通过上章sender线程的初始化源码我们可以知道,
sender线程的run方法是一个while死循环,一经启动就一直在运行,这篇会详细介绍sender是如何将元数据发送请求发送给到broker,以及如何处理broker发送回来的元数据响应。首先需要通过sender线程向broker拉取主题分区的元数据,在拉取元数据的过程中会跟broker建立网路连接,网络建立好后再将元数据消息请求发送至broker,broker处理请求返回响应,响应元数据的处理也是由sender线程完成的。
生产者拉取元数据流程
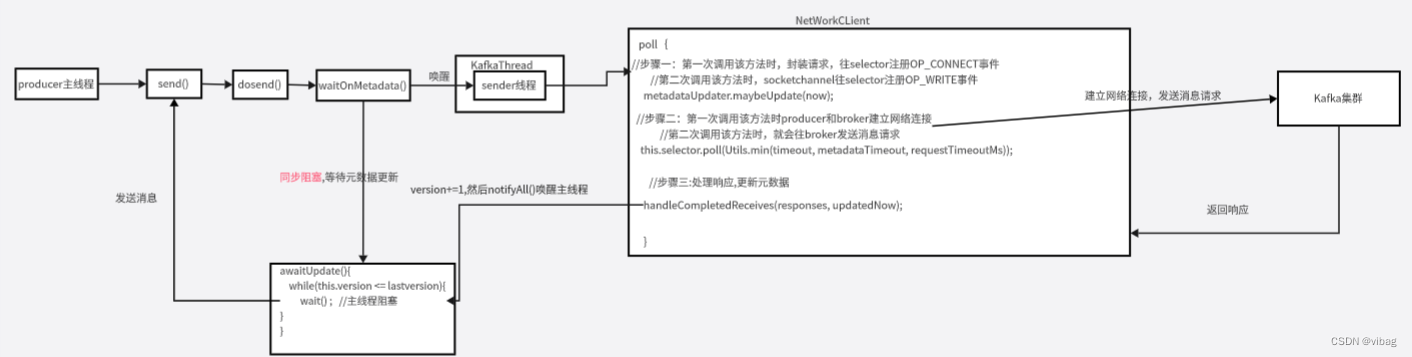
通过场景驱动的方式,生产者通过send()方法发送消息,然后主线程唤醒sender线程从broker拉取元数据,主线程这边通过在while循环里面判断元数据的version版本号是否拉取到元数据,从而阻塞等待,当sender线程拉取到元数据后对元数据version进行更新,然后唤醒主线程,主线程就可以往broker发送消息了,broker处理完消息后就后返回响应给生产者处理。
(一)元数据
首先来看看生产者要拉取的元数据的数据结构
public final class Metadata {
//两次更新元数据请求的最小时间间隔,默认值是100ms,目的是为了减少网络的压力
private final long refreshBackoffMs;
//间隔多长时间自动更新一次元数据,默认5分钟更新一次元数据
private final long metadataExpireMs;
//生产者每次更新元数据时,都会修版本号让版本号+1
private int version;
//上一次更新元数据的时间
private long lastRefreshMs;
//上一次成功更新元数据的时间。
//如果正常情况下,假设每次请求都是更新成功,那么lastRefreshMs和lastSuccessfulRefreshMs时相同的
private long lastSuccessfulRefreshMs;
//Kafka集群的元数据,包含主题分区等信息
private Cluster cluster;
//是否需要更新元数据的标志
private boolean needUpdate;
//记录了当前已有的topics
private final Map<String, Long> topics;
}
上面有三个核心成员,分别是cluster,needUpdate和version,生产者线程是通过元数据的version来判断是否拉取到元数据。
cluster的数据结构
public final class Cluster {
//存储broker的信息,每个node代表一个broker
private final List<Node> nodes;
//没有授权的topic
private final Set<String> unauthorizedTopics;
//kafka内部的主题
private final Set<String> internalTopics;
//这里存储着partition和partition对应的信息,之所生还要存储分区信息,是因为partition有副本
private final Map<TopicPartition, PartitionInfo> partitionsByTopicPartition;
//一个主题对应有哪些分区信息
private final Map<String, List<PartitionInfo>> partitionsByTopic;
//一个主题对应有哪些可用的分区信息
private final Map<String, List<PartitionInfo>> availablePartitionsByTopic;
//一个broker上面有哪些分区信息,这里用brokerId来表示服务器
private final Map<Integer, List<PartitionInfo>> partitionsByNode;
//服务器ID和服务器对应的关系,比如0,Node表示0号服务器是Node
private final Map<Integer, Node> nodesById;
//kafka集群的id信息
private final ClusterResource clusterResource;
}
cluster内部很多成员都用到了PartitionInfo
public class PartitionInfo {
//主题
private final String topic;
//分区号
private final int partition;
//leader副本在哪台broker上面
private final Node leader;
//这个分区的所有的副本都在哪些节点上面
private final Node[] replicas;
//ISR列表
private final Node[] inSyncReplicas;
}
(二)元数据的请求及响应
生产者发送元数据请求
生产者发送消息的代码
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>("first", "wang wu" + i), new Callback() {
public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata recordMetadata, Exception e) {
if(e == null){
System.out.println("主题"+recordMetadata.topic()+" 分区"+recordMetadata.partition());
}
}
send方法会先后调用以下方法
public Future<RecordMetadata> send(ProducerRecord<K, V> record) {
return send(record, null);
}
public Future<RecordMetadata> send(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
//设置拦截器
ProducerRecord<K, V> interceptedRecord = this.interceptors == null ? record : this.interceptors.onSend(record);
//关键代码
return doSend(interceptedRecord, callback);
}
private Future<RecordMetadata> doSend(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
TopicPartition tp = null;
try {
//步骤一:当前线程同步等待sender线程拉取元数据,maxBlockTimeMs表示最多可以等待多久
ClusterAndWaitTime clusterAndWaitTime = waitOnMetadata(record.topic(), record.partition(), maxBlockTimeMs);
//clusterAndWaitTime.waitedOnMetadataMs 表示拉取元数据用了多少时间。
//maxBlockTimeMs -clusterAndWaitTime.waitedOnMetadataMs = 还剩下多少的时间可以使用。
long remainingWaitMs = Math.max(0, maxBlockTimeMs - clusterAndWaitTime.waitedOnMetadataMs);
//更新集群的元数据
Cluster cluster = clusterAndWaitTime.cluster;
//步骤二:对消息的key和value进行序列化
byte[] serializedKey;
try {
serializedKey = keySerializer.serialize(record.topic(), record.key());
} catch (ClassCastException cce) {
throw new SerializationException("Can't convert key of class " + record.key().getClass().getName() +
" to class " + producerConfig.getClass(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG).getName() +
" specified in key.serializer");
}
byte[] serializedValue;
try {
serializedValue = valueSerializer.serialize(record.topic(), record.value());
} catch (ClassCastException cce) {
throw new SerializationException("Can't convert value of class " + record.value().getClass().getName() +
" to class " + producerConfig.getClass(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG).getName() +
" specified in value.serializer");
}
//步骤三:根据元数据信息获取消息应该发送到哪些分区
int partition = partition(record, serializedKey, serializedValue, cluster);
//步骤四:检查生产者发送的一条消息大小是否超过了最大值,一条消息默认最大值为1M
ensureValidRecordSize(serializedSize);
//步骤五:根据获取到的元数据信息,封装分区对象
tp = new TopicPartition(record.topic(), partition);
long timestamp = record.timestamp() == null ? time.milliseconds() : record.timestamp();
//步骤六:给发送的每条消息都绑定回调函数,broker处理请求后就是通过回调函数返回的响应信息的
Callback interceptCallback = this.interceptors == null ? callback : new InterceptorCallback<>(callback, this.interceptors, tp);
//步骤七: 把消息放入消息记录累加器accumulator(默认大小32M)的双端队列中
RecordAccumulator.RecordAppendResult result = accumulator.append(tp, timestamp, serializedKey, serializedValue, interceptCallback, remainingWaitMs);
//如果批次满了或者新创建出来一个批次
if (result.batchIsFull || result.newBatchCreated) {
log.trace("Waking up the sender since topic {} partition {} is either full or getting a new batch", record.topic(), partition);
//步骤八:唤醒sender线程,发送消息批次
this.sender.wakeup();
}
return result.future;
//将捕获到的异常一层一层往上抛
} catch (ApiException e) {
log.debug("Exception occurred during message send:", e);
if (callback != null)
callback.onCompletion(null, e);
this.errors.record();
if (this.interceptors != null)
this.interceptors.onSendError(record, tp, e);
return new FutureFailure(e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
this.errors.record();
if (this.interceptors != null)
this.interceptors.onSendError(record, tp, e);
throw new InterruptException(e);
} catch (BufferExhaustedException e) {
this.errors.record();
this.metrics.sensor("buffer-exhausted-records").record();
if (this.interceptors != null)
this.interceptors.onSendError(record, tp, e);
throw e;
} catch (KafkaException e) {
this.errors.record();
if (this.interceptors != null)
this.interceptors.onSendError(record, tp, e);
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (this.interceptors != null)
this.interceptors.onSendError(record, tp, e);
throw e;
}
}
首先先来看步骤一是如何让producer主线程阻塞,唤醒sender线程拉取元数据的
private ClusterAndWaitTime waitOnMetadata(String topic, Integer partition, long maxWaitMs) throws InterruptedException {
// 把当前的主题加入元数据里面
metadata.add(topic);
//尝试获取元数据
//第一次执行的时候由于只有broker的地址,所以拉取不到元数据,元数据为空
Cluster cluster = metadata.fetch();
//根据topic从cluster元数据里面查看分区的信息。
//第一次执行这段代码,由于拉取不到元数据,所以无法获取分区的信息。
Integer partitionsCount = cluster.partitionCountForTopic(topic);
//如果在元数据里面获取到了分区的信息则直接返回
//第一次执行这段代码时,条件不满足。
if (partitionsCount != null && (partition == null || partition < partitionsCount))
//直接返回cluster元数据信息以及拉取元数据花的时间。
return new ClusterAndWaitTime(cluster, 0);
//记录当前时间
long begin = time.milliseconds();
//还有剩余多少时间,默认值是最多可以等待的时间。
long remainingWaitMs = maxWaitMs;
//已经花了多少时间。
long elapsed;
do {
log.trace("Requesting metadata update for topic {}.", topic);
//在这个方法里面只做了两件事,把needUpdate 标识设置为true,然后返回当前元数据的版本
int version = metadata.requestUpdate();
//核心代码,唤醒sender线程拉取元数据(其实发送消息也是由sender线程完成的)
sender.wakeup();
try {
//核心代码,当前线程阻塞等待sender线程获取到元数据。
metadata.awaitUpdate(version, remainingWaitMs);
} catch (TimeoutException ex) {
throw new TimeoutException("Failed to update metadata after " + maxWaitMs + " ms.");
}
//尝试获取集群的元数据信息。
cluster = metadata.fetch();
//拉取元数据已经花了多少时间
elapsed = time.milliseconds() - begin;
//判断花的时间是否大于最大等待的时间,是就报超时异常。
if (elapsed >= maxWaitMs)
throw new TimeoutException("Failed to update metadata after " + maxWaitMs + " ms.");
//获取到了元数据但是topic没有授权
if (cluster.unauthorizedTopics().contains(topic))
throw new TopicAuthorizationException(topic);
//还有可以用的时间。
remainingWaitMs = maxWaitMs - elapsed;
//尝试获取发送消息的topic对应分区的信息。
partitionsCount = cluster.partitionCountForTopic(topic);
//获取到分区信息后就会退出循环。
} while (partitionsCount == null);
//返回集群的元数据cluster以及所花的时间elapsed
return new ClusterAndWaitTime(cluster, elapsed);
}
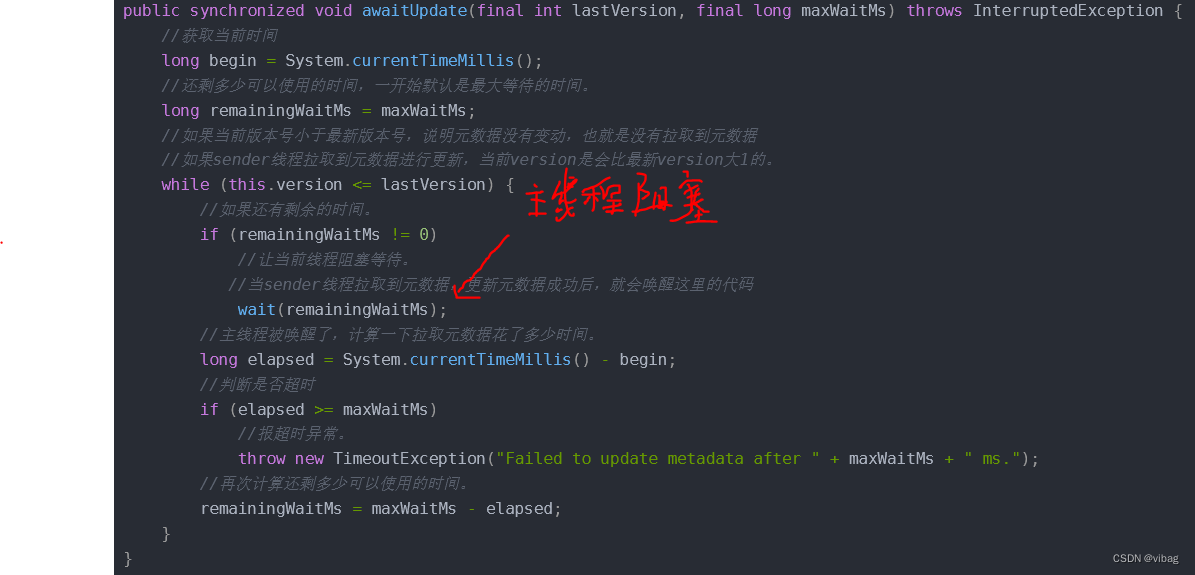
主线程先进入以下方法,然后阻塞等待
public synchronized void awaitUpdate(final int lastVersion, final long maxWaitMs) throws InterruptedException {
//获取当前时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//还剩多少可以使用的时间,一开始默认是最大等待的时间。
long remainingWaitMs = maxWaitMs;
//如果当前版本号小于最新版本号,说明元数据没有变动,也就是没有拉取到元数据
//如果sender线程拉取到元数据进行更新,当前version是会比最新version大1的。
while (this.version <= lastVersion) {
//如果还有剩余的时间。
if (remainingWaitMs != 0)
//让当前线程阻塞等待。
//当sender线程拉取到元数据,更新元数据成功后,就会唤醒这里的代码
wait(remainingWaitMs);
//主线程被唤醒了,计算一下拉取元数据花了多少时间。
long elapsed = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin;
//判断是否超时
if (elapsed >= maxWaitMs)
//报超时异常。
throw new TimeoutException("Failed to update metadata after " + maxWaitMs + " ms.");
//再次计算还剩多少可以使用的时间。
remainingWaitMs = maxWaitMs - elapsed;
}
}
接着唤醒sender线程,sender线程的run方法那边就会从broker拉取元数据
public class Sender implements Runnable {
public void run() {
while (running) {
try {
//再次调用下面run方法
run(time.milliseconds());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Uncaught error in kafka producer I/O thread: ", e);
}
}
}
void run(long now) {
//在这之前的代码由于还没有获取到元数据,所以之前的代码不会执行,直接执行这最后一行的方法
this.client.poll(pollTimeout, now);
}
}
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now);
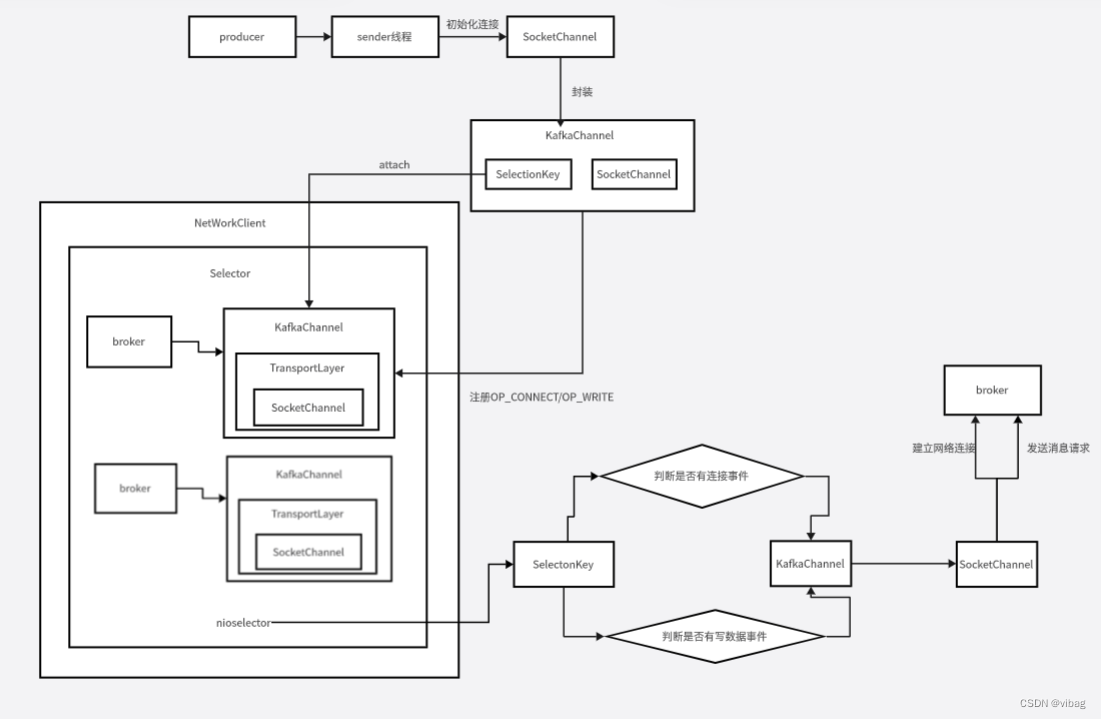
第一次调用poll()完成网络连接
@Override
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
//步骤一:第一次调用该方法时,封装拉取元数据的请求,在这个方法里面还会新建socketChannel
//往selector注册OP_CONNECT事件,然后监听连接事件,后面会详细介绍
//第二次调用该方法时,socketchannel往selector注册OP_WRITE事件
long metadataTimeout = metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now);
try {
//步骤二:第一次调用该方法时producer和broker建立网络连接
//第二次调用该方法时,就会往broker发送消息请求
this.selector.poll(Utils.min(timeout, metadataTimeout, requestTimeoutMs));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Unexpected error during I/O", e);
}
//记录当前时间
long updatedNow = this.time.milliseconds();
//列表用于存放broker发送过来的结果集
List<ClientResponse> responses = new ArrayList<>();
//处理inFlight的发送请求
handleCompletedSends(responses, updatedNow);
//步骤三:处理broker发送过来的响应,响应里面有元数据(包含主题的分区信息)。
handleCompletedReceives(responses, updatedNow);
//处理断开的连接
handleDisconnections(responses, updatedNow);
//处理连接,改变节点的连接状态
handleConnections();
//处理长时间没有接受到响应的请求
handleTimedOutRequests(responses, updatedNow);
for (ClientResponse response : responses) {
if (response.request().hasCallback()) {
try {
//生产者发送消息给broker时会携带一个回调函数,broker处理完消息后会将
//异常等信息通过回调函数返回给producer进行处理
response.request().callback().onComplete(response);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Uncaught error in request completion:", e);
}
}
}
return responses;
}
首先来看poll()方法步骤一
//步骤一:封装拉取元数据的请求,在这个方法里面还会新建socketChannel往selector注册OP_CONNECT,监听连接事件,后面会详细介绍
long metadataTimeout = metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now);
//调用这个借口
long maybeUpdate(long now);
//上面接口的实现类
public long maybeUpdate(long now) {
//这个方法里面会封装请求和注册连接事件。
maybeUpdate(now, node);
}
private void maybeUpdate(long now, Node node) {
//判断网络连接是否建立好了,建立好了才走这个分支
//第一次执行没有建立网络连接,所以第一次执行直接走else if条件语句
if (canSendRequest(nodeConnectionId)) {
this.metadataFetchInProgress = true;
MetadataRequest metadataRequest;
//判断是否需要所有主题的元数据
if (metadata.needMetadataForAllTopics())
//封装所有主题元数据的请求。
metadataRequest = MetadataRequest.allTopics();
else
//创建拉取指定主题的元数据请求
metadataRequest = new MetadataRequest(new ArrayList<>(metadata.topics()));
//将元数据请求封装成客户端请求
ClientRequest clientRequest = request(now, nodeConnectionId, metadataRequest);
//存储要发送的请求
doSend(clientRequest, now);
} else if (connectionStates.canConnect(nodeConnectionId, now)) {
//第一次执行走这个分支,初始化网络连接,注意这里网络并不会建立成功
initiateConnect(node, now);
} else {
this.lastNoNodeAvailableMs = now;
}
}
//初始化网络连接
private void initiateConnect(Node node, long now) {
try {
//尝试建立网络连接,注意这里并不会建立成功
selector.connect(nodeConnectionId,
new InetSocketAddress(node.host(), node.port()),
this.socketSendBuffer,
this.socketReceiveBuffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
connectionStates.disconnected(nodeConnectionId, now);
metadataUpdater.requestUpdate();
}
}
//调用这个接口
public void connect(String id, InetSocketAddress address, int sendBufferSize, int receiveBufferSize) throws IOException;
//接口的实现类
public void connect(String id, InetSocketAddress address, int sendBufferSize, int receiveBufferSize) throws IOException {
//获取SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
Socket socket = socketChannel.socket();
//这里不是开启长连接,而是表示TCP连接空闲时是否需要向对方发送探测包
socket.setKeepAlive(true);
//关闭Nagle算法,如果开启的话,有些数据包很小,Kafka就不发送了
socket.setTcpNoDelay(true);
boolean connected;
try {
//尝试去服务器去连接,能立马连接成功返回true,否则返回false
connected = socketChannel.connect(address);
} catch (UnresolvedAddressException e) {
socketChannel.close();
throw new IOException("Can't resolve address: " + address, e);
} catch (IOException e) {
socketChannel.close();
throw e;
}
//通过socketChannel在Selector上注册了一个OP_CONNECT
SelectionKey key = socketChannel.register(nioSelector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
//将socketChannel 封装成KafkaChannel
KafkaChannel channel = channelBuilder.buildChannel(id, key, maxReceiveSize);
//把selectionkey和KafkaChannel关联起来,这样可以通过key找到KafkaChannel
//也可以通过KafkaChannel找到key
key.attach(channel);
//将brokerId与其对应的连接进行缓存
this.channels.put(id, channel);
//判断上面的连接是否立马连接成功,一般不能立马连接成功,所以条件不满足
if (connected) {
immediatelyConnectedKeys.add(key);
// 取消前面注册的OP_CONNECT事件
key.interestOps(0);
}
}
至此步骤一的代码执行完成,此时socketChannel往selector上面注册了OP_CONNECT事件并监听连接事件,同时也完成了元数据请求的创建。
再来看看poll()方法的步骤二producer是如何与broker建立网络连接的
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
//步骤二:producer和broker建立网络连接
this.selector.poll(Utils.min(timeout, metadataTimeout, requestTimeoutMs));
}
调用的接口
public void poll(long timeout) throws IOException;
//接口的实现类
public void poll(long timeout) throws IOException {
//获取selector上面注册了多少个key事件
int readyKeys = select(timeout);
//由于步骤一socketchannel往selector注册了OP_CONNECT事件,此时readyKeys=1,满足条件
if (readyKeys > 0 || !immediatelyConnectedKeys.isEmpty()) {
//对Selector上面的连接事件进行处理,然后将broker发送过来的响应放入stagedReceives中
pollSelectionKeys(this.nioSelector.selectedKeys(), false, endSelect);
}
//对stagedReceives里面的响应进行处理
addToCompletedReceives();
}
private void pollSelectionKeys(Iterable<SelectionKey> selectionKeys,
boolean isImmediatelyConnected,
long currentTimeNanos) {
//获取到selector上面所有的key
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
//遍历所有的key
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
//处理完key后移除
iterator.remove();
//通过key找到对应的KafkaChannel
KafkaChannel channel = channel(key);
try {
//上面注册了监听了连接事件,所以这里满足条件
if (isImmediatelyConnected || key.isConnectable()) {
/在这里完成网络的连接,步骤一只是完成了网络连接的初始化。
if (channel.finishConnect()) {
//网络连接建立好了,就将channel存储到已经完成网络连接的列表
this.connected.add(channel.id());
} else
continue;
}
//处理OP_READ事件,也就是处理服务端发送过来的响应
if (channel.ready() && key.isReadable() && !hasStagedReceive(channel)) {
NetworkReceive networkReceive;
//不断的读取数据,读取数据涉及到粘包和拆包的一些问题,后面会详细介绍。
while ((networkReceive = channel.read()) != null)
//将broker发送过来的响应放入已经接收到但还没处理的队列中
addToStagedReceives(channel, networkReceive);
}
//处理OP_WRITE事件,也就是处理发送请求的事件
if (channel.ready() && key.isWritable()) {
//往服务端写数据,然后移除OP_WRITE
Send send = channel.write();
//已经完成响应消息的发送
if (send != null) {
//将请求放入已经完成发送的请求队列中
this.completedSends.add(send);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
String desc = channel.socketDescription();
if (e instanceof IOException)
log.debug("Connection with {} disconnected", desc, e);
else
log.warn("Unexpected error from {}; closing connection", desc, e);
close(channel);
this.disconnected.add(channel.id());
}
}
}
至此步骤二通过channel.finishConnect()已经完成网络的连接
第二次调用poll()发送元数据请求
(上面第一次调用poll()方法有完整代码,这里只展示第二次调用poll()的核心代码)
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
//步骤一:第二次调用该方法时,socketchannel往selector注册OP_WRITE事件
long metadataTimeout = metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now);
try {
//步骤二:第二次调用该方法时,就会往broker发送消息请求
this.selector.poll(Utils.min(timeout, metadataTimeout, requestTimeoutMs));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Unexpected error during I/O", e);
}
//步骤三:处理broker发送过来的响应,响应里面有元数据(包含主题的分区信息)。
handleCompletedReceives(responses, updatedNow);
return responses;
}
首先来看第二次调用poll()方法步骤一,主要完成写数据事件的注册
//步骤一:往selector注册OP_WRITE事件,然后就可以往broker写数据了
long metadataTimeout = metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now);
//调用这个借口
long maybeUpdate(long now);
//上面接口的实现类
public long maybeUpdate(long now) {
//这个方法里面会封装请求和注册连接事件。
maybeUpdate(now, node);
}
private void maybeUpdate(long now, Node node) {
//第二次调用,此时网络已经建立好,走这个分支
if (canSendRequest(nodeConnectionId)) {
//存储要发送的请求,注册写数据的事件
doSend(clientRequest, now);
}
}
private void doSend(ClientRequest request, long now) {
//将请求放入inFlightRequests队列,默认最多缓存5个发送出去但是还没有接收到响应的请求。
//处理成功后会移除请求,后面会详细介绍
this.inFlightRequests.add(request);
//注册写数据的事件
selector.send(request.request());
}
public void send(Send send);
//接口的实现类
public void send(Send send) {
//获取到一个KafakChannel
KafkaChannel channel = channelOrFail(send.destination());
try {
//重要代码
channel.setSend(send);
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
this.failedSends.add(send.destination());
close(channel);
}
}
public void setSend(Send send) {
//在selector注册了OP_WRITE事件,这样就可以往服务端发送请求了
this.transportLayer.addInterestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
此时经过第二次调用poll()方法步骤一,已经可以往broker发送消息请求了,而这个操作就是由第二次调用poll()方法的步骤二实现发送请求的来看看第二次执行poll()方法的步骤二。
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
//步骤二:producer向broker发送消息请求
this.selector.poll(Utils.min(timeout, metadataTimeout, requestTimeoutMs));
}
调用的接口
public void poll(long timeout) throws IOException;
//接口的实现类
public void poll(long timeout) throws IOException {
//获取selector上面注册了多少个key事件
int readyKeys = select(timeout);
//此时有OP_WRITE事件,满足条件
if (readyKeys > 0 || !immediatelyConnectedKeys.isEmpty()) {
//对Selector上面的OP_WRITE事件进行处理,然后将broker发送过来的响应放入stagedReceives中
pollSelectionKeys(this.nioSelector.selectedKeys(), false, endSelect);
}
//对stagedReceives里面的响应进行处理
addToCompletedReceives();
}
private void pollSelectionKeys(Iterable<SelectionKey> selectionKeys,
boolean isImmediatelyConnected,
long currentTimeNanos) {
//获取到selector上面所有的key
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
//遍历所有的key
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
//处理完key后移除
iterator.remove();
//通过key找到对应的KafkaChannel
KafkaChannel channel = channel(key);
try {
//处理OP_WRITE事件,也就是处理发送请求的事件
if (channel.ready() && key.isWritable()) {
//往服务端写数据,然后移除OP_WRITE
Send send = channel.write();
//已经完成响应消息的发送
if (send != null) {
//将请求放入已经完成发送的请求队列中
this.completedSends.add(send);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
String desc = channel.socketDescription();
if (e instanceof IOException)
log.debug("Connection with {} disconnected", desc, e);
else
log.warn("Unexpected error from {}; closing connection", desc, e);
close(channel);
this.disconnected.add(channel.id());
}
}
}
public Send write() throws IOException {
Send result = null;
//send完成请求的发送
if (send != null && send(send)) {
//存储发送结果
result = send;
send = null;
}
return result;
}
private boolean send(Send send) throws IOException {
//最终执行发送请求的代码是在这儿
send.writeTo(transportLayer);
//判断是否完成消息的发送
if (send.completed())
//消息发送成功,就移除OP_WRITE
transportLayer.removeInterestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
return send.completed();
}
至此通过第二次调用poll()方法的步骤二,已经完成消息请求的发送。
生产者处理元数据的响应
服务端broker处理完消息请求后就会返回响应(至于broker怎么处理生产者发送过来的消息,后面会详细介绍)。
来看看poll方法的步骤三是如何处理broker发送回来的响应的
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
//步骤三:处理broker发送过来的响应,响应里面有元数据(包含主题的分区信息)。
handleCompletedReceives(responses, updatedNow);
return responses;
}
private void handleCompletedReceives(List<ClientResponse> responses, long now) {
for (NetworkReceive receive : this.selector.completedReceives()) {
//获取broker的ID号
String source = receive.source();
//从inFlightRequests的双端队列中移除已经接收到响应的请求。
ClientRequest req = inFlightRequests.completeNext(source);
//解析broker发送回来的响应
Struct body = parseResponse(receive.payload(), req.request().header());
//处理元数据信息的响应
if (!metadataUpdater.maybeHandleCompletedReceive(req, now, body))
//req是生产者发送的请求,body是响应的内容,解析完了就封装成ClientResponse对象存入列表中
responses.add(new ClientResponse(req, now, false, body));
}
}
boolean maybeHandleCompletedReceive(ClientRequest request, long now, Struct body);
//接口的实现类
public boolean maybeHandleCompletedReceive(ClientRequest req, long now, Struct body) {
short apiKey = req.request().header().apiKey();
if (apiKey == ApiKeys.METADATA.id && req.isInitiatedByNetworkClient()) {
//处理broker发送回来的响应
handleResponse(req.request().header(), body, now);
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void handleResponse(RequestHeader header, Struct body, long now) {
this.metadataFetchInProgress = false;
//由于broker发送过来的是二进制的数据,需要解析,然后封装成一个MetadataResponse对象。
MetadataResponse response = new MetadataResponse(body);
//获取响应里面的元数据信息
Cluster cluster = response.cluster();
//如果获取到了元数据信息
if (cluster.nodes().size() > 0) {
//更新元数据的信息
this.metadata.update(cluster, now);
} else {
log.trace("Ignoring empty metadata response with correlation id {}.", header.correlationId());
this.metadata.failedUpdate(now);
}
}
这里就是更新元数据最开头介绍的两个核心成员needUpdate和version,通过版本号来判断主线程是否拉取到元数据,version加1后才会退出while的死循环进行之后的业务流程。
public synchronized void update(Cluster cluster, long now) {
//将需要更新元数据的标志设置为false
this.needUpdate = false;
//将版本号+1,唤醒主线程后会退出while循环
this.version += 1;
//唤醒之前阻塞的主线程,之前主线在唤醒sender线程拉取元数据后进入阻塞
//等待(while循环里面通过version版本号判断是否继续等待)
notifyAll();
}
总结
本文详细介绍了producer是如何通过sender线程从broker集群中拉取到元数据,在拉取的过程中是如何建立网络连接的,以及如何发送消息请求给broker和处理broker发送回来的响应。主要流程就是通过第一次调用poll()方法的步骤一先是往selector上注册OP_CONNECT事件,然后步骤二检测到selector上面有监听事件,通过监听事件的key找到对应的kafkachannel,从而获取到kafkachannel里面的socketchannel,将socketchannel与broker建立网络连接;因为sender线程的run方法一直在循环启动,在第二次调用poll()的步骤一时就会往selector注册OP_WRITE事件,此时就可以往服务端broker发送消息了,通过步骤二完成消息的发送,最后在步骤三处理broker发送过来的响应。至于生产者对请求的内存管理,满足发送条件以及broker集群如何处理请求的讲解,将在下篇文章详细介绍,喜欢阅读源码的可以点赞加个关注哦。




















 1390
1390











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








