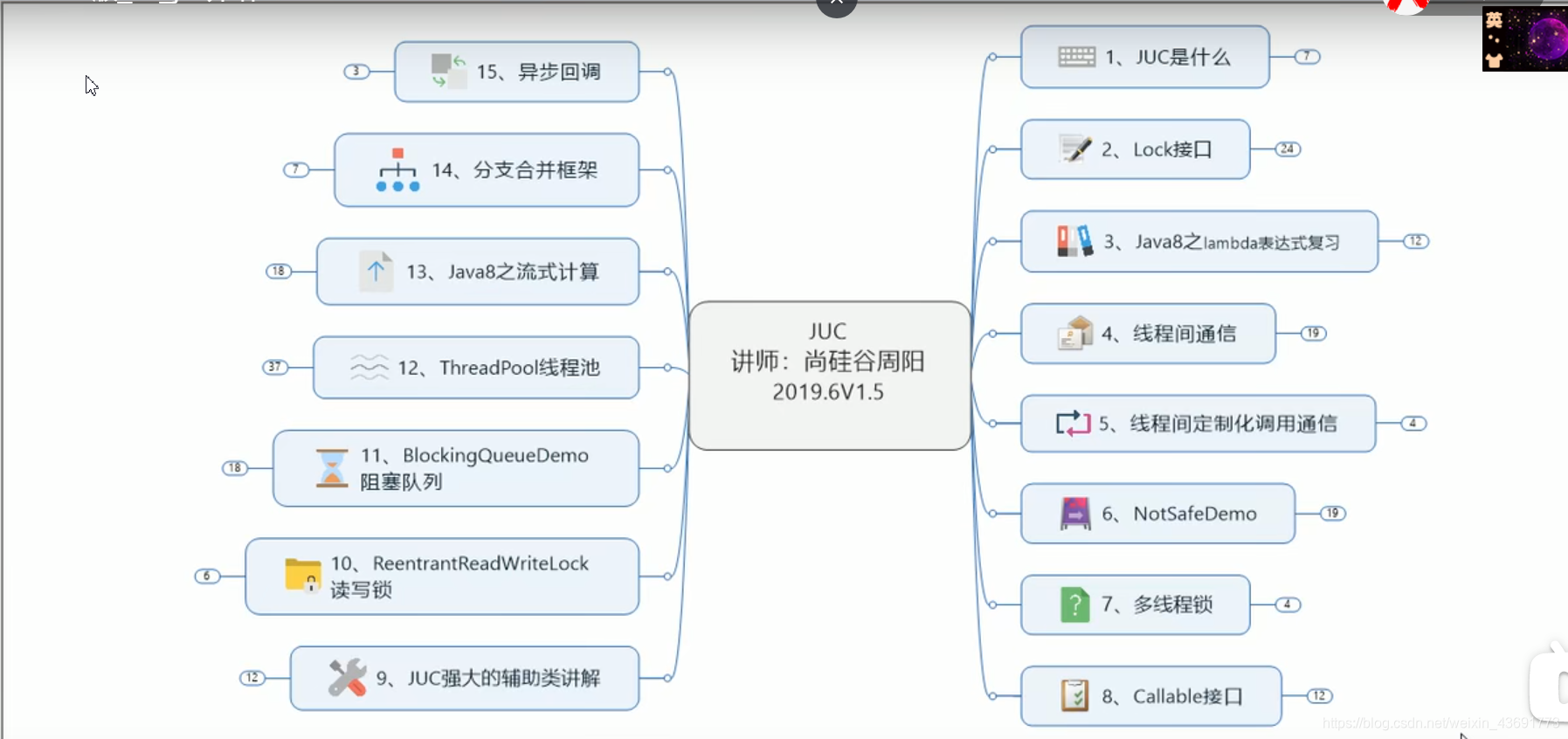
这里写目录标题
- 一 JUC 介绍
- 二 卖票算法的企业级模板实现
- 三 Lambda Expression 快速复习
- 四 浅谈java8接口的变化
- 四 线程间的通信
- 五 多线程8锁的现象和解释
- 六 List不安全
- 六 Set不安全
- 七 Map线程不安全
- 八 Callable
- 九 JUC强大的辅助类
- 十 ReentrantReadWriteLock 读写锁
- 十一 BlockingQueueDemo 阻塞队列
- 十二 线程池
- 十三 四大函数式接口
- 十四 Java8Stream流式计算
- 十五 分支合并框架ForkJoin
- 十五 异步回调CompletableFuture
一 JUC 介绍
1 进程线程介绍介绍
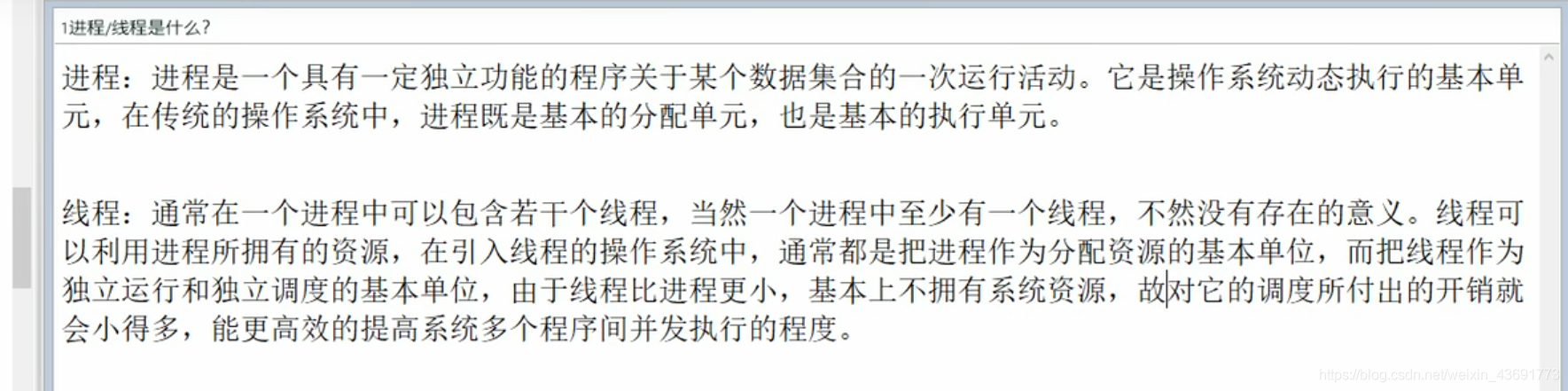
进程 : 后台运行的一个程序就是一个进程 比如 运行IDEA程序
线程 : 进捏的组成部分 如 IDEA进程内的语法检查功能 就是一个线程
2 并发并行的介绍
并发(concurrent)同一时刻多个线程在访问同一个资源,多个线程对一个点
例子:小米9今天上午10点,限量抢购
春运抢票
电商秒杀…
并行 多项工作一起执行,之后再汇总
例子:泡方便面,电水壶烧水,一边撕调料倒入桶中
3 wait 和 sleep的区别
wait放开手去睡,放开手里的锁
sleep握紧手去睡,醒了手里还有锁
4 线程的状态
NEW,(新建)
RUNNABLE,(准备就绪)
BLOCKED,(阻塞)
WAITING,(不见不散)没定时间
TIMED_WAITING,(过时不候) 定了时间
TERMINATED;(终结)
二 卖票算法的企业级模板实现
企业级简单实现(synchronized)
没有像以往的那样使用接口 使类0污染比较干净
package com.luyi.demo;
/**
* 卖票 企业级套路 + 模板
* 1. 在高内聚低耦合的前提下: 线程 操作(对外暴露的调用方法) 资源类
* 高内聚: 资源类对外暴露的功能只在自己身上实现 低耦合: 调用者和 资源类之间并无关系
* @author 卢意
* @create 2021-01-10 9:42
*/
public class SaleTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 资源类
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
// 线程 Thread(Runnable target, String ThreadName)
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 30 ; i++) {
ticket.saleTicket();
}
}
}, "售票员A").start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 30 ; i++) {
ticket.saleTicket();
}
}
}, "售票员B").start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 30 ; i++) {
ticket.saleTicket();
}
}
}, "售票员C").start();
}
}
// 资源类
class Ticket {
private int number = 30;
// 操作
public synchronized void saleTicket(){
if(number > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t卖出第" + (number--) + "\t 还剩下:" + number);
}
}
}
juc优化卖票
进一步优化锁的粒度
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
class Ticket {
private int number = 30;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();// 可重入锁
// 操作
public void saleTicket(){
lock.lock();
try {
if(number > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t卖出第" + (number--) + "\t 还剩下:" + number);
}
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
lambda优化
package com.luyi.demo;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 卖票 企业级套路 + 模板
* 1. 在高内聚低耦合的前提下: 线程 操作(对外暴露的调用方法) 资源类
* 高内聚: 资源类对外暴露的功能只在自己身上实现 低耦合: 调用者和 资源类之间并无关系
* @author 卢意
* @create 2021-01-10 9:42
*/
public class SaleTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 资源类
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
// 线程 Thread(Runnable target, String ThreadName)
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i <= 30 ; i++) ticket.saleTicket(); }, "售票员A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i <= 30 ; i++) ticket.saleTicket(); }, "售票员B").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i <= 30 ; i++) ticket.saleTicket(); }, "售票员C").start();
}
}
// 资源类
class Ticket {
private int number = 30;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();// 可重入锁
// 操作
public void saleTicket(){
lock.lock();
try {
if(number > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t卖出第" + (number--) + "\t 还剩下:" + number);
}
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
三 Lambda Expression 快速复习
接口内如果只有一个声明的方法 就是函数式接口@FunctionalInterface(只有一个方法 默认加上)
interface Foo {
public void sayHello();
}
在函数式接口的情况下
口诀
拷贝小括号(复制小括号的内容) 写死右箭头 落地大箭头 () -> {}Foo foo = () -> System.out.println(“Hello”);
有参数方法
interface Foo {
public int add(int x, int y);
}
Foo foo = (int x, int y) -> {
System.out.println(“add method”);
return x + y;
};
System.out.println(foo.add(1, 2));
// add method
// 3
甚至可以去除参数的类型
Foo foo = (x, y) -> {
System.out.println(“add method”);
return x + y;
};
四 浅谈java8接口的变化
java8以后允许接口内定义接口的实现
interface Foo {
public int add(int x, int y);
default int div(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
default int div2(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
}
上面的接口还是算一个函数式接口
我们可以知道 default影响函数式接口的定义
接口支持静态方法
interface Foo {
public int add(int x, int y);
default int div(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
default int div2(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
public static int div3(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
}
四 线程间的通信
线程间的横向交互
线程的生产者消费者(synchronized)
package com.luyi.demo;
/**
* 两个线程操作一个变量 一个线程让他加一 一个线程让他减一
* 实现交替操作 10轮 让这个变量的结果还是为0
* 1. 高内聚低耦合的前提下, 线程 操作 资源类
* 2. 判断 干活 通知
* @author 卢意
* @create 2021-01-10 15:16
*/
public class ThreadWaitNotifyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AirConditioner airConditioner = new AirConditioner();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
}
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
airConditioner.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "加一线程").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
airConditioner.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "减一线程").start();
}
}
// 资源类
class AirConditioner{
private int number = 0;
public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {
// 判断
if(number != 0) {
this.wait();
}
// 干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);
// 通知
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
// 判断
if (number == 0) {
this.wait();
}
// 干活
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 863
863











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








