ch.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException var7) {
try {
ch.close();
} catch (IOException var6) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Failed to close a partially initialized socket.", var6);
}
}
throw new ChannelException("Failed to enter non-blocking mode.", var7);
}
}
// 省略
}
selectionkey在NIO中相当于channel的唯一标识
SelectableChannel ch原生nio对象.
private final SelectableChannel ch;
readInterestOp,nio事件.
EventLoop中消耗selectedkeys,准备就绪的key会被消耗.
package io.netty.channel.nio;
注册channel
@Override
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().selector, 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (!selected) {
// Force the Selector to select now as the "canceled" SelectionKey may still be
// cached and not removed because no Select.select(..) operation was called yet.
eventLoop().selectNow();
selected = true;
} else {
// We forced a select operation on the selector before but the SelectionKey is still cached
// for whatever reason. JDK bug ?
throw e;
}
}
}
}
遍历就绪的selectedkeys
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() {
for(int i = 0; i < this.selectedKeys.size; ++i) {
SelectionKey k = this.selectedKeys.keys[i];
this.selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;
Object a = k.attachment();
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
this.processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel)a);
} else {
NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask)a;
processSelectedKey(k, task);
}
if (this.needsToSelectAgain) {
this.selectedKeys.reset(i + 1);
this.selectAgain();
i = -1;
}
}
}
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();
if (!k.isValid()) {
NioEventLoop eventLoop;
try {
eventLoop = ch.eventLoop();
} catch (Throwable var6) {
return;
}
if (eventLoop == this && eventLoop != null) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
} else {
try {
int readyOps = k.readyOps();
if ((readyOps & 8) != 0) {
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= -9;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
if ((readyOps & 4) != 0) {
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
}
if ((readyOps & 17) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException var7) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
}
}
- OP_ACCEPT=16
- OP_CONNECT=8
- OP_READ=1
- OP_WRITE=4
- ==0是没有绑定,就是注册了下.
selector
在netty中selector基本看不见的,过程被封装的很全。 调度,全在eventLoop中,其实没必要仔细看。这个要是改了,估计直接整体框架会垮掉,这个应该是最不容易修改的部分。想要爽爽这个可以试试NIO还是上面那个链接。
handler
netty修改比较重要的地方,用了很多设计模式。
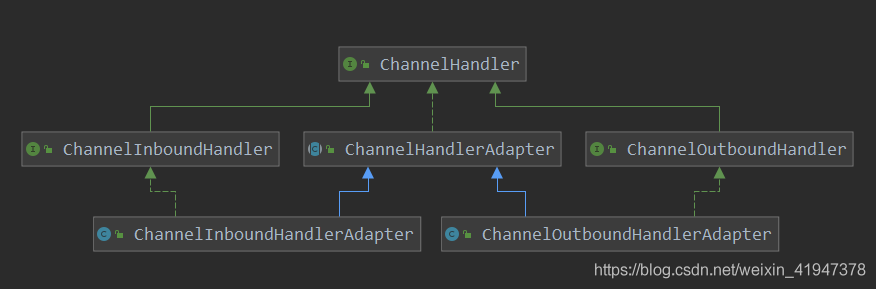
public class ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter extends ChannelHandlerAdapter implements ChannelInboundHandler
public class ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter extends ChannelHandlerAdapter implements ChannelOutboundHandler
public abstract class ChannelHandlerAdapter implements ChannelHandler
使用了策略设计模式,基本都是handler但是行为的不同,决定了他们是不同的handler,拥有inbound操作的handler和outbound操作的handler。就好比是,你我都是人类,我选择了上车操作,你选择了下车操作,实现了不同的接口。
pipeline
用来储存多个handler的双向链表。逻辑链表,很多人的图都是逻辑处理过的,实际的数据结构就是双向链表。
流向
head->tail会判断是不是inboudinghandler,从tail在到head会判断是不是ouboundinghandler。
channelHandlerContext
abstract class AbstractChannelHandlerContext extends DefaultAttributeMap implements ChannelHandlerContext, ResourceLeakHint {
volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext next;
volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev;
AbstractChannelHandlerContext(DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor, String name, boolean inbound, boolean outbound) {
this.name = (String)ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(name, "name");
this.pipeline = pipeline;
this.executor = executor;
this.inbound = inbound;
this.outbound = outbound;
this.ordered = executor == null || executor instanceof OrderedEventExecutor;
}
}
我们所使用的ctx大部分是defaultchannelhandercontext。
final class DefaultChannelHandlerContext extends AbstractChannelHandlerContext {
private final ChannelHandler handler;
DefaultChannelHandlerContext(DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
super(pipeline, executor, name, isInbound(handler), isOutbound(handler));
if (handler == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("handler");
} else {
this.handler = handler;
}
}
public ChannelHandler handler() {
return this.handler;
}
//many
}
一个每次add一个channelHandler都会创建一个channelHandlerContext与之绑定,channelHandlerContext的作用就是管理它所关联的channelHandler和在同一个pipeline中的其他channelHandler之间的交互,他是什么?他与某个channelHandler绑定,权利有限,只能从当前他所绑定的channelHandler开始搞事情。
ctx的write
//AbstractChannelHandlerContext
private void write(Object msg, boolean flush, ChannelPromise promise) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = this.findContextOutbound();
Object m = this.pipeline.touch(msg, next);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
if (flush) {
next.invokeWriteAndFlush(m, promise);
} else {
next.invokeWrite(m, promise);
}
} else {
Object task;
if (flush) {
task = AbstractChannelHandlerContext.WriteAndFlushTask.newInstance(next, m, promise);
} else {
task = AbstractChannelHandlerContext.WriteTask.newInstance(next, m, promise);
}
safeExecute(executor, (Runnable)task, promise, m);
}
}
private void invokeWriteAndFlush(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
if (this.invokeHandler()) {
this.invokeWrite0(msg, promise);
this.invokeFlush0();
} else {
this.writeAndFlush(msg, promise);
}
}
public ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
if (msg == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("msg");
} else if (this.isNotValidPromise(promise, true)) {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
return promise;
} else {
this.write(msg, true, promise);
return promise;
}
}
他只会找到当前handler后的第一个outhandler来处理write过程。然后继续把write过程传递下去。重要一点是重写的write方法是属于handler的,而不是handlercontext,而ctx的的write方法如上,就会将这个write传递给下一个outbound。
public Channel channel() {
return this.pipeline.channel();
}
//而pipeline的write,是从最后的尾部tail进行写
public final ChannelFuture write(Object msg) {
return this.tail.write(msg);
}
所以ctx和ctx.channel()或者pipeline的write是有区别的,直接使用是当前位置开始寻找,而后者则是直接到尾部开始寻找。
inboud
inboud责任链模式,从名字可以知道适合链表,他会遍历整个链表,找到合适的人来受理事件就会处理事件,不会再往后走,但如果找不到受理,就会一直往后,直到任务结束。我开始写netty demo的时候就遇到过,channelactive执行第一个后不执行其他的。因为覆盖了fire所以,变相的找到了处理人。
//absChannelHandlerContext里面
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
}
public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelActive() {
invokeChannelActive(this.findContextInbound());
return this;
}
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextInbound() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
ctx = ctx.next;
} while(!ctx.inbound);
return ctx;
}
static void invokeChannelActive(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next) {
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeChannelActive();
} else {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelActive();
}
});
}
}
private void invokeChannelActive() {
if (this.invokeHandler()) {
try {
((ChannelInboundHandler)this.handler()).channelActive(this);
} catch (Throwable var2) {
this.notifyHandlerException(var2);
}
} else {
this.fireChannelActive();
}
}
这个在责任链模式中会认为它无法处理这个,需要设置到下一个处理。如果没有fire任何执行都会到该地方中止,在此链循环中。
}
private void invokeChannelActive() {
if (this.invokeHandler()) {
try {
((ChannelInboundHandler)this.handler()).channelActive(this);
} catch (Throwable var2) {
this.notifyHandlerException(var2);
}
} else {
this.fireChannelActive();
}
}
这个在责任链模式中会认为它无法处理这个,需要设置到下一个处理。如果没有fire任何执行都会到该地方中止,在此链循环中。
























 608
608











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








