1.简述Makefile的作用
makefile关系到整个工程的编译规则。Makefile定义了一系列的规则来指定那些文件需要先编译,哪些文件需要后编译
甚至于进行更复杂的功能操作,因为Makefile就像一个shell脚本一样,其中也可以执行操作系统的命令。
2.sizeof与strlen的区别:
sizeof是运算符,他计算的是分配空间的实际字节,而strlen是函数,他计算的是空间中字符的个数;
sizeof可以以类型、函数做参数,而strlen只能以字符串做参数。
sizeof不能计算动态分配空间的大小。
3.什么是野指针?如何避免野指针。
野指针的定义:指向一个已经删除的对象或者未申请访问受限的内存区域的指针
规避:(1)、初始化时置NULL;(2)、释放时置NULL;(3)、使用malloc分配内存
4.c语言分配内存的方式有哪些?
c语言中常见的内存错误有哪些?
内存分配的方式:
(1)、从静态存储区域分配。内存在程序编译的时候就已经分配好了,这块内存在程序整个运行期间都存在,例如全局变量;
(2)、在栈上创建。在执行函数时,函数内局部变量的存储单元都可以在栈上创建,函数执行结束时这些存储单元自动被释放,
栈内存分配运算内置于处理器的指令集中,效率高,凡是分配的内存容量有限。
(3)、从堆上分配。也称动态内存分配。有malloc、calloc、realloc和释放函数free。
5.Static全局变量与普通变量的区别?
区别:(1)static全局变量编译使初始化,在main()函数之前初始化并且仅初始化一次
(2)static全局变量限定了作用的范围,仅在定义该变量的源文件中有效,由于静态全局变量的作用域局限于一个源文件内,即
文件作用域,只能为该源文件内的函数公用,因此可以避免在其他源文件中引起错误。全局变量可以跨越多个源文件有效,当然,其他的
不包括全局变量定义的源文件需要用extern关键字再次声明这个全局变量。
Static局部变量与普通局部变量的区别?
(1)static局部变量只被初始化一次,自从第一次被初始化直到程序结束都一直存在。普通局部变量,只在函数被执行期间存在,函数的一次调用
执行结束后,其所占的空间被收回。
(2)静态局部变量在静态存储区分配空间,局部变量在栈里分配空间。
static函数与普通函数的区别?
普通函数的定义和声明默认情况下是extern的,但静态函数只是在声明他的文件当中可见,不能被其他的文件所用。
6.#include <> 和 #include “” 有什么区别?
尖括号表示这个文件是一个工程或标准的头文件,在预处理查找过程中会首先检查系统预定义的目录,如果没有找到就报错
双引号表明这是一个用户自定义的头文件,查找文件的时候会先在当前文件目录中查找,如果没有找到再去系统预定义的目录中查找,如果没有找到就报错。
7.char *const p; char const *p; const char *p 三者的区别。
char *const p 只能改变字符串的内容,不能改地址;
char const *p 只能改地址,但字符串的内容不能改;
const char *p 只能改地址,但不能改内容。
8.写一个 宏MIN,这个宏输入两个参数并返回较小的一个。
另外,当你写下面代码时会发生什么事? least = MIN(*p++,b);
#define MIN(x,y) ((x)<(y) ? (x):(y))
发现输出的是b的值。这是因为集合性的问题,先是p++到了下一个地址,然后显示这个地址的值,而这个地址的值我们没有分配,所以我们未知。
9.找出题中错误,并解释
void test1()
{
char string[10];
char* str1 = “0123456789”
strcpy(string, str1);
}
这题错在strcpy函数的前提是string这个字符型数组的空间要足够大,大到能全部放下str所指的字符串。
10.找出题中错误,并解释
void GetMemory( char *p )
{
p = (char *) malloc( 100 );
}
void Test( void )
{
char *str = NULL;
GetMemory( str );
strcpy( str, “hello world” );
printf("%s", str);
}
这道题错在没有吧str的地址传过去,也就是p没有定义成二级指针,所以这题只是给p分配了空间,而没有给str分配空间。
11: 输入一段字符串,无论是否有重复字母出现,都只打印出现过的小写字母,并按照小写字母顺序打印。
(如输入qewqwr322rqw<>211qESFSSEraZz, 打印aeqrwz)
/*****************************************************
copyright (C), 2014-2015, Lighting Studio. Co., Ltd.
File name:
Author:Jerey_Jobs Version:0.1 Date:
Description:
Funcion List:
*****************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
int Choose(char str[],char ptr[])
{
int i = 0;
int t = 0;
while(str[i] != '\0')
{
if(str[i] >= 'a' && str[i] <= 'z')
{
ptr[t] = str[i];
t++;
i++;
}
else
{
i++;
}
}
ptr[t] = '\0';
return t;
}
void Sort(char ptr[100],int t)
{
char mtr[100];
int m = 0,j = 0,i;
char temp;
for(j = 0; j < t - 1; j++)
{
m = j;
for(i = j + 1; i < t; i++)
{
if(ptr[m] > ptr[i])
{
m = i;
}
}
if(m != j)
{
temp = ptr[m];
ptr[m] = ptr[j];
ptr[j] = temp;
}
}
i = 0;
j = 0;
while(ptr[i] != '\0')
{
if(ptr[i] == ptr[i+1])
{
while(ptr[i] == ptr[i+1])
{
i++;
}
mtr[j++] = ptr[i];
}
else
{
mtr[j++] = ptr[i];
}
i++;
}
mtr[j] = '\0';
for(i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
printf("%c",mtr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
char str[100] = "\0";
char ptr[100] = "\0";
int t;
gets(str);
t = Choose(str,ptr);
Sort(ptr,t);
return 0;
}
结果:

12:输入某个月的第N周和这一周的第M天,通过int *GetDay() 函数获取参数并返回结果,来得出这一天是这个月的第多少天。
(如输入:3,4,即这个月的第3周的第4天,即这个月的第18天)
/*****************************************************
copyright (C), 2014-2015, Lighting Studio. Co., Ltd.
File name:
Author:Jerey_Jobs Version:0.1 Date:
Description:
Funcion List:
*****************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
int is_runyear(int year)
{
int flag;
if((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0) || year % 400 == 0)
{
flag = 1;
}
else
{
flag = 0;
}
}
int *Get_day(int week,int *day)
{
*day = week * 7 - (7 - *day);
return day;
}
int main()
{
int day,week;
int flag;
printf("Please input the day and week of the month:");
scanf("%d%d",&week,&day);
day = *Get_day(week,&day);
printf("这一天是这个月的第%d天\n",day);
return 0;
}
结果:
```
13:(1)建立一个顺序表,要求从键盘输入10个整数,并将该顺序表的元素从屏幕显示出来。
(2)用函数实现在顺序表中查找其中一个元素,如果找到,返回该元素在顺序表中的位置和该元素的值,否则提示无此元素。
(3)用函数实现顺序表的插入和删除操作。由用户输入待插入元素及插入位置,将完成插入后的顺序表输出;由用户输入删除第几个元素,将完成删除后的顺序表输出。
/*****************************************************
copyright ©, 2014-2015, Lighting Studio. Co., Ltd.
File name:
Author:Jerey_Jobs Version:0.1 Date:
Description:
Funcion List:
*****************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
void sort(int a[])
{
int i,j,k;
int temp;
for(i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
k = i;
for(j = i + 1; j < 10; j++)
{
if(a[k] > a[j])
{
k = j;
}
}
if(k != i)
{
temp = a[k];
a[k] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
}
}
}
void search_num(int a[],int n)
{
int i,k;
int flag;
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if(n == a[i])
{
flag = 1;
k = i;
}
}
if(flag == 1)
{
printf("位置=%d,数值=%d\n",k+1,a[k]);
}
else
{
printf("no found!\n");
}
}
void incret_num(int a[],int m,int loc)
{
int b[100];
int i,j = 0;
for(i = 0; i< 10; i++)
{
if(loc == i + 1)
{
b[j++] = m;
}
b[j++] = a[i];
}
for(i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
printf("%d\n",b[i]);
}
}
void delet_num(int a[],int doc)
{
int i,j = 0;
int c[10];
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if(doc == i + 1)
{
i++;
}
c[j++] = a[i];
}
for(i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
printf("%d\n",c[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[10];
int i,n;
int m,loc;
int doc;
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
sort(a);
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d\n",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("Please input you want to search number:");
scanf("%d",&n);
search_num(a,n);
printf("\n");
printf("请输入你要插入的元素和位置m,loc:");
scanf("%d%d",&m,&loc);
incret_num(a,m,loc);
printf("\n");
printf("Please input the dispion of you want to delet:");
scanf("%d",&doc);
delet_num(a,doc);
return 0;
}
结果:



链表练习
1、创立一个链表,要求实现插入节点时,边插边排序(用随机函数生成)
/*****************************************************
copyright ©, 2014-2015, Lighting Studio. Co., Ltd.
File name:
Author:Jerey_Jobs Version:0.1 Date:
Description:
Funcion List:
*****************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node Node;
typedef struct node * Link;
struct node
{
int num;
Link next;
};
void is_malloc_ok(Link new_node)
{
if(new_node == NULL)
{
printf(“malloc error!\n”);
exit(-1);
}
}
void creat_link(Link *head)
{
*head = NULL;
}
void creat_node(Link *new_node)
{
*new_node = (Link)malloc(sizeof(Node));
is_malloc_ok(*new_node);
}
void incret_node_sort(Link *head,Link new_node)
{
Link p,q;
q = p = *head;
if(*head == NULL)
{
*head = new_node;
new_node -> next = NULL;
}
else
{
if(p -> num > new_node -> num)
{
new_node -> next = p;
*head = new_node;
}
else
{
while(p != NULL && p -> num < new_node -> num)
{
q = p;
p = p -> next;
}
if(p == NULL)
{
q -> next = new_node;
new_node -> next = NULL;
}
else
{
q -> next = new_node;
new_node -> next = p;
}
}
}
}
void incret_num(Link *head,Link new_node)
{
Link p,q;
q = p = *head;
if(new_node -> num < (*head) -> num)
{
new_node -> next = *head;
*head = new_node;
}
else
{
while(p != NULL && p -> num < new_node -> num)
{
q = p;
p = p -> next;
}
q -> next = new_node;
new_node -> next = p;
}
}
void release_node(Link *head)
{
Link p;
p = *head;
while(*head != NULL)
{
*head = (*head) -> next;
free§;
p = *head;
}
}
void display_node(Link head)
{
Link p;
p = head;
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("The node is empty!\n");
return;
}
while(p != NULL)
{
printf("%d\n",p -> num);
p = p -> next;
}
}
int main()
{
Link head = NULL;
Link new_node = NULL;
int i;
int m;
creat_link(&head);
srand((unsigned int) time(NULL));
for(i = 0; i< 10; i++)
{
creat_node(&new_node);
new_node -> num = rand() % 100;
incret_node_sort(&head,new_node);
}
display_node(head);
printf("\n");
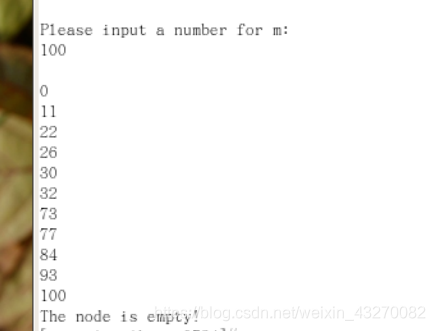
printf("Please input a number for m:\n");
scanf("%d",&m);
creat_node(&new_node);
new_node -> num = m;
incret_num(&head,new_node);
printf("\n");
display_node(head);
release_node(&head);
display_node(head);
return 0;
}
结果:

2、程序功能:建立一个带有头结点的单向链表,并将存储在数组中的字符依次转储到链表的各个结点中。
/*****************************************************
copyright ©, 2014-2015, Lighting Studio. Co., Ltd.
File name:
Author:Jerey_Jobs Version:0.1 Date:
Description:
Funcion List:
*****************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node Node;
typedef struct node * Link;
struct node
{
char str;
Link next;
};
void creat_link(Link *head)
{
*head = NULL;
}
void is_malloc_ok(Link new_node)
{
if(new_node == NULL)
{
printf(“malloc error!\n”);
exit(-1);
}
}
void creat_node(Link *new_node)
{
*new_node = (Link)malloc(sizeof(Node));
is_malloc_ok(*new_node);
}
void incret_node(Link *head,Link new_node)
{
Link p,q;
p = q = *head;
if(*head == NULL)
{
*head = new_node;
new_node -> next = NULL;
}
else
{
if(p -> str >= new_node -> str)
{
new_node -> next = p;
*head = new_node;
}
else
{
while(p != NULL && p -> str < new_node -> str)
{
q = p;
p = p -> next;
}
q -> next = new_node;
new_node -> next = p;
}
}
}
void release_node(Link *head)
{
Link p;
p = *head;
while(*head != NULL)
{
*head = (*head) -> next;
free(p);
p = *head;
}
}
void display_node(Link head)
{
Link p;
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("The node is empty!\n");
return;
}
while(p != NULL)
{
printf("%c\n",p -> str);
p = p -> next;
}
}
int main()
{
Link head = NULL;
Link new_node = NULL;
char a[100];
int i = 0;
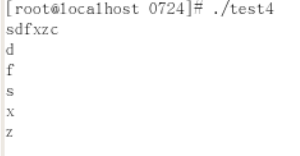
gets(a);
creat_link(&head);
while(a[i] != '\0')
{
creat_node(&new_node);
new_node -> str = a[i];
incret_node(&head,new_node);
i++;
}
display_node(head);
printf("\n");
release_node(&head);
display_node(head);
return 0;
}
结果:
3、编写程序STUDENT *Create(STUDENT studs[],int n)。STUDENT是一个结构类型,包含姓名、成绩和指针域。studs数组中存储了n个STUDENT记录。create函数的功能是根据studs数组建立一个链表,链表中结点按成绩降序排列,函数返回链表头指针。
/*****************************************************
copyright ©, 2014-2015, Lighting Studio. Co., Ltd.
File name:
Author:Jerey_Jobs Version:0.1 Date:
Description:
Funcion List:
*****************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node STUDENT;
typedef struct node * Link;
struct node
{
int score;
char name[10];
Link next;
};
void is_malloc_ok(Link new_node)
{
if(new_node == NULL)
{
printf(“malloc error!\n”);
exit(-1);
}
}
void creat_link(Link *head)
{
*head = NULL;
}
void creat_node(Link *new_node)
{
*new_node = (Link)malloc(sizeof(STUDENT));
is_malloc_ok(*new_node);
}
void incret_node(Link *head,Link new_node)
{
Link p,q;
q = p = *head;
if(*head == NULL)
{
new_node -> next = *head;
*head = new_node;
}
else
{
if(p -> score <= new_node -> score)
{
new_node -> next = p;
*head = new_node;
}
else
{
while(p != NULL && p -> score > new_node -> score)
{
q = p;
p = p -> next;
}
q -> next = new_node;
new_node -> next = p;
}
}
}
void release_node(Link *head)
{
Link p;
p = *head;
while(*head != NULL)
{
*head = (*head) -> next;
free(p);
p = *head;
}
}
void search_score(Link head,int m)
{
Link p;
p = head;
int i = 0;
while(p != NULL && p -> score != m)
{
i++;
p = p -> next;
}
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("没有找到!\n");
}
else
{
printf("姓名:%s 分数:%3d 名次:%d\n",p -> name,p -> score,i+1);
}
}
void display_node(Link head)
{
Link p;
p = head;
if(head == NULL)
{
printf(“The node is empty!\n”);
return;
}
while(p != NULL)
{
printf("分数:%3d 姓名:%s\n",p->score,p -> name);
p = p -> next;
}
}
int main()
{
Link head = NULL;
Link new_node = NULL;
int i,n,m;
creat_link(&head);
printf("请输入班级有多少学生n:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("\n");
printf("请输入学生成绩和姓名:");
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
creat_node(&new_node);
scanf("%d%s",&new_node->score,&new_node->name);
incret_node(&head,new_node);
}
printf("\n");
display_node(head);
printf("\n");
printf("请输入要查找的分数:");
scanf("%d",&m);
search_score(head,m);
release_node(&head);
display_node(head);
return 0;
}
结果:






















 5796
5796

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








