this是什么
-
this的作用:
-
- 它在方法(准确的说是实例方法或非static的方法)内部使用,表示调用该方法的对象
-
- 它在构造器内部使用,表示该构造器正在初始化的对象
-
this可以调用的结构:成员变量、方法和构造器
什么时候使用this
实例方法或构造器中,如果使用当前类的成员变量或成员方法,可以在其前面添加this,增强程序的可读性,不过通常我们都习惯省略this。
但是当形参与成员变量同名时,如果在方法内或构造器内需要使用成员变量,必须添加this来表明该变量是类的成员变量。即:我们可以用this来区分 成员变量 和局部变量。
举例:我们在声明一个属性对应的setXxx方法时,通过形参给对应的属性赋值。如果形参名和属性名同名了,该如何在方法内区分这两个变量呢?
具体来说,使用this修饰的变量,表示的是属性;没有使用this修饰的,表示的是形参。
1.下面这段代码,给Person类的p1成员的age属性赋值为10
package this_super;
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.setAge(10);
System.out.println(p1.age);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public void setAge(int a){
//这里,int a为形参;
//在实际应用中,为了代码便于理解,一般形参a会被建议和实际属性age取名一致。
//所以实际应用时,建议a改写为age,但是改写完出现了两个age,程序变得难以运行,于是引入this关键字
age = a;
}
}
- 引入this关键字,用于区分形参(原本的a)和属性(原本的age):
package this_super;
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.setAge(12);
System.out.println(p1.age);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age; //属性为age
public void setAge(int age){
//age = a;
//这里,int a为形参;
// 在实际应用中,为了代码便于理解,一般形参a会被建议和实际属性age取名一致。
// 所以实际应用时,建议将a改写为age,但是改写完出现了两个age,程序变得难以运行。于是迫切需要引入this关键字
//注意:如果写成了age = age;也就等同于a=a;根据就近原则,属于形参a赋值给形参a,没有属性age什么事了,程序运行 System.out.println(p1.age)输出只会得到0。
//具体来说,在程序员想表达属性的变量前面,加“this.”
//下面这一行里面 this.age 表达的是属性;age代表的是形参。
this.age = age; //这种情况下,需要区分属性和形参,必须要用到this
}
}
- 添加新的属性email,并且构建了Person的constructor,包含新的属性email
package this_super;
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.setAge(12);
//System.out.println(p1.age);
System.out.println(p1.getAge());
Person p2 = new Person("Tom","tomelza@gmail.com");
System.out.println("name: "+p2.name+"; email: "+p2.email);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age; //属性为age
String email;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, String email) {
//构造器里面使用this
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public void setAge(int age){
//age = a;
//这里,int a为形参;
// 在实际应用中,为了代码便于理解,一般形参a会被建议和实际属性age取名一致。
// 所以实际应用时,建议将a改写为age,但是改写完出现了两个age,程序变得难以运行。于是迫切需要引入this关键字
//注意:如果写成了age = age;也就等同于a=a;根据就近原则,属于形参a赋值给形参a,没有属性age什么事了,程序运行 System.out.println(p1.age)输出必然会得到0。
//具体来说,在程序员想表达属性的变量前面,加“this.”
//下面这一行里面 this.age 表达的是属性;age代表的是形参。
this.age = age; //这种情况下,需要区分属性和形参,必须要用到this
//错误写法: p1.age=age;
// 因为需要将形参age赋值给动态的属性XXX.age,使用p1.age就直接限制了属性的动态特性。下次p2调用动态的属性XXX.age就无法使用了。
}
public int getAge(){
//方法里面调用属性,谁(this)调用这个方法,这个属性就是谁的
return this.age; //这句等同于下面一句;这里的this可省略
//return age;
}
}
总结:
- this可以调用的结构为成员变量,注意只能调用成员变量。
不能调用局部变量(比如第一个例子的setAge(int a),this调用不了那个int a)
- this可以调用方法。
- this可以调用构造器(本节最后讲)。
this调用方法举例( 在eat()方法中 调用了sleep()方法 ):
public void eat(){
System.out.println("人吃饭");
this.sleep();//谁调用eat方法,谁将来就继续去调用sleep
//sleep();这一句和上一句功能是一样的
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("人睡觉");
}
this怎么理解?表示 当前对象(在方法调用时) 或 当前正在创建的对象(在构造器中调用时)
this调用属性和方法
【针对于方法内的使用情况(准确的说是“非static修饰的”方法)】
一般情况:我们通过对象a调用方法,可以在方法内调用当前对象a的属性或其他方法。此时,我们可以在属性和其他方法前使用“this.”表示当前属性或其他方法所属的对象a。但是,一般情况下,我们都选择省略此"this."结构。
特殊情况:如果方法的形参和对象的属性同名(比如刚才例子里的age=age),我们必须使用this进行区分。使用this.修饰的变量即为属性(或成员变量),没有使用this修饰的变量,即为局部变量。
【针对于构造器内的使用情况】
一般情况:我们通过构造器创建对象时,可以在构造器内调用当前对象的属性或方法。此时,我们可以在属性和方法前使用“this.”表示当前属性或方法所属的对象。但是,一般情况下,我们都选择省略此"this."结构。
public Person(String n) {
//this.name = n;
name = n; //等同于上句
//this.eat();
eat();//等同于上句
}
特殊情况:如果方法的形参和正在创建的对象的属性同名,我们必须使用this进行区分。使用this.修饰的变量即为属性(或成员变量),没有使用this修饰的变量,即为局部变量。
public Person(String name, String email) {
//这是一个正在创建的对象
//构造器里面使用this
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
this调用构造器
举例:假设对象创建时,需要初始化50行代码。
同时构建了多个构造器,每个构造器的局部变量不同,如果每个构造器在模拟对象创建时都需要初始化50行代码,那么代码量就会很大出现冗余。
解决方案,在空参构造器里写入那初始化用到的50行代码,其余构造器使用这块代码时候去调用空参构造器。
参考代码:
package this_super;
public class UserTest {
String name;
int age;
}
class User{
String name;
int age;
public User() {
//假设对象创建时,需要初始化50行代码
}
public User(String name) {
//假设对象创建时,需要初始化50行代码,每次都写50行代码,有冗余
//可以在 User()里面写上这50行代码,然后每次在其他需要的地方调用空参的 User()
//调用空参的User(),可以用this()--代表调用了空参的 User(),注意这里直接写User()用不成
this();
this.name = name;
}
public User(String name, int age) {
//假设对象创建时,需要初始化50行代码,每次都写50行代码,有冗余
//可以在 User()里面写上这50行代码,然后每次在其他需要的地方调用空参的 User()
this();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
上例的简化问题
思考 构造器3和构造器2同时用了 this(); this.name = name,如何简化?
思路:可以让构造器3调用有参String name构造器2:public User(String name) ,
并将构造器3形参中的一个String name传给这个有参构造器2,
有参构造器2运行时候,再去调用无参构造器1。
参考代码:
package this_super;
public class UserTest {
String name;
int age;
}
class User{
String name;
int age;
public User() {
//构造器1,无参构造器
//假设对象创建时,需要初始化50行代码
}
public User(String name) {
//构造器2
this(); //这句相当于构造器2调用了无参构造器1
this.name = name;
}
public User(String name, int age) {
//构造器3
this(name);
//这句相当于构造器3调用了有参String name的构造器2--public User(String name)
// 并将构造器3形参中的一个String name传给了这个有参构造器2
this.age = age;
}
}
总结
- this调用构造器
- 格式
this(形参列表/也可无形参)(比如this();this(XXname)) - 使用时,在类的构造器中,调用当前类中指定的构造器
- 要求
this(形参列表/也可无形参)必须声明子必须声明在当前构造器的首行 - 结论
this(形参列表/也可无形参)在构造器中最多声明一个 - 如果一个类中声明了n个构造器,则最多有n-1个构造器可以声明有
this(形参列表/也可无形参)结构(简单可理解为类似计算阶乘n!的结构,一层一层调用别人,不断计算n*(n-1)!,总得有第一个干活的人1!==1 不然成了闭环,就算不出结果了)
举例1,Boy class和Girl class均带有name,age属性。
在Girl class里面建立marry方法,此方法会自动触发形参boy内部的marry方法。
在Boy class里面建立marry方法,此方法会和输入形参Girl完成marry;在Boy class里面建立shout方法, Boy>22才可以结婚。
参考代码:
Boy class的构建
package this_super;
public class Boy {
private String name;
private int age;
public Boy() {
}
public Boy(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;
}
public void marry(Girl girl){
System.out.println("I want to marry: " + girl.getName());
}
public void shout(){
if(this.age >= 22){
System.out.println("She said YES!");
}
else {
System.out.println("I have to wait a bit...");
}
}
}
Girl class的构建
package this_super;
public class Girl {
private String name;
private int age;
public Girl() {
//空参构造器必须有
}
public Girl(String name, int age) {
//this();//这句-调用上面的空参构造器-被系统隐藏了,因为空参构造器没有执行内容,所以看不出来
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public void marry(Boy boy){
System.out.println("I want to marry "+boy.getName());
boy.marry(this); //需要marry调用这个方法的girl,那就是当前的this对象
}
/*
* 比较两个Girl的年纪大小
* @return 正数:当前对象大; 负数:当前对象小(行参girl年纪大); 0:相等
*
* */
public int compare(Girl girl){
if(this.age > girl.age){
return 1;
}
else if(this.age < girl.age){
return -1;
}
else return 0;
}
}
BoyGirlTest测试部分
package this_super;
import javax.swing.*;
public class BoyGirlTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boy boy1 = new Boy("Tom",22);
Girl girl1 = new Girl("Lily",18);
girl1.marry(boy1);
boy1.shout();
Girl girl2 = new Girl("Lisa",16);
int compare = girl1.compare(girl2);
if(compare > 0){
System.out.println(girl1.getName()+"年龄更大");
}
else if (compare < 0){
System.out.println(girl2.getName()+"年龄更大");
}
else System.out.println("年龄一样大");
}
}
举例2:
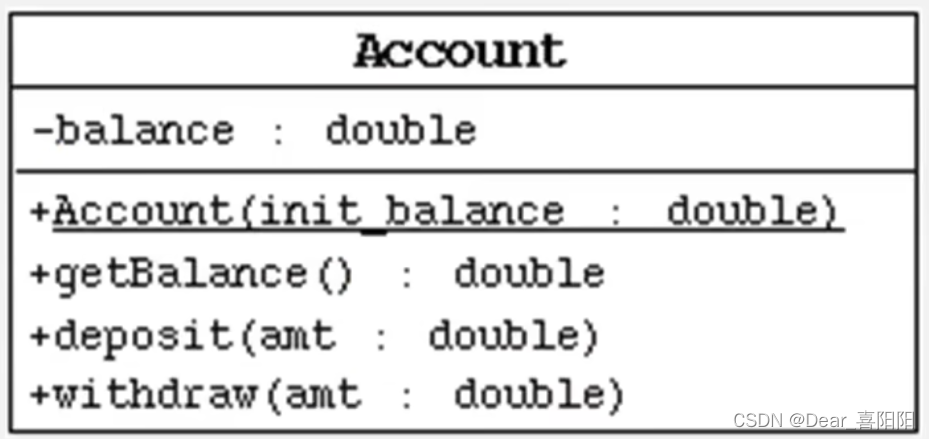
1.按照下图,创建Account类,提供必要的结构
- 在提款方法withdraw中需要判断用户余额是否能够满足提款数额的要求,如果不能,应给出提示。
- deposit方法表示存款
2.按照下图,创建Customer类,提供必要的结构

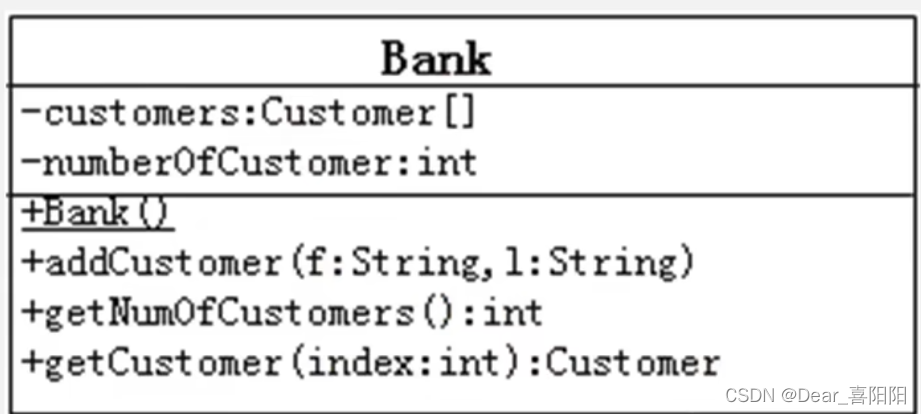
3.按照下图,创建Bank类,提供必要的结构。
- addCustomer方法必须按照参数(姓,名)构建一个新的Customer对象,然后把它放进customer数组中,还必须把numberOfCustomer属性的值加1.
- getNumOfCustomers方法返回numberofCustomers属性值。
- getCustomer方法返回与给出的index参数相关的客户
4.创建BankTest类,进行测试。
参考代码
- Account代码部分
package this_super;
public class Account {
private double balance =0;
public Account() {
}
public Account(double init_balance) {
this.balance = init_balance;
}
public double getBalance(){
return this.balance;
}
public void deposit(double amt){
if(amt >0){
this.balance+=amt;
System.out.println("成功存入了"+amt);
}
}
public void withdraw(double amt){
if(this.balance>=amt && amt >0){
this.balance -= amt;
System.out.println("成功取出 "+amt);
}
else {System.out.println("输入有误或资金不足");}
}
}
- Customer 代码部分
package this_super;
public class Customer {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private Account account;
public Customer(String f, String l) {
this.firstName = f;
this.lastName = l;
}
public String getFirstName(){
return this.firstName;
}
public String getLastName(){
return this.lastName;
}
public Account getAccount(){
//this.account.getBalance(); //我加的这行代码
return this.account;
}
public void setAccount(Account acct){
this.account = acct;
}
}
- Bank 代码部分
package this_super;
public class Bank {
//private Customer[] customers = new Customer[10]; //方法1:希望调用Bank的时候把数组创建好,直接赋值
// 也可以用方法2 在下面Bank()构造器里创建数组
private Customer[] customers ; //用于保存多个客户,有可能这个长度为10,和下面的numberOfCustomer不是一个概念。
private int numberOfCustomer=0; //用于记录存钱的客户的个数,有可能这个长度为3,表示当前只有三个各户存钱了
public Bank() {
//方法2:希望调用Bank的时候把数组创建好,构造器赋值
customers = new Customer[10];
}
/*
*
public Bank(Customer[] customer, int numberOfCustomer) {
this.customers = customer;
this.numberOfCustomer = numberOfCustomer;
}
* * */
//将指定姓名的客户保存在银行的客户列表中
public void addCustomer(String f, String l){
//this.customers[numberOfCustomer].Customer(f,l);
//numberOfCustomer+=1;
Customer cust= new Customer(f,l);
//写法1:
//customers[numberOfCustomer] =cust;
//numberOfCustomer++;
//写法2:
customers[numberOfCustomer++] =cust;
}
public int getNumOfCustomers(){
return this.numberOfCustomer;
}
public Customer getCustomer(int index){
if(index <0 || index >= numberOfCustomer){
return null;
}
return this.customers[index];
}
}
测试主程序:
package this_super;
import test.A;
import test.B;
public class BankTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试Account部分是否工作
Account acc1 = new Account(100);
System.out.println("current Balance"+acc1.getBalance());
acc1.deposit(20);//成功存入了20.0
System.out.println("current Balance"+acc1.getBalance());
acc1.deposit(30);
System.out.println("current Balance"+acc1.getBalance());
acc1.withdraw(59);
System.out.println("current Balance"+acc1.getBalance());
acc1.withdraw(159);
System.out.println("current Balance"+acc1.getBalance());
//测试Customer部分是否工作
Customer cust1 = new Customer("James","Green");
System.out.println(cust1.getLastName());
System.out.println(cust1.getFirstName());
cust1.setAccount(new Account(1000));
System.out.println(cust1.getAccount().getBalance());
//测试Bank部分是否工作
Bank bank = new Bank();
bank.addCustomer("Aman","Xie");
bank.addCustomer("Yuanyuan","Liu");
bank.getCustomer(0).setAccount(new Account(1000));
bank.getCustomer(0).getAccount().withdraw(50);
System.out.println(bank.getCustomer(0).getAccount().getBalance());//950.0
System.out.println(bank.getNumOfCustomers());//2
System.out.println(bank.getCustomer(1).getFirstName()); //Yuanyuan
}
}
运行结果:
current Balance100.0
成功存入了20.0
current Balance120.0
成功存入了30.0
current Balance150.0
成功取出 59.0
current Balance91.0
输入有误或资金不足
current Balance91.0
Green
James
1000.0
成功取出 50.0
950.0
2
Yuanyuan
Process finished with exit code 0
示例2:要求制作拼夕夕客户系统,可以从交互界面(电脑显示屏幕和键盘)【增删改查用户】;并且每次删掉一个用户,则用户编码会自动更新(前移一位)。
思路提示:
-
Customer客户类结构

-
CustomerList类设计
CustomerList为Customer对象的管理模块,内部用数组来管理一组Customer对象。
CustomerList类封装以下信息
- Customer[] customer //保存客户对象的数组
- int total = 0 //记录保存的客户对象的数量
- 增删改查方法都应该在此类中完成。

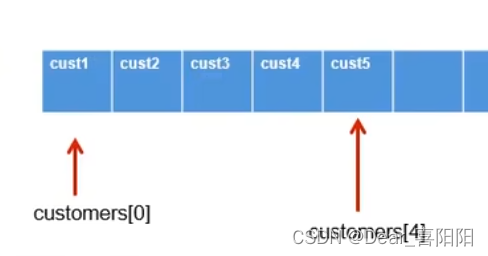
注意构建deleteCustomer时将后面的元素往前挪,当全部挪动完毕后,原本最后一个元素的位置会空出来,应该用null将其赋值,完全抹杀。
例如下图的cust5,需要将其赋值null彻底删掉。
- CustomerView类的设计
主模块,负责菜单的显示,和处理用户操作。

代码示例:
Customer.java
package this_super.pinxixi;
public class Customer {
private String name;
private char gender;
private int age;
private String phone;
private String email;
public Customer() {
//空参构造器,还是写上双保险。
}
public Customer(String name, char gender, int age, String phone, String email) {
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
this.phone = phone;
this.email = email;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public char getGender() {
return gender;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setGender(char gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getDetails() {
return this.name +"\t"+ this.gender +"\t"+ this.age +"\t"+ this.phone +"\t"+ this.email +"";
}
}
CustomerList.java
package this_super.pinxixi;
public class CustomerList {
private Customer[] customers; //用来保护客户对象的数组
private int total = 0 ;//用来记录保护客户对象的数量,注意这个值并不等于customers.length,
// customers.length取决于customers在建立的时候,硬性控制的数组长度
// total表示customers里面放了几个有效的数据,从理论上讲customers.length肯定是比total大的
/*
* 用途:构造器,用来初始化customer数组
* 参数:totalCustomer指定Customers数组的最大空间
* */
public CustomerList(int totalCustomer) {
this.customers = new Customer[totalCustomer];
//this.total = totalCustomer; 并不在此处限制数组的长度
}
/*
* 用途:将参数customer添加至数组中最后一个客户对象纪录之后
* 参数:customer 指定要添加的客户对象
* 添加成功返回true: false表示数组已满,无法添加
* */
public boolean addCustomer (Customer customer){
if(total < customers.length){
this.customers[this.total]=customer;
this.total +=1;
//先赋值完毕,total再+1,否则就成为用输入的customer赋值给this.customers[1],
// 而this.customers[1]根本不存在,就会报越界的错
//this.total++;也有++写在这里的
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*
* 用途:用参数cust替换数组中由index位置原来的对象,
* 注意:本方法是修改已经存在的客户元素,而不是在新的空间增加原来不存在的新客户对象。
* index是指定所替换对象在数组中的位置(角标),index >= 0
* cust指定替换的新的客户对象
* 返回:替换成功返回true; 索引无效,无法替换则返回false
*
* */
public boolean replaceCustomer(int index, Customer cust){
if(index >=0 && index < total){
//当total为1的时候,表明只有一个有效客户对象,index最多只能从0->0范围选择,
// 所以上面使用index < total而不是index <= total
this.customers[index]=cust;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*
* 用途:从数组中删除参数index指定位置原来的客户对象,
* index是指定所删除对象在数组中的位置(角标),index >= 0
* 返回:删除成功返回true; 索引无效或无法删除则返回false
*
* */
public boolean deleteCustomer(int index){
if (index >= this.total || index < 0){
return false;
}
for (int i = index; i < this.total-1; i++) {
//第一种方法: 后一位往前挪动一位
Customer tempcust = this.customers[i+1];
this.customers[i] = tempcust;
// 第二种方法:后一位往前挪动一位,也可以这样写,一步就完成了。
// this.customers[i] = this.customers[i+1];
}
//第一种方法:将有效位置的最后一个位置置空
this.customers[this.total-1]=null;
this.total--; //最后更新total的最新值,对其减1。
//第二种方法:将有效位置的最后一个位置置空
// 比如共6个元素 total=6,删除一个元素后total=5
// 删除任务结束后,角标customers[i]最后有效的i只能取到4,需要将原来customers[5]那个位置赋值为null
// 所以下面,先--this.total再赋值为null,将有效位置的最后一个位置置空
// this.customers[--this.total]=null;
return true;
}
/**
* 用途:返回数组记录的所有客户对象
* 返回:Customer[] 数组中包含了当前所有客户对象,该数组长度与对象个数相同。
* 注意:需要返回的是有效的客户对象信息,并不是数组总共长度的所有信息,因为数组后面可能没放满,全是空的。直接return this.customers则有过多null,是不对的。
* */
public Customer[] getAllCustomers(){
//这种方法是错误的:
//for (Customer each : this.customers) {
// System.out.println("Name: "+each.getName()+";Age: " + each.getAge() +";Gender: "+ each.getGender()+";Phone: " + each.getPhone() +";Email: "+ each.getEmail());
//}
//return this.customers;
Customer[] cust = new Customer[total];
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++) {
cust[i]=customers[i];
}
return cust;
}
/*
* 用途:返回参数index返回指定索引位置的客户对象记录
* index指定所要获取的客户在数组中的索引位置,从0开始
* return封装了客户信息的Customer对象
* */
public Customer getCustomer(int index){
if (index < 0 || index >= this.total)
{return null;}
return this.customers[index];
}
/*
* 获取客户列表中客户的数量
*
* */
public int getTotal(){
return this.total;
}
}
程序运行主程序:
CustomerView.java
package this_super.pinxixi;
public class CustomerView {
//创建最大包含10个客户对象的CustomerList对象,供以下各成员方法使用
CustomerList customerList = new CustomerList(10);
/*
* 进入主界面的方法:自建写法1
public void enterMainMenu(){
Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("----------拼夕夕电商管理系统----------");
System.out.println("----------1.添加客户----------");
System.out.println("----------2.修改客户----------");
System.out.println("----------3.删除客户----------");
System.out.println("----------4.客户列表----------");
System.out.println("----------5.退出----------");
System.out.println("请输入1-5: ");
if (x.hasNextInt()){//7.5
int option = x.nextInt();
switch (option) {
// 注意注意,下面的case '1'不要写成了case 1!
case '1': //添加客户
{System.out.println("添加客户");addNewCustomer();break;}
case '2': //修改客户
{System.out.println("修改客户");modifyCustomer();break;}
case '3': //删除客户
{System.out.println("删除客户");deleteCustomer();break;}
case '4': //客户列表
{System.out.println("客户列表");listAllCustomer();break;}
case '5': //退出
{System.out.println("退出");break;}
default: {break;}
}
}
else{
System.out.println("输入不合法,请输入1-5数字");
}
}
*
* */
/*
* 进入主界面的方法:写法2
*
* */
public void enterMainMenu(){
boolean isFlag = true;
while(isFlag) {
//显示界面
System.out.println("----------拼夕夕电商管理系统----------");
System.out.println("----------1.添加客户----------");
System.out.println("----------2.修改客户----------");
System.out.println("----------3.删除客户----------");
System.out.println("----------4.客户列表----------");
System.out.println("----------5.退出----------");
System.out.println("请输入1-5: ");
//获取用户选择
char key = Utility_org.readMenuSelection();//自建类自建方法,用来判断用户输入的选项,如果不是1-5,就会不断要求用户重新输入
//isFlag = false;
//注意注意,下面的case '1'不要写成了case 1!
switch (key) {
case '1': //添加客户
{
System.out.println("添加客户");
addNewCustomer();
break;
}
case '2': //修改客户
{
System.out.println("修改客户");
modifyCustomer();
break;
}
case '3': //删除客户
{
System.out.println("删除客户");
deleteCustomer();
break;
}
case '4': //客户列表
{
System.out.println("客户列表");
listAllCustomer();
break;
}
case '5': //退出
{
System.out.println("确认是否退出(Y/N):");
char isExit = Utility_org.readConfirmSelection();
if (isExit == 'Y')
{ isFlag = false;}
break;
}
}
}
}
/*
*
* 新增用户
* */
/*
*
public void addNewCustomer() {
Customer cust = new Customer();
while(true){
System.out.println("输入新客户姓名:");
Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = x.nextLine();
cust.setName(name);
break;
}
while(true){
System.out.println("输入新客户年龄(0-140):");
Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in);
int age = x.nextInt();
if(age>0 && age <=140){
cust.setAge(x.nextInt());
break;
}
else {
System.out.println("输入不合法。");
}
}
while(true){
System.out.println("输入新客户性别(F/M):");
Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in);
String gender = x.next();
if(gender.equals("F")){
cust.setGender('F');
break;
}
else if(gender.equals("M")){
cust.setGender('M');
break;
}
else{
System.out.println("输入不合法。");
}
}
while(true){
System.out.println("输入新客户邮箱:");
Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in);
String email = x.next();
cust.setEmail(email);
break;
}
while(true){
System.out.println("输入新客户电话:");
Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in);
String phone = x.next();
cust.setPhone(phone);
break;
}
}
*
* */
/*
* 新增用户
* */
public void addNewCustomer() {
System.out.println("----------添加客户----------");
System.out.println("请输入name");
String myname = Utility_org.readString(20);
System.out.println("请输入gender");
char mygender = Utility_org.readChar();
System.out.println("请输入age");
int myage = Utility_org.readInt();
System.out.println("请输入phone");
String myphone = Utility_org.readString(20);
System.out.println("请输入email");
String myemail = Utility_org.readString(30);
//将上面的信息收集完毕,汇总成一个mycust变量,准备赋值
Customer mycust = new Customer(myname,mygender,myage,myphone,myemail);
boolean flag = customerList.addCustomer(mycust);
if (flag) {
System.out.println("----------添加完成----------");
} else {
System.out.println("----------用户存储空间已满,无法添加----------");
}
}
public void modifyCustomer() {
System.out.println("----------修改客户----------");
int index=0 ;//客户编号
Customer cust = null;
for(;;) {
System.out.println("----------请输入客户编号(-1退出)----------");
index = Utility.readInt();
if (index == -1) {
return;
}
cust = customerList.getCustomer(index - 1);
if (cust == null) {
System.out.println("无法找到指定客户。");
} else {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("name(" + cust.getName() + "):");
String name = Utility.readString(20, cust.getName());
System.out.println("gender(" + cust.getGender() + "):");
char gender = Utility.readChar(cust.getGender());
System.out.println("age(" + cust.getAge() + "):");
int age = Utility.readInt(cust.getAge());
System.out.println("phone(" + cust.getPhone() + "):");
String phone = Utility.readString(20, cust.getPhone());
System.out.println("email(" + cust.getEmail() + "):");
String email = Utility.readString(20, cust.getEmail());
cust = new Customer(name, gender, age, phone, email);
boolean flag = customerList.replaceCustomer(index - 1, cust);
if (flag) {
System.out.println("----------修改完成----------");
} else {
System.out.println("----------找不到指定用户,修改失败----------");
return;
}
}
public void deleteCustomer(){
System.out.println("----------删除客户----------");
int index = 0;
Customer cust = null;
for(;;){
System.out.println("请选择删除客户编号(-1)退出:");
index = Utility.readInt();
if(index == -1){
return;
}
cust = customerList.getCustomer(index -1);
if(cust ==null){
System.out.println("无法找到指定客户。");
}else break;
}
System.out.println("确认是否删除(Y/N):");
char yn = Utility.readConfirmSelection();
if(yn=='N'){
return;
}
boolean flag = customerList.deleteCustomer(index -1);
if(flag){
System.out.println("----------删除完成----------");
}else{
System.out.println("----------无法找到指定客户,删除失败----------");
}
}
public void listAllCustomer(){
System.out.println("------客户列表----------");
Customer[] custs= customerList.getAllCustomers();
if(custs.length ==0){
System.out.println("未找到客户记录。");
}
else{
System.out.println("编号\t姓名\t性别\t年龄\t电话\t邮箱");
for (int i = 0; i < custs.length; i++) {
//System.out.println((i+1)+"\t"+custs[i].getName + "\t"+custs[i].getGender + "\t"+custs[i].getAge + "\t"+custs[i].getPhone + "\t"+custs[i].getEmail +"");
System.out.println((i+1)+"\t"+custs[i].getDetails());
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CustomerView view = new CustomerView();
//调用enterMainMenu方法,程序开跑
view.enterMainMenu();
}
}
Utility.java
package this_super.pinxixi;
import java.util.*;
/**
Utility工具类:
将不同的功能封装为方法,就是可以直接通过调用方法使用它的功能,而无需考虑具体的功能实现细节。
*/
public class Utility {
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
/**
用于界面菜单的选择。该方法读取键盘,如果用户键入’1’-’5’中的任意字符,则方法返回。返回值为用户键入字符。
*/
public static char readMenuSelection() {
char c;
for (; ; ) {
String str = readKeyBoard(1, false);
c = str.charAt(0);
if (c != '1' && c != '2' &&
c != '3' && c != '4' && c != '5') {
System.out.print("选择错误,请重新输入:");
} else break;
}
return c;
}
/**
从键盘读取一个字符,并将其作为方法的返回值。
*/
public static char readChar() {
String str = readKeyBoard(1, false);
return str.charAt(0);
}
/**
从键盘读取一个字符,并将其作为方法的返回值。
如果用户不输入字符而直接回车,方法将以defaultValue 作为返回值。
*/
public static char readChar(char defaultValue) {
String str = readKeyBoard(1, true);
return (str.length() == 0) ? defaultValue : str.charAt(0);
}
/**
从键盘读取一个长度不超过2位的整数,并将其作为方法的返回值。
*/
public static int readInt() {
int n;
for (; ; ) {
String str = readKeyBoard(2, false);
try {
n = Integer.parseInt(str);
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.print("数字输入错误,请重新输入:");
}
}
return n;
}
/**
从键盘读取一个长度不超过2位的整数,并将其作为方法的返回值。
如果用户不输入字符而直接回车,方法将以defaultValue 作为返回值。
*/
public static int readInt(int defaultValue) {
int n;
for (; ; ) {
String str = readKeyBoard(2, true);
if (str.equals("")) {
return defaultValue;
}
try {
n = Integer.parseInt(str);
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.print("数字输入错误,请重新输入:");
}
}
return n;
}
/**
从键盘读取一个长度不超过limit的字符串,并将其作为方法的返回值。
*/
public static String readString(int limit) {
return readKeyBoard(limit, false);
}
/**
从键盘读取一个长度不超过limit的字符串,并将其作为方法的返回值。
如果用户不输入字符而直接回车,方法将以defaultValue 作为返回值。
*/
public static String readString(int limit, String defaultValue) {
String str = readKeyBoard(limit, true);
return str.equals("")? defaultValue : str;
}
/**
用于确认选择的输入。该方法从键盘读取‘Y’或’N’,并将其作为方法的返回值。
*/
public static char readConfirmSelection() {
char c;
for (; ; ) {
String str = readKeyBoard(1, false).toUpperCase();
c = str.charAt(0);
if (c == 'Y' || c == 'N') {
break;
} else {
System.out.print("选择错误,请重新输入:");
}
}
return c;
}
private static String readKeyBoard(int limit, boolean blankReturn) {
String line = "";
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
line = scanner.nextLine();
if (line.length() == 0) {
if (blankReturn) return line;
else continue;
}
if (line.length() < 1 || line.length() > limit) {
System.out.print("输入长度(不大于" + limit + ")错误,请重新输入:");
continue;
}
break;
}
return line;
}
}
运行时候启动主程序CustomerView,根据要求键入数字,即可完成相应的功能。





















 2204
2204

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








