一 前言
回顾一下:自定义View的时候,根据不同条件设置不同颜色,那么需要提供对外的方法设置颜色。而View可以在xml里引用,我们想当然的认为是否能够在xml里根据不同条件设置颜色属性呢?这样的话就很灵活了。当然,Android系统已经为我们准备好了,接下来我们来分析其解析原理及其使用。
通过本篇文章,你将了解到:
- 1、自定义属性基础明晰
- 2、自定义属性使用
- 3、attr/style/theme联系与区别
- 4、自定义属性加载优先级
- 5、自定义属性加载源码分析
二 自定义属性基础明晰
attrs.xml
注 为表述方便,以下的"属性声明" 指的是该属性声明了但没有赋值;而"属性定义”指的是该属性被使用,也即被赋值了。
在res->values目录下新建attrs.xml文件,该文件用来声明属性名及其接受的数据格式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<attr name="attr_str" format="string"></attr>
<attr name="attr_bool" format="boolean"></attr>
<attr name="attr_int" format="integer"></attr>
<attr name="attr_ref" format="reference"></attr>
</resources>
其中 name表示属性名,format表示其接受的输入格式。
以上声明了三个属性,分别代表string、boolean、integer、reference格式。reference指向其它资源。
format还有其它格式,如:
1. reference:参考某一资源ID。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "background" format = "reference" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<ImageView
Android:layout_width = "42dip"
android:layout_height = "42dip"
android:background = "@drawable/图片ID"
/>
2. color:颜色值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "textColor" format = "color" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<TextView
android:layout_width = "42dip"
android:layout_height = "42dip"
android:textColor = "#00FF00"
/>
3. boolean:布尔值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "focusable" format = "boolean" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<Button
android:layout_width = "42dip"
android:layout_height = "42dip"
android:focusable = "true"
/>
4. dimension:尺寸值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "layout_width" format = "dimension" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<Button
android:layout_width = "42dip"
android:layout_height = "42dip"
/>
5. float:浮点值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "AlphaAnimation">
<attr name = "fromAlpha" format = "float" />
<attr name = "toAlpha" format = "float" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<alpha
android:fromAlpha = "1.0"
android:toAlpha = "0.7"
/>
6. integer:整型值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "AnimatedRotateDrawable">
<attr name = "visible" />
<attr name = "frameDuration" format="integer" />
<attr name = "framesCount" format="integer" />
<attr name = "pivotX" />
<attr name = "pivotY" />
<attr name = "drawable" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<animated-rotate
xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:drawable = "@drawable/图片ID"
android:pivotX = "50%"
android:pivotY = "50%"
android:framesCount = "12"
android:frameDuration = "100"
/>
7. string:字符串。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "MapView">
<attr name = "apiKey" format = "string" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<com.google.android.maps.MapView
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:apiKey = "0jOkQ80oD1JL9C6HAja99uGXCRiS2CGjKO_bc_g"
/>
8. fraction:百分数。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name="RotateDrawable">
<attr name = "visible" />
<attr name = "fromDegrees" format = "float" />
<attr name = "toDegrees" format = "float" />
<attr name = "pivotX" format = "fraction" />
<attr name = "pivotY" format = "fraction" />
<attr name = "drawable" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<rotate xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:interpolator = "@anim/动画ID"
android:fromDegrees = "0"
android:toDegrees = "360"
android:pivotX = "200%"
android:pivotY = "300%"
android:duration = "5000"
android:repeatMode = "restart"
android:repeatCount = "infinite"
/>
9. enum:枚举值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name="名称">
<attr name="orientation">
<enum name="horizontal" value="0" />
<enum name="vertical" value="1" />
</attr>
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
>
</LinearLayout>
10. flag:位或运算。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name="名称">
<attr name="windowSoftInputMode">
<flag name = "stateUnspecified" value = "0" />
<flag name = "stateUnchanged" value = "1" />
<flag name = "stateHidden" value = "2" />
<flag name = "stateAlwaysHidden" value = "3" />
<flag name = "stateVisible" value = "4" />
<flag name = "stateAlwaysVisible" value = "5" />
<flag name = "adjustUnspecified" value = "0x00" />
<flag name = "adjustResize" value = "0x10" />
<flag name = "adjustPan" value = "0x20" />
<flag name = "adjustNothing" value = "0x30" />
</attr>
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<activity
android:name = ".StyleAndThemeActivity"
android:label = "@string/app_name"
android:windowSoftInputMode = "stateUnspecified | stateUnchanged | stateHidden">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name = "android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name = "android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
注意:
属性定义时可以指定多种类型值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "background" format = "reference|color" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<ImageView
android:layout_width = "42dip"
android:layout_height = "42dip"
android:background = "@drawable/图片ID|#00FF00"
/>
三 自定义属性使用TypedArray
依旧在attrs.xml里改造:
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="MyStyleable">
<attr name="attr_str" format="string"></attr>
<attr name="attr_bool" format="boolean"></attr>
<attr name="attr_int" format="integer"></attr>
<attr name="attr_ref" format="reference"></attr>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
相比我们刚开始声明的属性而言,增加了“declare-styleable”标签,意思是将若干个属性声明归结到MyStyleable里,这些属性声明属于"同一组"。declare-styleable 的name默认提示与自定义View的类名一致,但不是必须的。
再来看看如何解析这些属性。
public MyAttrView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
//R.styleable.MyStyleable 指的是想要解析的属性
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyStyleable);
//count 表示解析出来的个数
int count = typedArray.getIndexCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
int indexValue = typedArray.getIndex(i);
//通过属性index找到属性值
switch (indexValue) {
case R.styleable.MyStyleable_attr_str:
String strValue = typedArray.getString(indexValue);
Log.d(TAG, "str value:" + strValue);
break;
case R.styleable.MyStyleable_attr_bool:
boolean boolValue = typedArray.getBoolean(indexValue, false);
Log.d(TAG, "bool value:" + boolValue);
break;
case R.styleable.MyStyleable_attr_int:
int intValue = typedArray.getInt(indexValue, 0);
Log.d(TAG, "int value:" + intValue);
break;
case R.styleable.MyStyleable_attr_ref:
float refValue = typedArray.getDimension(indexValue, 0);
Log.d(TAG, "float value:" + refValue);
break;
}
}
//typedArray 存放在缓存池,因此用完归还到缓存池
typedArray.recycle();
}
运行效果如下:
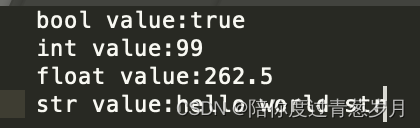
看得出来,尺寸的结果已经转换为实际值了。
重点方法如下:
context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyStyleable)
public final TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(
@Nullable AttributeSet set, @NonNull @StyleableRes int[] attrs) {
return getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(set, attrs, 0, 0);
}
两个参数:
AttributeSet set :当前xml声明的属性集合
int[] attrs :想要取得属性值的属性名集合
可以看出R.styleable.MyStyleable实际上就是个整形数组。与res目录下的其它资源类似,其索引在编译时期生成在R.java里。
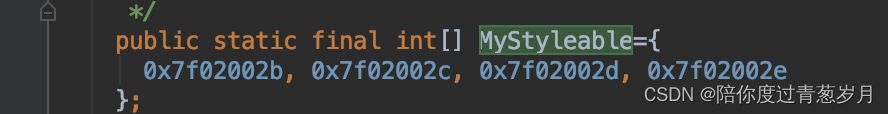
数组里的元素值就是MyStyleable声明里的属性索引,同样的在R.java里找到其索引: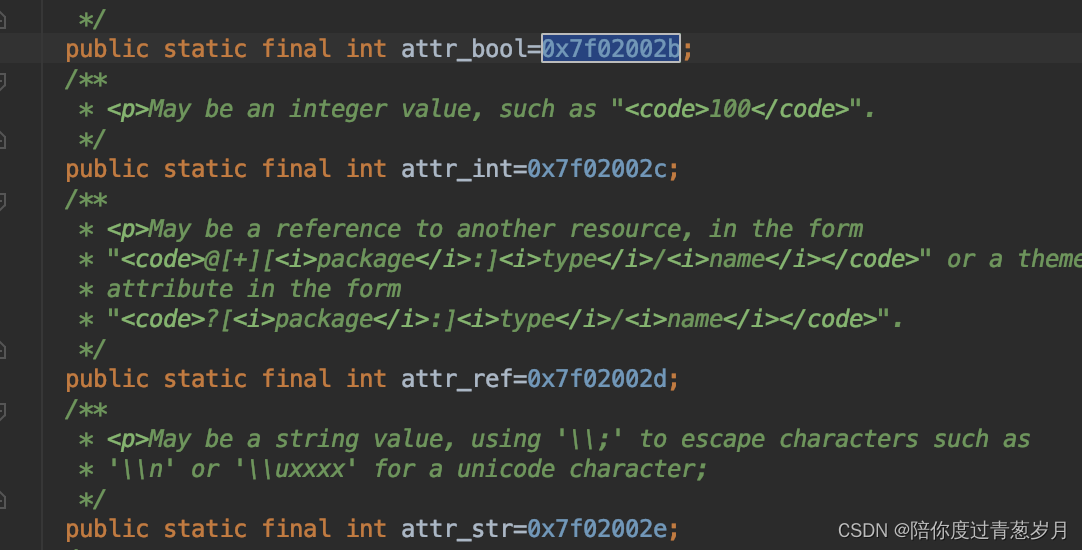 可以看出,R.styleable.MyStyleable就是我们想要解析的属性名集合。
可以看出,R.styleable.MyStyleable就是我们想要解析的属性名集合。
AttributeSet set 与 int attrs[]关系:
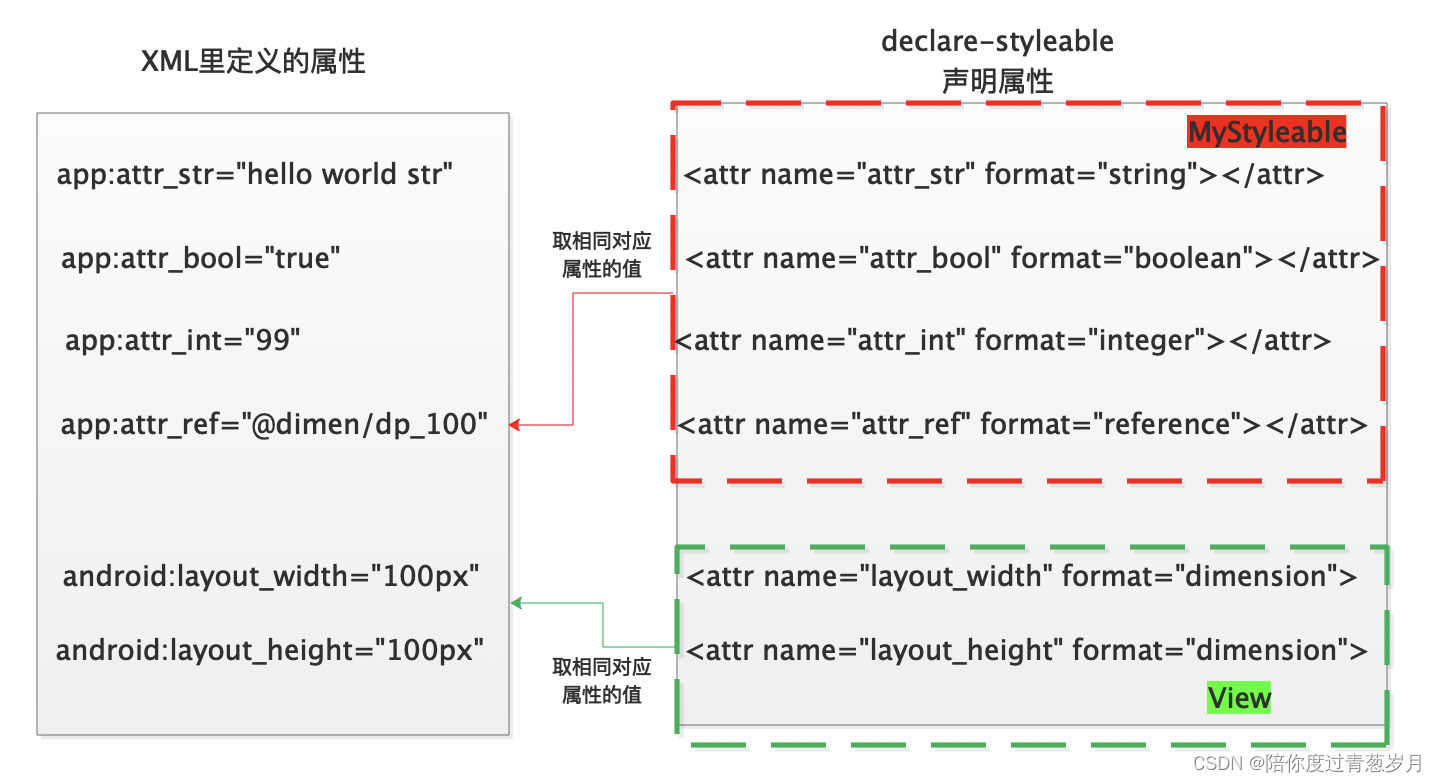
obtainStyledAttributes 方法返回值类型:TypedArray。该类型记录了获取到的属性值集合(记录在数组里),而通过数组下标索引即可找到对应的属性值。索引下标通过R.styleable.MyStyleable_xx获取,“xx"表示属性名,一般命名为"styleable名” + “_” + “属性名”。同样的,这些值也记录在R.java里: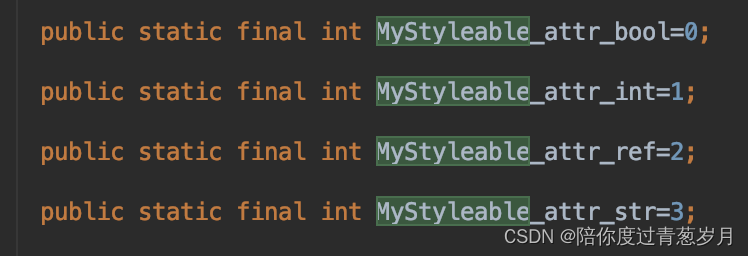
在R.java里
- MyStyleable_attr_bool 代表数组索引下标
- MyStyleable 代表属性数组
- attr_bool 代表属性
总结来说:通过下标取数组里属性
四 attr/style/theme联系与区别
4.1 style 由来与作用
在res->values目录下,找到styles.xml文件(没有则新建):
<resources>
<style name="myStyle">
<item name="attr_str">str in myStyle</item>
<item name="attr_bool">true</item>
</style>
</resources>
可以看出style批量定义了一批属性。这样做的好处显而易见:利于复用属性集合。
比如我们自定义的MyAttrView作为公共控件使用:
<com.fish.myapplication.attr.MyAttrView
app:attr_str="hello world str"
app:attr_bool="true"
android:layout_width="100px"
android:layout_height="100px">
</com.fish.myapplication.attr.MyAttrView>
使用的属性值都是一样的,那么可以将这些属性提取出来作为一个style项,在引用的时候引用style即可,不用到处重复定义属性。
<com.fish.myapplication.attr.MyAttrView
style="@style/myStyle"
android:layout_width="100px"
android:layout_height="100px">
</com.fish.myapplication.attr.MyAttrView>
4.2 theme 由来与作用
在res->values目录下,找到themes.xml文件(没有则新建)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<style name="myTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar">
<item name="attr_str">str in myTheme</item>
<item name="attr_bool">true</item>
</style>
</resources>
theme实际上也是用了style语法,parent表示其父类主题,子类继承父类属性。theme如何使用呢?
之前说过style为了View之间复用属性集,那么theme是为了Activity/Application复用属性集。因此,我们将theme配置给Activity或者Application。
可以看出引用theme是通过style引用的,因此我们可以直接将style条目作为theme使用,只是一般为了直观定义了themes.xml文件,该文件里的style作为theme使用。
总结来说三者关系:
- style 是定义属性的集合,使用style标签,作用于View
- theme 是定义属性的集合,使用style标签,作用于Application/Activity
- declare-styleable 是声明属性的集合,使用declare-styleable标签
五 自定义属性加载优先级
通过上述分析,定义属性的方式目前看来有以下3种:
1、在布局文件里定义属性
2、在style里定义属性
3、在theme里定义属性
再重新来看看obtainStyledAttributes(xx)方法:
public final TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(
@Nullable AttributeSet set, @NonNull @StyleableRes int[] attrs) {
return getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(set, attrs, 0, 0);
}
public TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(@Nullable AttributeSet set,
@NonNull @StyleableRes int[] attrs, @AttrRes int defStyleAttr,
@StyleRes int defStyleRes) {
return mThemeImpl.obtainStyledAttributes(this, set, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
第二个方法有4个参数,前面两个前面分析过,来看看后边两个:
@AttrRes int defStyleAttr 形参限制为AttrRes,说明是属性类型
@StyleRes int defStyleRes 形参限制为StyleRes,说明是style类型
从形参名字来看,显然是默认的属性与默认的style。
由此看出,obtainStyledAttributes(xx)方法负责解析了来自5个地方的属性:
- 1、在布局文件里定义属性
- 2、在style里定义属性
- 3、在theme里定义属性
- 4、默认的属性
- 5、默认的style
问题来了:如果上述5个来处都定义了同一个属性,那么该以哪个属性值为准呢?在真相尚未揭开之前,用最基本的方法,一一测试来看规律。
首先先将各个属性来处定义,以"attr_str"属性为例:
1、在布局里定义属性并使用:
#layout.xml 定义并使用
<com.fish.myapplication.attr.MyAttrView
app:attr_str="str in myLayout"
android:layout_width="100px"
android:layout_height="100px">
</com.fish.myapplication.attr.MyAttrView>
2、在style定义属性并使用:
#styles.xml 定义
<style name="myStyle">
<item name="attr_str">str in myStyle</item>
</style>
#layout.xml 里使用style
<com.fish.myapplication.attr.MyAttrView
style="@style/myStyle"
android:layout_width="100px"
android:layout_height="100px">
</com.fish.myapplication.attr.MyAttrView>
3、使用默认属性:
#themes.xml定义
#attr_ref 是引用类型的属性,这里指向style
<style name="myTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar">
<item name="attr_ref">@style/myDefaultAttr</item>
</style>
#styles.xml
<style name="myDefaultAttr">
<item name="attr_str">str in myDefaultAttr</item>
</style>
#MyAttrView.java 里解析 传入R.attr.attr_ref,最终找到myDefaultAttr里的attr_str属性
context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyStyleable, R.attr.attr_ref, 0);
4、使用默认style:
#在styles.xml里定义
<style name="myDefaultStyle">
<item name="attr_str">str in myDefaultStyle</item>
</style>
#MyAttrView.java 里解析 传入R.style.myDefaultStyle,最终找到myDefaultStyle里的attr_str属性
context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyStyleable, 0, R.style.myDefaultStyle);
5、使用theme里定义的属性:
#themes.xml里定义
<style name="myTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar">
<item name="attr_str">str in myTheme</item>
</style>
context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyStyleable, 0, 0);
为了区分属性值取自哪,我们在不同的地方打印了相应的关键字。上面定义了
1~ 5个不同来处的属性,现在倒序从5 ~ 1依次添加这些属性定义。使用TypedArray解析出属性值:
public MyAttrView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
//R.styleable.MyStyleable 指的是想要解析的属性
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, null, 0, R.style.myDefaultStyle);
//count 表示解析出来的个数
int count = typedArray.getIndexCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
int indexValue = typedArray.getIndex(i);
//通过属性index找到属性值
switch (indexValue) {
case R.styleable.MyStyleable_attr_str:
String strValue = typedArray.getString(indexValue);
Log.d(TAG, "str value:" + strValue);
break;
}
}
typedArray.recycle();
}
五次运行结果如下:
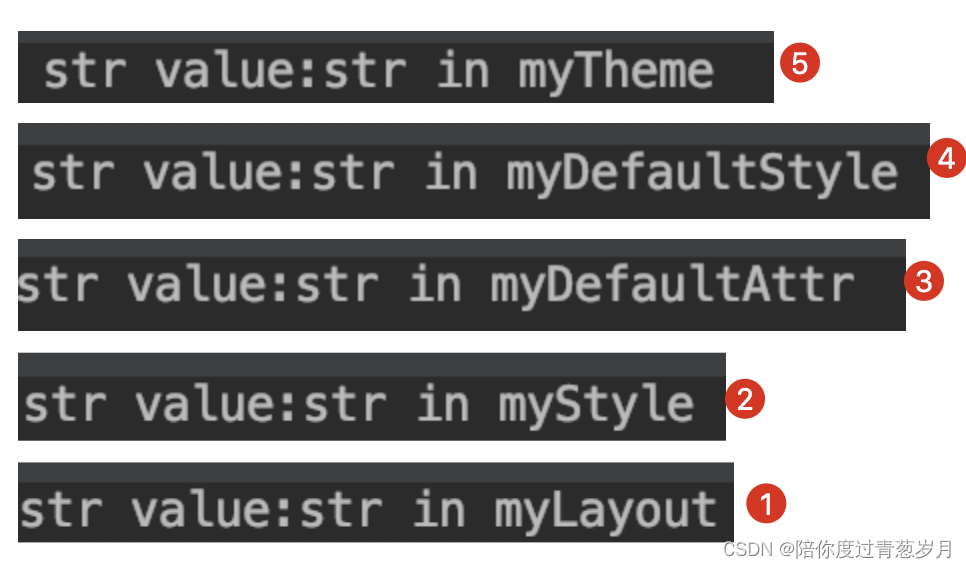
我们依次添加的属性定义,后面添加的将前面覆盖了,说明后面添加的优先级更高,因此总结来说,自定义属性优先级自高到低是:
- 1、在布局文件里定义属性
- 2、在style里定义属性
- 3、在theme里定义属性
- 4、默认的属性
- 5、默认的style
自定义属性加载源码分析
虽然以上通过测试说明了属性是如何解析及其解析的优先级,但是为了更好地理解其实际运作过程,我们需要分析源码。从TypedArray和obtainStyledAttributes(xx)方法入手。
来看看obtainStyledAttributes(xx)调用流程: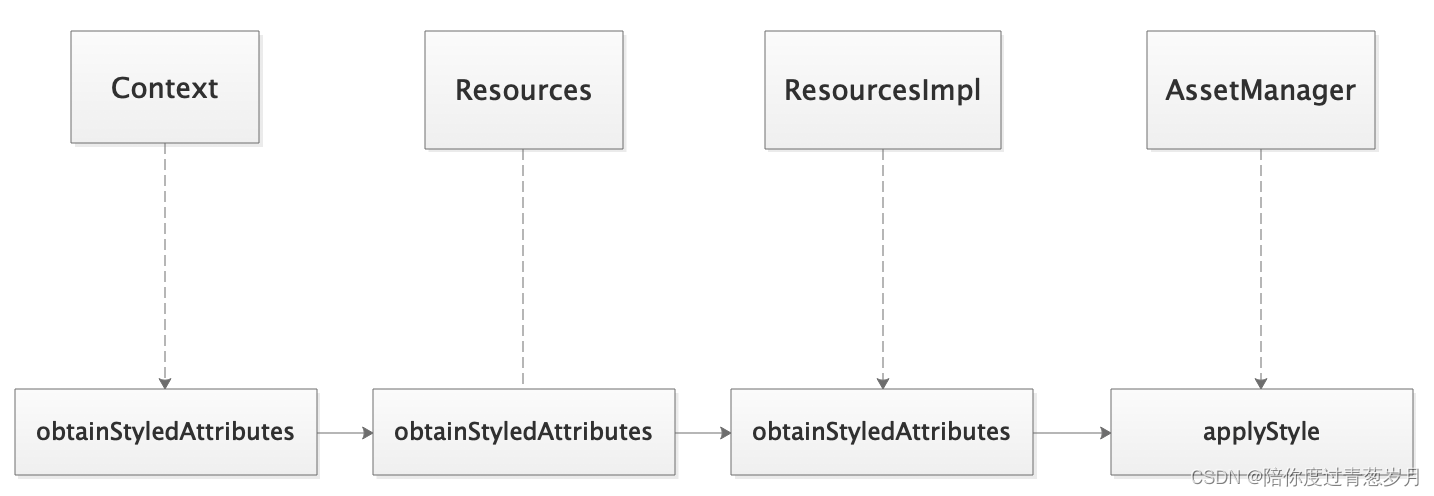
applyStyle调用了native方法:
nativeApplyStyle(mObject, themePtr, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes,
parser != null ? parser.mParseState : 0, inAttrs, outValuesAddress,
outIndicesAddress);
注意到最后两个参数,分别对应TypedArray两个参数:
outValuesAddress --> int[] mData;
outIndicesAddress --> int[] mIndices最终调用了AttributeResolution.cpp 的ApplyStyle(xx)方法:
void ApplyStyle(Theme* theme, ResXMLParser* xml_parser, uint32_t def_style_attr,
uint32_t def_style_resid, const uint32_t* attrs, size_t attrs_length,
uint32_t* out_values, uint32_t* out_indices) {
//省略...
int indices_idx = 0;
uint32_t def_style_flags = 0u;
//如果传入了默认属性
if (def_style_attr != 0) {
Res_value value;
//加载默认属性
if (theme->GetAttribute(def_style_attr, &value, &def_style_flags) != kInvalidCookie) {
if (value.dataType == Res_value::TYPE_REFERENCE) {
//并将值赋值给默认style,可以看出默认属性优先级高于默认style
def_style_resid = value.data;
}
}
}
//遍历属性名集合,也就是declare-styleable 声明的属性集合
for (size_t ii = 0; ii < attrs_length; ii++) {
//1、先加载XM里定义的属性
if (xml_attr_idx != xml_attr_finder.end()) {
// We found the attribute we were looking for.
xml_parser->getAttributeValue(xml_attr_idx, &value);
}
if (value.dataType == Res_value::TYPE_NULL && value.data != Res_value::DATA_NULL_EMPTY) {
//2、上一步如果没找到,继续在xml里的style里找
if (entry != xml_style_attr_finder.end()) {
// We found the attribute we were looking for.
cookie = entry->cookie;
type_set_flags = style_flags;
value = entry->value;
value_source_resid = entry->style;
}
}
if (value.dataType == Res_value::TYPE_NULL && value.data != Res_value::DATA_NULL_EMPTY) {
//3、还是没找到,找默认style
//这里需要注意的是,上面用默认attr赋值给默认style,因此如果attr不为空,那么先加载了attr
//如果为空,那么加载默认style
if (entry != def_style_attr_finder.end()) {
cookie = entry->cookie;
type_set_flags = def_style_flags;
value = entry->value;
}
}
if (value.dataType != Res_value::TYPE_NULL) {
//省略
} else if (value.data != Res_value::DATA_NULL_EMPTY) {
ApkAssetsCookie new_cookie = theme->GetAttribute(cur_ident, &value, &type_set_flags);
if (new_cookie != kInvalidCookie) {
//4、前面步骤都找不到,最后尝试加载theme里的属性
new_cookie =
assetmanager->ResolveReference(new_cookie, &value, &config, &type_set_flags, &resid);
if (new_cookie != kInvalidCookie) {
cookie = new_cookie;
}
}
}
//out_values存放类型、属性值,资源id,密度等
out_values[STYLE_TYPE] = value.dataType;
out_values[STYLE_DATA] = value.data;
out_values[STYLE_ASSET_COOKIE] = ApkAssetsCookieToJavaCookie(cookie);
out_values[STYLE_RESOURCE_ID] = resid;
out_values[STYLE_CHANGING_CONFIGURATIONS] = type_set_flags;
out_values[STYLE_DENSITY] = config.density;
out_values[STYLE_SOURCE_RESOURCE_ID] = value_source_resid;
if (value.dataType != Res_value::TYPE_NULL || value.data == Res_value::DATA_NULL_EMPTY) {
indices_idx++;
//记录数组的值,ii即为属性名的
out_indices[indices_idx] = ii;
}
//步长,out_values存放属性值,类型等,因此需要步长来区分某个属性存放块的开始
out_values += STYLE_NUM_ENTRIES;
}
//out_indices 的第一个元素存放着找到有效属性值的个数
out_indices[0] = indices_idx;
}
该方法比较长,省略了一些地方,主要做了两件事:
- 1、上面的1~4步骤实际上就是确定了加载属性的优先级
- 2、记录查询到的属性值放在TypedArray里。
来看看和TypedArray关系
typedArray.getIndexCount():
public int getIndexCount() {
if (mRecycled) {
throw new RuntimeException("Cannot make calls to a recycled instance!");
}
//这个值存放的是加载到有效属性个数
return mIndices[0];
}
typedArray.getIndex(i);
public int getIndex(int at) {
//第一个元素记录着个数,因此往后+1
return mIndices[1+at];
}
mIndices[]记录着属性名索引,还记得之前说过的在R.java里生成的
public static final int MyStyleable_attr_bool=0;
public static final int MyStyleable_attr_int=1;
public static final int MyStyleable_attr_ref=2;
public static final int MyStyleable_attr_str=3;
记录着就是如上的值。而这些又可以索引到具体的属性:
public static final int[] MyStyleable={
0x7f02002b, 0x7f02002c, 0x7f02002d, 0x7f02002e
};
再来看看获取属性值:
indexValue = typedArray.getIndex(i);
typedArray.getString(indexValue);
最终从TypedArray int[] mData里寻找,该数组在上面的ApplyStyle里填充。
最后来直观理解typedArray.getIndexCount()与TypedArray的mLength关系
<com.fish.myapplication.attr.MyAttrView
app:attr_str="str in myLayout"
app:attr_bool="true"
android:layout_width="100px"
android:layout_height="100px">
</com.fish.myapplication.attr.MyAttrView>
#attrs.xml
<declare-styleable name="MyStyleable">
<attr name="attr_str" format="string"></attr>
<attr name="attr_bool" format="boolean"></attr>
<attr name="attr_int" format="integer"></attr>
<attr name="attr_ref" format="reference"></attr>
</declare-styleable>
以上我们只是定义了两个属性,而MyStyleable里声明了4个属性,因此TypedArray mIndices[] 有效属性个数为2。而mLength 表示mIndices[]数组长度。
值得注意的是:
- TypedArray 实例是可以复用的,mIndices[] 长度只会变长。因此也许你调试的时候发现mIndices[] 并不一定等于4,有可能更大。
六 XML布局文件中使用自定义属性——命名空间
- 系统的命名空间:xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
通用命名空间:
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
包名命名空间:
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/包名"xmlns:app 是自定义的属性引用名, URL:http://schemas.android.com/apk/res 是默认的资源标识,实际是不可访问的
命名空间作用域:声明到根布局则全局使用,声明到单个 View 则只能在单个 View 内使用
属性的使用 :
<com.bin.MyIconView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher"
app:iconWidth="35dp"
app:iconHeight="35dp" />android:src 的 : 号是转意的语法,左边的名称是来自哪个命名空间的属性.





















 1127
1127

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








