Pytorch全连接层原理和使用
参考资料:PyTorch快速入门教程二(线性回归以及logistic回归)
矩阵乘法实现全连接层
方法1:矩阵乘法
x = torch.arange(0, 100, 0.01,dtype=torch.float32)
y = (10 * x + 5 + np.random.normal(0, 1, x.size())).float()
batch_size = 100
w = torch.randn((1,), requires_grad=True,dtype=torch.float32)
b = torch.randn((1,), requires_grad=True,dtype=torch.float32)
loss = nn.MSELoss()
iter_time = x.size()[0]//batch_size
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([w,b], lr=0.1,weight_decay=0.1)
for e in range(5):
for t in range(iter_time):
train_x=x[batch_size*t:batch_size*(t+1)].clone()
train_y = y[batch_size * t:batch_size * (t + 1)].clone()
z = torch.einsum('i,j->ij',train_x,w)+b #z=w*x+b
output = loss(train_y,z)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output.backward() #通过loss反向传播
optimizer.step()
print(e,t,output/batch_size)
#w=9.9682
#b=8.1066
方法2:利用nn.Parameters()
模型中可学习的参数由nn.Parameters()注册到模型中。
class Linear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features: int, out_features: int, bias: bool = True) -> None:
super(Linear, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_features, in_features))
if bias:
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_features))
else:
self.register_parameter('bias', None)
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self) -> None:
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight, a=np.sqrt(5))
if self.bias is not None:
fan_in, _ = nn.init._calculate_fan_in_and_fan_out(self.weight)
bound = 1 / np.sqrt(fan_in)
nn.init.uniform_(self.bias, -bound, bound)
def forward(self, input: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
output = input.matmul(self.weight.t())
if self.bias is not None:
output += self.bias
return output
linear= Linear(1,1)
num_epochs = 5
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(linear.parameters(), lr=0.1,weight_decay=0.1)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for t in range(iter_time):
train_x=x[batch_size*t:batch_size*(t+1)].clone()
train_y = y[batch_size * t:batch_size * (t + 1)].clone()
train_x=train_x.unsqueeze(1)
train_y=train_y.unsqueeze(1)
# forward
out = linear(train_x) # 前向传播
loss = criterion(out, train_y) # 计算loss
# backward
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度归零
loss.backward() # 方向传播
optimizer.step() # 更新参数
if (t+1) % 20 == 0:
print('Epoch[{}/{}], loss: {:.6f}'.format(epoch+1,t,loss.data))
#w=9.9577
#b=9.0406
使用nn.Linear层
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1, 1) # an affine operation: y = Wx + b
def forward(self, x):
x=self.fc1(x)
return x
net = Net()
net
'''神经网络的结构是这样的
Net (
(fc1): Linear (1 -> 1)
)
'''
num_epochs = 5
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.05,weight_decay=0.1)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for t in range(iter_time):
train_x=x[batch_size*t:batch_size*(t+1)].clone()
train_y = y[batch_size * t:batch_size * (t + 1)].clone()
train_x=train_x.unsqueeze(1)
train_y=train_y.unsqueeze(1)
inputs = Variable(train_x)
target = Variable(train_y)
# forward
out = net(inputs) # 前向传播
loss = criterion(out, target) # 计算loss
# backward
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度归零
loss.backward() # 方向传播
optimizer.step() # 更新参数
if (t+1) % 20 == 0:
print('Epoch[{}/{}], loss: {:.6f}'.format(epoch+1,t+1,loss.data))
#w=9.9515
#b=8.6728
PyTorch激活函数原理和使用
参考资料:GELU 激活函数
torch.nn.GELU
G E L U ( x ) = x P ( X < = x ) = x Φ ( x ) GELU(x)=xP(X<=x)=xΦ(x) GELU(x)=xP(X<=x)=xΦ(x)
这里$Φ ( x ) 是 正 太 分 布 的 概 率 函 数 , 可 以 简 单 采 用 正 太 分 布 是正太分布的概率函数,可以简单采用正太分布 是正太分布的概率函数,可以简单采用正太分布N ( 0 , 1 ) 要 , 或 者 使 用 参 数 化 的 正 太 分 布 要,或者使用参数化的正太分布 要,或者使用参数化的正太分布N ( μ , σ )$ ,然后通过训练得到 μ μ μ。
对于假设为标准正太分布的
G
E
L
U
(
x
)
GELU(x)
GELU(x),论文中提供了近似计算的数学公式,如下:
G
E
L
U
(
x
)
=
0.5
x
(
1
+
t
a
n
h
[
2
/
π
(
x
+
0.044715
x
3
)
]
)
GELU(x) = 0.5x(1+tanh[\sqrt{2/\pi}(x+0.044715x^3)])
GELU(x)=0.5x(1+tanh[2/π(x+0.044715x3)])
bert源码给出的GELU代码pytorch版本表示如下:
def gelu(input_tensor):
cdf = 0.5 * (1.0 + torch.erf(input_tensor / torch.sqrt(2.0)))
return input_tesnsor*cdf
e r f ( x ) = 2 π ∫ 0 x e − t 2 d t erf(x)= \frac{2}{π}∫_0^xe^{−t^2}dt erf(x)=π2∫0xe−t2dt
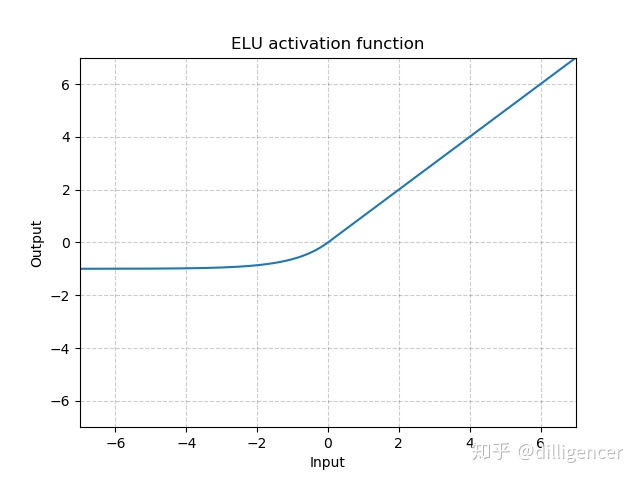
torch.nn.ELU(alpha=1.0,inplace=False)
def elu(x,alpha=1.0,inplace=False):
return max(0,x)+min(0,alpha∗(exp(x)−1))
α是超参数,默认为1.0
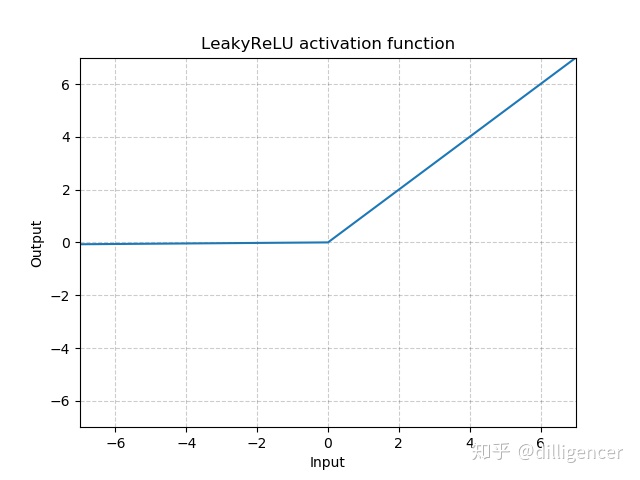
torch.nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01,inplace=False)
def LeakyReLU(x,negative_slope=0.01,inplace=False):
return max(0,x)+negative_slope∗min(0,x)
其中 negative_slope是超参数,控制x为负数时斜率的角度,默认为1e-2
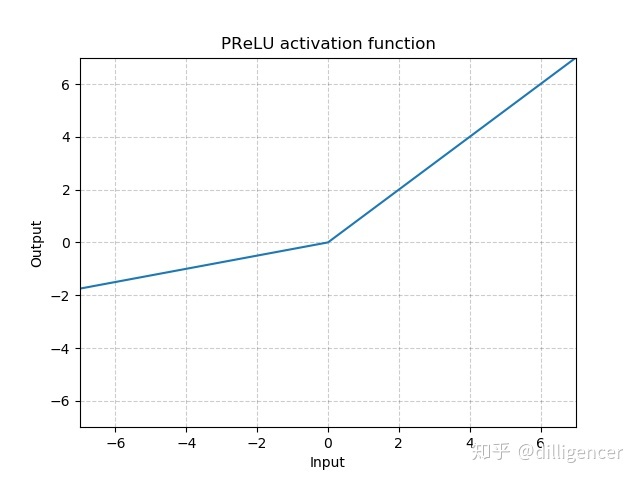
torch.nn.PReLU(num_parameters=1,init=0.25)
def PReLU(x,num_parameters=1,init=0.25):
return max(0,x)+init∗min(0,x)
其中a 是一个可学习的参数,当不带参数调用时,即nn.PReLU(),在所有的输入通道上使用同一个a,当带参数调用时,即nn.PReLU(nChannels),在每一个通道上学习一个单独的a。
注意:当为了获得好的performance学习一个a时,不要使用weight decay。
num_parameters:要学习的a的个数,默认1
init:a的初始值,默认0.25
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
CNN中最常用ReLu。
def ReLU(x,inplace=False):
return max(0,x)

torch.nn.ReLU6(inplace=False)
def ReLU6(x,inplace=False):
return min(max(0,x),6)

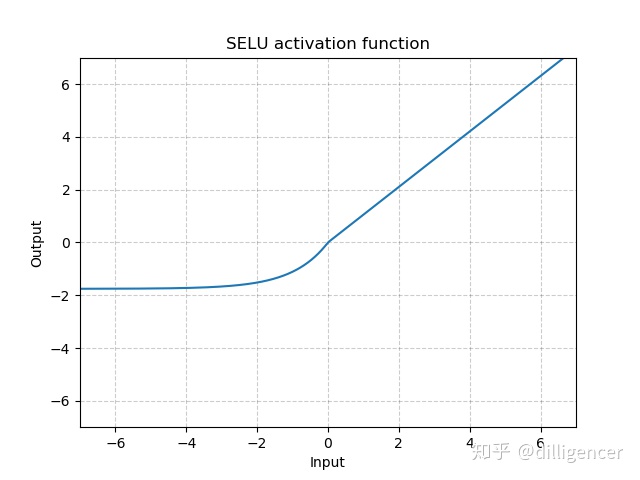
torch.nn.SELU(inplace=False)
def SELU(x,inplace=False):
alpha=1.6732632423543772848170429916717
scale=1.0507009873554804934193349852946
return scale∗(max(0,*x*)+min(0,alpha∗(exp(x)−1)))
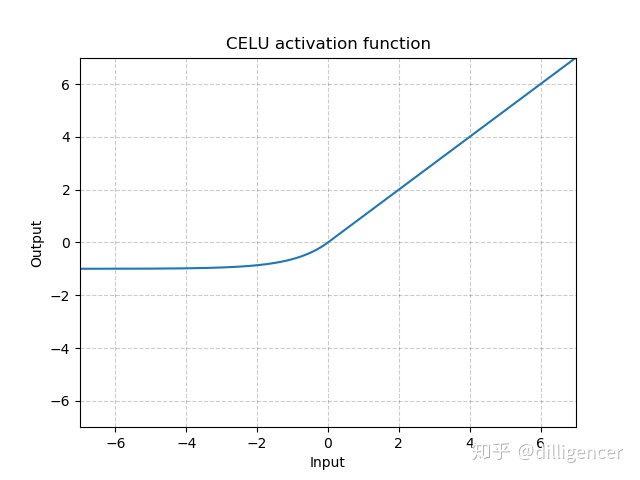
torch.nn.CELU(alpha=1.0,inplace=False)
def CELU(x,alpha=1.0,inplace=False):
return max(0,x)+min(0,alpha∗(exp(x/alpha)−1))
其中α 默认为1.0
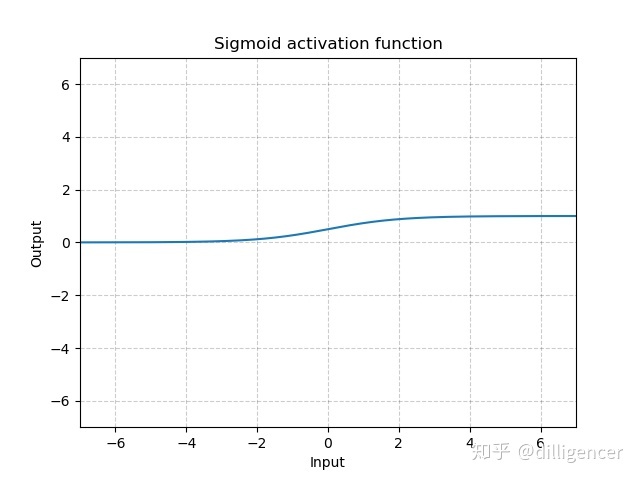
torch.nn.Sigmoid
S i g m o i d ( x ) = 1 1 + e x p ( − x ) Sigmoid(x)=\frac{1}{1+exp(-x)} Sigmoid(x)=1+exp(−x)1
def Sigmoid(x):
return 1/(np.exp(-x)+1)
torch.nn.LogSigmoid
L o g S i g m o i d ( x ) = l o g ( 1 1 + e x p ( − x ) ) LogSigmoid(x)=log(\frac{1}{1+exp(-x)}) LogSigmoid(x)=log(1+exp(−x)1)
def LogSigmoid(x):
return np.log(1/(np.exp(-x)+1))

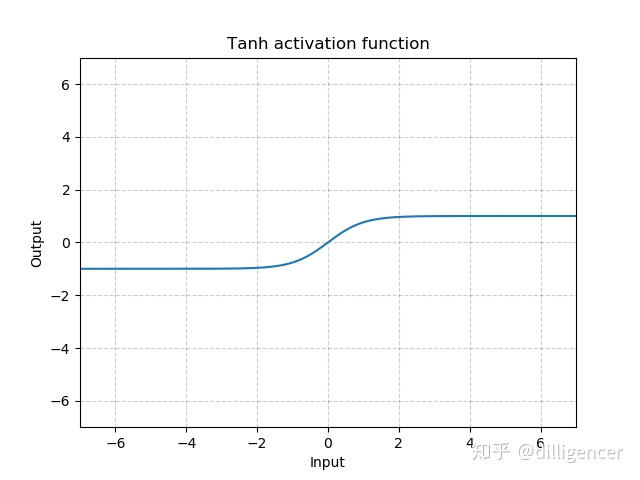
torch.nn.Tanh
T a n h ( x ) = t a n h ( x ) = e x − e − x e x + e − x Tanh(x)=tanh(x)=\frac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}} Tanh(x)=tanh(x)=ex+e−xex−e−x
def Tanh(x):
return (np.exp(x)-np.exp(-x))/(np.exp(x)+np.exp(-x))
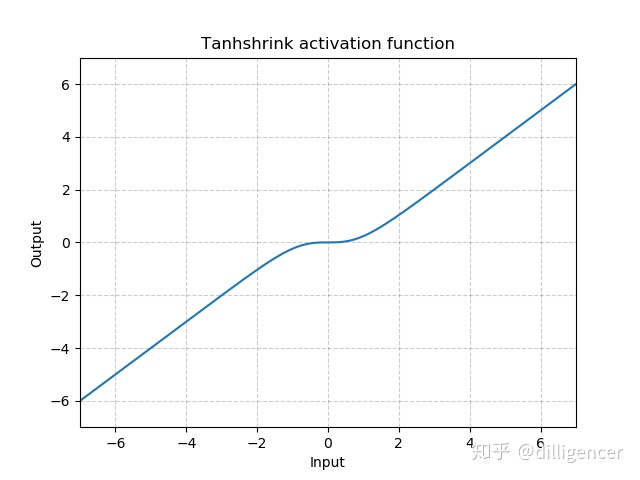
torch.nn.Tanhshrink
T a n h s h r i n k ( x ) = x − T a n h ( x ) Tanhshrink(x)=x−Tanh(x) Tanhshrink(x)=x−Tanh(x)
def Tanhshrink(x):
return x-(np.exp(x)-np.exp(-x))/(np.exp(x)+np.exp(-x))
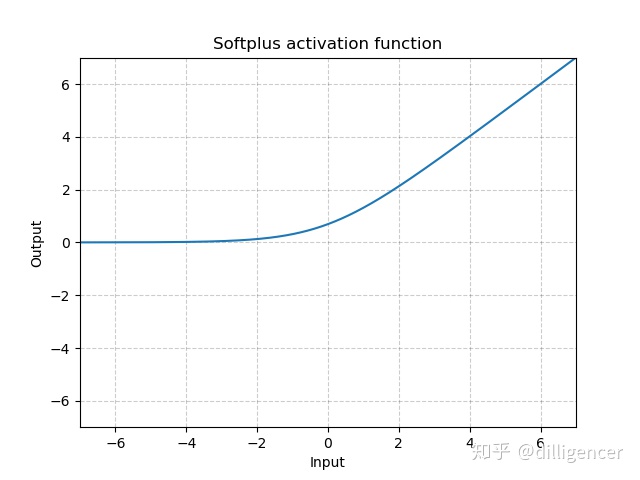
torch.nn.Softplus(beta=1,threshold=20)
S o f t p l u s ( x ) = 1 β ∗ l o g ( 1 + e x p ( β ∗ x ) ) Softplus(x)=\frac{1}{\beta}*log(1+exp(\beta*x)) Softplus(x)=β1∗log(1+exp(β∗x))
该函数可以看作是ReLu的平滑近似。
def Softplus(x,beta=1,threshold=20):
return np.log(1+np.exp(beta*x))/beta
torch.nn.Softshrink(lambd=0.5)
S o f t S h r i n k a g e ( x ) = { x − λ , if x > λ x + λ , if x < − λ 0 , otherwise SoftShrinkage(x) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} x-\lambda, & \textrm{if $x>\lambda$}\\ x+\lambda, & \textrm{if $x<-\lambda$}\\ 0, & \textrm{otherwise} \end{array} \right. SoftShrinkage(x)=⎩⎨⎧x−λ,x+λ,0,if x>λif x<−λotherwise
λ的值默认设置为0.5
def Softshrink(x,lambd=0.5):
if x>lambd:return x-lambd
elif x<-lambd:return x+lambd
else:return 0























 749
749











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








