文章目录
一、字符串类的兼容性
问题:string 类对象还具备 C 方式字符串的灵活性吗?还能直接访问单个字符吗?
- string 类最大限度的考虑了 C 字符串的兼容性
- 可以按照使用 C 字符串的方式使用 string 对象

下面看一个用 C 方式使用 string 类的示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "a1b2c3d4e";
int n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
{
if (isdigit(s[i]))
{
n++;
}
}
cout << n << endl;
return 0;
}输出结果如下:

二、重载数组访问操作符
问题:类的对象怎么支持数组的下标访问?
- 被忽略的事实
- 数组访问符是 C/C++ 中的内置操作符
- 数组访问符的原生意义是数组访问和指针运算

下面进行指针与数组的复习:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[5] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
a[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cout << *(a + i) << endl; //cout << a[i] << endl;
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
i[a] = i + 10; //cout << a[i] <<endl;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cout << *(i + a) << endl;
}
return 0;
}输出结果如下:

- 数组访问操作符([ ])
- 只能通过类的成员函数重载重载
- 函数能且仅能使用一个参数
- 可以定义不同参数的多个重载函数
#include <iostream>
//#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int a[5];
public:
int& operator [] (int i)
{
return a[i];
}
int& operator [] (const string& s)
{
if (s == "1st")
{
return a[0];
}
else if (s == "2nd")
{
return a[1];
}
else if (s == "3rd")
{
return a[2];
}
else if (s == "4th")
{
return a[3];
}
else if (s == "5th")
{
return a[4];
}
}
int length()
{
return 5;
}
};
int main()
{
Test t;
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++)
{
t[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++)
{
cout << t[i] << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << t["5th"] << endl;
cout << t["4th"] << endl;
cout << t["3rd"] << endl;
cout << t["2nd"] << endl;
cout << t["1st"] << endl;
return 0;
}输出结果如下:

这个示例说明可以将字符串作为下标访问数组。
所以之前写的数组类的代码可以进一步完善啦:
IntArray.h:
#ifndef _INTARRAY_H_
#define _INTARRAY_H_
class IntArray
{
private:
int m_length;
int* m_pointer;
IntArray(int len);
IntArray(const IntArray& obj);
bool construct();
public:
static IntArray* NewInstance(int length);
int length();
bool get(int index, int& value);
bool set(int index ,int value);
int& operator [] (int index);
IntArray& self();
~IntArray();
};
#endif
IntArray.cpp:
#include "IntArray.h"
IntArray::IntArray(int len)
{
m_length = len;
}
bool IntArray::construct()
{
bool ret = true;
m_pointer = new int[m_length];
if( m_pointer )
{
for(int i=0; i<m_length; i++)
{
m_pointer[i] = 0;
}
}
else
{
ret = false;
}
return ret;
}
IntArray* IntArray::NewInstance(int length)
{
IntArray* ret = new IntArray(length);
if( !(ret && ret->construct()) )
{
delete ret;
ret = 0;
}
return ret;
}
int IntArray::length()
{
return m_length;
}
bool IntArray::get(int index, int& value)
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < length());
if( ret )
{
value = m_pointer[index];
}
return ret;
}
bool IntArray::set(int index, int value)
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < length());
if( ret )
{
m_pointer[index] = value;
}
return ret;
}
int& IntArray::operator [] (int index)
{
return m_pointer[index];
}
IntArray& IntArray::self()
{
return *this;
}
IntArray::~IntArray()
{
delete[]m_pointer;
}
main.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "IntArray.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
IntArray* a = IntArray::NewInstance(5);
if( a != NULL )
{
IntArray& array = a->self();
cout << "array.length() = " << array.length() << endl;
array[0] = 1;
for(int i=0; i<array.length(); i++)
{
cout << array[i] << endl;
}
}
delete a;
return 0;
}
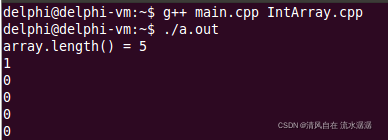
输出结果如下:
三、小结
- string 类最大程度的兼容了 C 字符串的用法
- 数组访问符的重载能够使得对象模拟数组的行为
- 只能通过类的成员函数重载数组访问符
- 重载函数能且仅能使用一个参数






















 1444
1444











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










