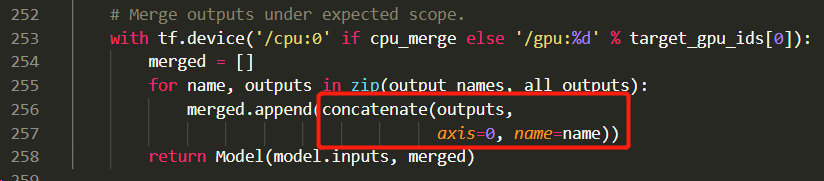
qqwweee/keras-yolo3提供的版本代码没有多GPU选项,因为网络的输出是一个loss,使用keras提供的multi_gpu_model函数时会报错,因为multi_gpu_model的原理是将一个batch的数据划分到多个GPU上同时运行,最后将所有GPU的张量拼接起来,下面是官方multi_gpu_model函数的源代码,可以看到最后汇总多个GPU的结果使用了concatenate函数,axis=0,即沿纵轴把输出张量拼接,而现在yolov3的输出是一个loss,拼接自然会报错。
我们想要的是这个batch的loss,因此只需要将所有GPU的输出(loss)全部加起来求平均即可,所以我们需要把concatenate修改为add,如下,当然还有一些其它细节
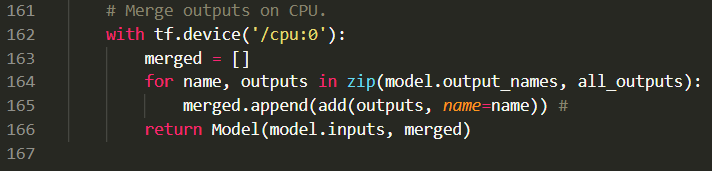
这里给出一份overwrite multi_gpu_model函数的代码,参考自
import keras.backend as K
import tensorflow as tf
from keras.layers import Lambda, add
from keras.models import Model
def _normalize_device_name(name):
name = '/' + ':'.join(name.lower().replace('/', '').split(':')[-2:])
return name
def _get_available_devices():
return [x.name for x in K.get_session().list_devices()]
def multi_gpu_model(model, gpus=None):
"""Replicates a model on different GPUs.
Specifically, this function implements single-machine
multi-GPU data parallelism. It works in the following way:
- Divide the model's input(s) into multiple sub-batches.
- Apply a model copy on each sub-batch. Every model copy
is executed on a dedicated GPU.
- Concatenate the results (on CPU) into one big batch.
E.g. if your `batch_size` is 64 and you use `gpus=2`,
then we will divide the input into 2 sub-batches of 32 samples,
process each sub-batch on one GPU, then return the full
batch of 64 processed samples.
This induces quasi-linear speedup on up to 8 GPUs.
This function is only available with the TensorFlow backend
for the time being.
# Arguments
model: A Keras model instance. To avoid OOM errors,
this model could have been built on CPU, for instance
(see usage example below).
gpus: Integer >= 2 or list of integers, number of GPUs or
list of GPU IDs on which to create model replicas.
# Returns
A Keras `Model` instance which can be used just like the initial
`model` argument, but which distributes its workload on multiple GPUs.
# Example
```python
import tensorflow as tf
from keras.applications import Xception
from keras.utils import multi_gpu_model
import numpy as np
num_samples = 1000
height = 224
width = 224
num_classes = 1000
# Instantiate the base model (or "template" model).
# We recommend doing this with under a CPU device scope,
# so that the model's weights are hosted on CPU memory.
# Otherwise they may end up hosted on a GPU, which would
# complicate weight sharing.
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
model = Xception(weights=None,
input_shape=(height, width, 3),
classes=num_classes)
# Replicates the model on 8 GPUs.
# This assumes that your machine has 8 available GPUs.
parallel_model = multi_gpu_model(model, gpus=8)
parallel_model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer='rmsprop')
# Generate dummy data.
x = np.random.random((num_samples, height, width, 3))
y = np.random.random((num_samples, num_classes))
# This `fit` call will be distributed on 8 GPUs.
# Since the batch size is 256, each GPU will process 32 samples.
parallel_model.fit(x, y, epochs=20, batch_size=256)
# Save model via the template model (which shares the same weights):
model.save('my_model.h5')
```
# On model saving
To save the multi-gpu model, use `.save(fname)` or `.save_weights(fname)`
with the template model (the argument you passed to `multi_gpu_model`),
rather than the model returned by `multi_gpu_model`.
"""
if K.backend() != 'tensorflow':
raise ValueError('`multi_gpu_model` is only available '
'with the TensorFlow backend.')
available_devices = _get_available_devices()
available_devices = [_normalize_device_name(
name) for name in available_devices]
if not gpus:
# Using all visible GPUs when not specifying `gpus`
# e.g. CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,2 python3 keras_mgpu.py
gpus = len([x for x in available_devices if 'gpu' in x])
if isinstance(gpus, (list, tuple)):
if len(gpus) <= 1:
raise ValueError('For multi-gpu usage to be effective, '
'call `multi_gpu_model` with `len(gpus) >= 2`. '
'Received: `gpus=%s`' % gpus)
num_gpus = len(gpus)
target_gpu_ids = gpus
else:
if gpus <= 1:
raise ValueError('For multi-gpu usage to be effective, '
'call `multi_gpu_model` with `gpus >= 2`. '
'Received: `gpus=%d`' % gpus)
num_gpus = gpus
target_gpu_ids = range(num_gpus)
import tensorflow as tf
target_devices = ['/cpu:0'] + ['/gpu:%d' % i for i in target_gpu_ids]
for device in target_devices:
if device not in available_devices:
raise ValueError(
'To call `multi_gpu_model` with `gpus=%d`, '
'we expect the following devices to be available: %s. '
'However this machine only has: %s. '
'Try reducing `gpus`.' % (gpus,
target_devices,
available_devices))
def get_slice(data, i, parts):
shape = tf.shape(data)
batch_size = shape[:1]
input_shape = shape[1:]
step = batch_size // parts
if i == num_gpus - 1:
size = batch_size - step * i
else:
size = step
size = tf.concat([size, input_shape], axis=0)
stride = tf.concat([step, input_shape * 0], axis=0)
start = stride * i
return tf.slice(data, start, size)
all_outputs = []
for i in range(len(model.outputs)):
all_outputs.append([])
# Place a copy of the model on each GPU,
# each getting a slice of the inputs.
for i, gpu_id in enumerate(target_gpu_ids):
with tf.device('/gpu:%d' % gpu_id):
with tf.name_scope('replica_%d' % gpu_id):
inputs = []
# Retrieve a slice of the input.
for x in model.inputs:
input_shape = tuple(x.get_shape().as_list())[1:]
slice_i = Lambda(get_slice,
output_shape=input_shape,
arguments={'i': i,
'parts': num_gpus})(x)
inputs.append(slice_i)
# Apply model on slice
# (creating a model replica on the target device).
outputs = model(inputs)
if not isinstance(outputs, list):
outputs = [outputs]
# Save the outputs for merging back together later.
for o in range(len(outputs)):
all_outputs[o].append(outputs[o])
# Merge outputs on CPU.
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
merged = []
for name, outputs in zip(model.output_names, all_outputs):
merged.append(add(outputs, name=name)) #
return Model(model.inputs, merged)
可以将这份代码作为一个单独的文件,在主函数中import进来,就可以像普通网络模型一样多GPU训练了。






















 6926
6926











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








