Sinc重采样方法
有些计算需要对原始数据进行重采样(加密)操作。Sinc插值是个理想选择,Sinc插值不会对原始信号的频谱进行破坏,也不会引入假频成分。
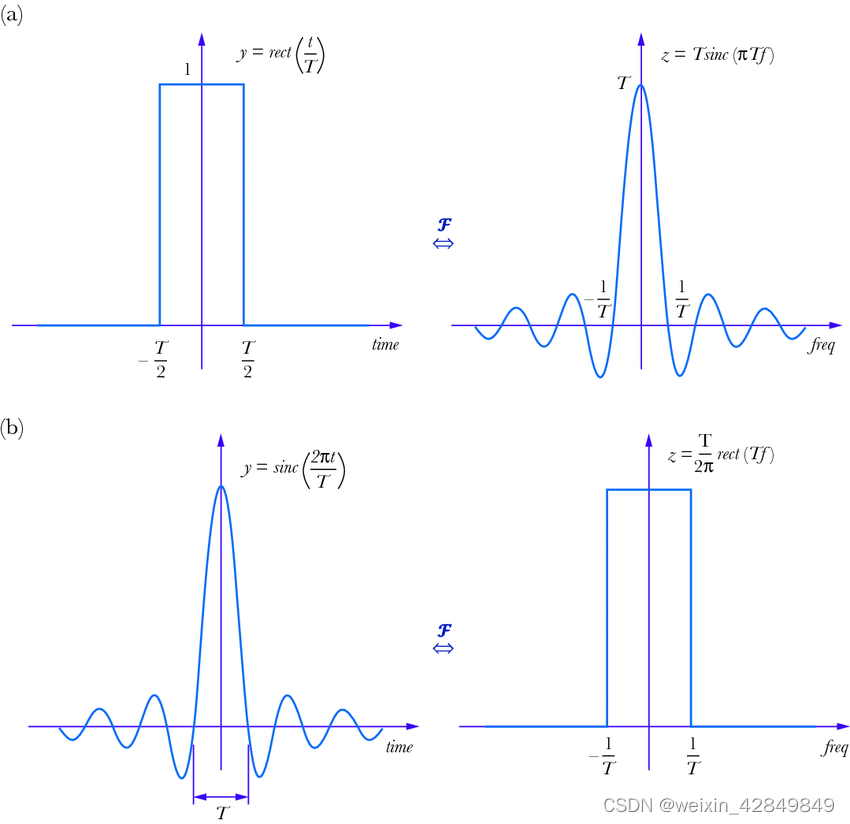
Sinc加密重采样的原理如下。对于长度为n的原始信号,通过Sinc插值加密为m*n长度的信号数据,其中m是加密倍数,步骤如下:
- 将原始信号FFT变换到频率域
- 对频率域数据在最高频成分尾部进行补零操作(ZERO PADDING),补零的长度是(m-1)*nfft, 其中nfft是频率域数据长度(注: 频率域数据是复数). ZERO PADDING能增加变换域中分辨率(数据更密了),但不会增加其信号所携带信息,要增加信号携带信息只能靠加长采样时间窗口长度!
- 将补零后的频率域数据进行IFFT变换,即获得原始数据加密m倍后的结果
- 一般对于原始输入数据或是其FFT后频率域数据的尾部加个斜坡函数,使之能平滑过渡到零值,避免突变引入高频噪音。
使用cuFFT的一个实现,主要代码部分:
//对数据data[nbatch][0:ilow]乘上比例因子
//对数据data[nbatch][ilow:ihigh]进行补零
template<typename T, bool FLAG=false>
__global__ void kernel_scale_and_padding_zero(T *d_data, const SIZE_TYPE ndata,
const INDEX_TYPE ilow, const INDEX_TYPE ihigh, const SIZE_TYPE nbatch, const T scale)
{
static_assert(std::is_same_v<T,float>||std::is_same_v<T,double>);
auto zero=T(0);
INDEX_TYPE tid=threadIdx.x;
SIZE_TYPE nthread=blockDim.x;
INDEX_TYPE bid=blockIdx.x;
SIZE_TYPE nblock=gridDim.x;
for(INDEX_TYPE x=bid; x<nbatch; x+=nblock)
{
T *data=d_data+x*ndata;
INDEX_TYPE y;
for(y=tid; y<ilow; y+=nthread)
{
data[y]*=scale;
}
for(;y<ihigh;y+=nthread)
{
data[y]=zero;
}
//参考matlab实现resampleFDZP
if(FLAG)
{
if(tid==0)
{
//最高频率项乘以0.5
data[ilow-1]/=2;
data[ilow-2]/=2;
}
}
}
return;
}
//频率域补零,加密重采样
template<typename T>
void resample_fdzp(T* __restrict__ d_in, const SIZE_TYPE n, const SIZE_TYPE lda,
T* __restrict__ d_out, const SIZE_TYPE no,
const SIZE_TYPE m,
const SIZE_TYPE nbatch )
{
static_assert(std::is_same_v<T,float> || std::is_same_v<T,double>);
assert(n>0);
assert(m>0);
assert(no>m*n);
assert(no%2==0);
assert(nbatch>0);
//real to complex: R2C, D2Z
int rank=1;
int ns[]={n};
int inembed[]={lda};
int onembed[]={no/2};
int istride=1;
int ostride=1;
int idist=lda;
int odist=no/2;
cufftType_t fft_type;
cufftHandle plan_forward, plan_backward;
if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T,float>)
{
fft_type=CUFFT_R2C;
}
else if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T,double>)
{
fft_type=CUFFT_D2Z;
}
CHECK(cufftPlanMany(&plan_forward,rank,ns,inembed,istride,idist,onembed,ostride,odist,fft_type,nbatch));
//输入信号变换到频率域
cufft_real_to_complex(plan_forward,d_in,d_out);
int nm=n*m; //new length of resampled signals
int infft=(n/2+1); //real to complex
int onfft=(nm/2+1); //real to complex after zeros padding
//频率数据进行补零和归一化
T scale=T(1)/n;
if(n%2)
kernel_scale_and_padding_zero<T,false><<<32,32>>>(d_out,no,2*infft,no,nbatch, scale);
else
kernel_scale_and_padding_zero<T,true><<<32,32>>>(d_out,no,2*infft,no,nbatch, scale);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//complex to real: C2R,Z2D
ns[0]=nm;
inembed[0]=no/2;
onembed[0]=no;
istride=1;
ostride=1;
idist=no/2;
odist=no;
if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T,float>)
{
fft_type=CUFFT_C2R;
}
else if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T,double>)
{
fft_type=CUFFT_Z2D;
}
CHECK(cufftPlanMany(&plan_backward,rank,ns,inembed,istride,idist,onembed,ostride,odist,fft_type,nbatch));
//补零后的频率域数据IFFT反变换到信号域,获得加密m倍的信号
cufft_complex_to_real(plan_backward,d_out,d_out);
CHECK(cufftDestroy(plan_forward));
CHECK(cufftDestroy(plan_backward));
}
template<typename T, int N, int M, int NO, int NBATCH, int LDA=N>
void test_fdzp()
{
static_assert(std::is_same_v<T,float> || std::is_same_v<T,double>);
static_assert(NO%2==0);
static_assert(NO>=2*(N*M/2+1));
static_assert(N>0 && M >0 && NBATCH>0);
thrust::host_vector<T> h_x(N*NBATCH);
//thrust::generate(h_x.begin(),h_x.end(),MyRandom<T>());
thrust::sequence(h_x.begin(),h_x.end(),T(0.1),T(0.01));
print_array(h_x,"input h_x");
thrust::device_vector<T> d_x=h_x;
thrust::device_vector<T> d_y(NO*NBATCH);
thrust::fill(d_y.begin(),d_y.end(),T(1.1111));
T *d_in=thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_x.data());
T *d_out=thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_y.data());
resample_fdzp(d_in,N,LDA,d_out,NO,M,NBATCH);
thrust::host_vector<T> h_y=d_y;
print_array(h_y,"output resampled h_y");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
std::cout<<"\n------------> test double:\n";
test_fdzp<double,9,3,30,3>();
std::cout<<"\n------------> test float:\n";
test_fdzp<float,8,3,30,3>();
return(0);
}
Matlab 插值函数
时间域重采样(Time Domain Sinc Interpolation)
function yp = resampleSINC(y,m)
% TIME-DOMAIN SINC INTERPOLATION (RESAMPLING)
%
% Syntax:
% yp = resampleSINC(y, m)
%
% Input:
% y = input signal to be resampled to higher sampling rate (y must be a row vector)
%
% m = resampling factor (e.g., if y is 100 sps and yp will be
% 200 sps, then m is 200/100 = 2)
% yp = resampled signal
%
% Example: Input is 15 Hz sinusoidal signal sampled at 200 sps. It will
% be resampled to 400 sps using time-domain sinc interpolation
%
% n = 256;
% dt = 1/200;
% t = dt*(0:n-1);
% T = dt*n;
% y = sin(2*pi*15*t/T);
% m = 2;
% yp = resampleSINC(y,m);
% u = linspace(0,length(y),length(y));
% up = linspace(0,length(y),length(y)*m);
% plot(u,y,'-ob'); hold on; plot(up,yp,'-*r');
%
% See also resampleFDZP
%
% Written by Dr. Erol Kalkan, P.E. (ekalkan@usgs.gov)
% $Revision: 1.0 $ $Date: 2016/09/06 13:03:00 $
u = linspace(0,length(y),length(y)*m);
x = 0:length(y)-1;
for i=1:length(u)
yp(i) = sum(y.*sinc(x-u(i)));
end
频率域重采样(ZERO-PADDING, 等价时间域Sinc插值)
function yp = resampleFDZP(y, m)
% FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ZERO-PADDING (FDZP) RESAMPLING (INTERPOLATION)
%
% Syntax:
% yp = resampleFDZP(y, m)
%
% Input:
% y = input signal to be resampled (y must be a row vector)
%
% m = resampling factor (e.g., if y is 100 sps and yp will be
% 200 sps, then m is 200/100 = 2)
% yp = resampled signal
%
%
% The method is based on the procedure given in p. 779 of Lyons (2011).
%
% Lyons, R.G. (2014). Understanding Digital Signal Processing, Prentice
% Hall, 3rd ed.
%
% Written by Dr. Erol Kalkan, P.E. (ekalkan@usgs.gov)
% $Revision: 2.0 $ $Date: 2016/08/31 13:03:00 $
%
% Calculate number of padding zeros
padlen = length(y)*(m - 1);
% Compute number of half points in FFT
zlen = ceil((length(y)+1)/2);
% Compute FFT
z = fft(y);
% Construct a new spectrum (row vector) by centering zeros
zp = [z(1:zlen) zeros(1, padlen) z(zlen+1:end)];
if ~mod(length(y), 2); % even number
zp(zlen) = zp(zlen)/2; zp(zlen+padlen) = zp(zlen);
end
% Compute inverse FFT and scale by m
yp = real(ifft(zp))*m;
斜坡函数(Taper Function)
在区间
[
0
,
1
]
[0,1]
[0,1]寻找一个斜坡多项式函数
T
(
x
)
T(x)
T(x), 满足
T
(
0
)
=
0
,
T
′
(
0
)
=
0
T
(
1
)
=
1
,
T
′
(
1
)
=
0
T(0)=0, T^\prime(0)=0 \\ T(1)=1, T^\prime(1)=0
T(0)=0,T′(0)=0T(1)=1,T′(1)=0
假设
T
(
x
)
=
a
x
3
+
b
x
2
+
c
x
+
d
T(x)=ax^3+bx^2+cx+d
T(x)=ax3+bx2+cx+d,根据上面条件有
T
(
x
)
=
x
2
(
3
−
2
x
)
T(x)=x^2(3-2x)
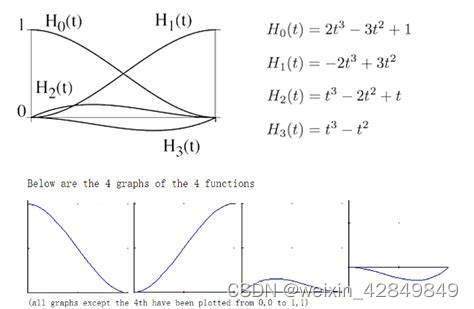
T(x)=x2(3−2x),即Hermite三次样条函数
H
1
H_1
H1.
图形
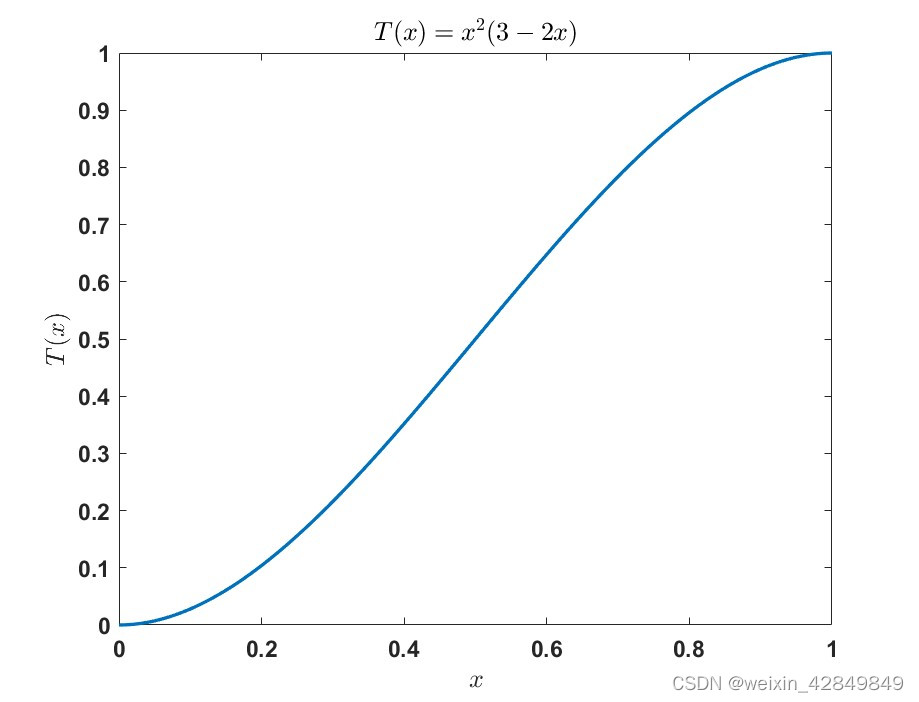
对频率数据进行Zero Padding前,一般对一定比例的高频数据施加斜坡窗口函数,避免跳变对加密数据引入高频噪声。
Hermite 三次样条函数






















 567
567











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








