前言,基于上个简单的ssm项目整合shiro配置
此片写的不太详细,不过基本能理解看懂,详解见之前的boot整合shiro,地址:详解shiro
shiro 所需包,ehcache引入pom.xml
<!-- apache shiro 核心 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- shiro的web整合 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-web</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- shiro的aop代理 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-aspectj</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- shiro spring整合 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- ehcache的缓存框架 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache-core</artifactId>
<version>2.6.10</version>
</dependency>
<!-- shiro整合ehcache -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
在webapp-WEB-INFO下web.xml中配置shiro过滤器,注意一定配置在mvc之前
<!-- 配置Shiro的代理过滤器 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>shiroFilter</filter-name>
<!-- 该过滤器不是一个真正的过滤器实现,是一个代理的过滤器, 自动到Spring容器中获取以 filter-name的名字为名字的bean作为过滤器
的对象 -->
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
<init-param>
<!-- 设置过滤器的生命周期(销毁)是否是由web容器控制 -->
<param-name>targetFilterLifecycle</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>shiroFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
编写 application-shiro.xml 在applicationContext.xml(即spring主配置文件) 引入读取

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 配置Shiro核心Filter,bean的id必须和过滤器的名字一样 -->
<bean id="shiroFilter" class="org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean">
<!-- 安全管理器 -->
<property name="securityManager" ref="securityManager"/>
<!-- 未认证,跳转到哪个页面 ,如果认证失败,跳转的默认页面 -->
<property name="loginUrl" value="/login/login"/>
<!-- 登录页面页面,如果认证成功,则默认跳转的页面 -->
<property name="successUrl" value="/hello"/>
<!-- 如果没有授权,则默认跳转到该页面 -->
<property name="unauthorizedUrl" value="/login/hello"/>
<!-- shiro URL控制过滤器规则:配置的小过滤器链(过滤器栈):执行从上倒下有顺序 -->
<property name="filterChainDefinitions">
<value>
/login/** = anon
/static/**=anon
/customersss/list = perms[customer:add]
/pages/base/area.html* = roles[base]
/** = authc
</value>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 安全管理器 -->
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager">
<property name="realm" ref="bosRealm"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="bosRealm" class="com.example.realm.MyRealm"/>
</beans>

anon 无需认证的路径
authc 需要认证的路径
perms[“所需的权限字符串”] 所需的权限
roles[“所需要拥有的角色”] 要拥有的角色
注意:路径的拦截是自上而下的,如果满足一个,就不会再走下面的设置
编写自定义myRealm继承shiro的 AuthorizingRealm类
package com.example.realm;
import com.example.entity.User;
import com.example.service.UserService;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.LockedAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
/**
* @author zhaozeren
* @version 1.0
* @date 2019/3/18
*/
public class MyRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
//授权
//获取当前登录的用户
User user = (User) SecurityUtils.getSubject().getPrincipal();
//授权类
SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
if ("admin".equals(user.getName())) {
//获取所有权限集合,循环添加
authorizationInfo.addStringPermission("customer:add");
//获取所有角色集合,循环添加
authorizationInfo.addRole("经理");
} else {
//根据用户去查找用户所有的权限,循环添加
// authorizationInfo.addStringPermission("customer:add");
//根据用户去查找用户所用有的角色,循环添加
//authorizationInfo.addRole("创始人");
}
return authorizationInfo;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//用户的认证
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token;
//用户所输入的同户名
String username = usernamePasswordToken.getUsername();
//根据用户名去数据库查找
User user = userService.getUserByName(username);
if (user == null) {// 没找到帐号
throw new UnknownAccountException();
}
if (user.getStatus() == 0) {// 帐号未启用(或账号被锁定)
throw new LockedAccountException();
}
SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, user.getPassword(), super.getName());
return simpleAuthenticationInfo;
}
}
编写loginController
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.service.UserService;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.DisabledAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.LockedAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
/**
* @author zhaozeren
* @version 1.0
* @date 2019/3/18
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("login")
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* 登录页面
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("login")
public String login() {
return "login";
}
/**
* 登录验证
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("loginUser")
@ResponseBody
public String loginUser(String userName, String passWord) {
//获取shiro大管家
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//获取token,将前台传入的用户名和密码放入UsernamePasswordToken
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken(userName, passWord);
try {
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
return "success";
} catch (UnknownAccountException e){
return "没找到帐号";
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e){
return "密码错误";
} catch (LockedAccountException e){
return "账号被锁定";
}catch (DisabledAccountException e){
return "禁用的账号";
} catch (Exception e){
return "登录失败";
}
}
@RequestMapping("logout")
public String logout() {
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
subject.logout();
return "login";
}
@RequestMapping("unauthorized")
public String unauthorized() {
return "unauthorized";
}
}
测试 访问 http://localhost:8007/user/getUser
结果被拦截到 登录页面
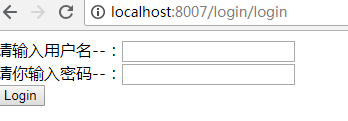
分析:

授权 思路同上
加入ehcache缓存,理由:我们不能每次操作都去数据库中查询一次,看拥有什么权限或角色。解决:加入缓存
编写:
applicationContext-cache.xml 记得引入spring主配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd">
<!-- 配置ehcache的对象EhCacheManager -->
<bean id="ehCacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean">
<!-- 注入ehcache核心配置文件的位置 Default is "ehcache.xml" in the root of the class
path, or if not found, "ehcache-failsafe.xml" in the EhCache jar (default
EhCache initialization). 可以不配置,默认找类路径下的ehcache.xml -->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:ehcache.xml"/>
</bean>
<!-- Spring整合Ehache -->
<!-- Spring的平台缓存管理器 -->
<bean id="springCacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager">
<!-- 注入ehcache的对象 -->
<property name="cacheManager" ref="ehCacheManager"></property>
</bean>
<!-- spring的缓存注解驱动 -->
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="springCacheManager"/>
</beans>
编写ehcache.xml在classpath下
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd">
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/>
<!-- 默认的缓存空间 -->
<!--
缓存策略:
maxElementsInMemory:内存中最大存放的元素的个数
eternal:缓存的数据是否永生不灭-不会销毁,
timeToIdleSeconds:发呆(没有读取、使用)多久清除,单位秒
timeToLiveSeconds:存活多久就清除,单位秒
maxElementsOnDisk:缓存到硬盘上最大的元素个数
strategy="localTempSwap":当内存元素个数满了,会溢出到硬盘上缓存。
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:过期轮询时间,单位秒
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:内存存储和清除策略,默认三个策略,分别为LRU(最近最少使用)、LFU(最常用的)、FIFO(先进先出)。
-->
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap"/>
</defaultCache>
</ehcache>
在application-shiro.xml 中添加ehcache配置
<!-- 安全管理器 -->
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager">
<property name="realm" ref="bosRealm"></property>
<!-- 开启Shiro缓存功能,需要在shiro安全管理器中注入shiro的 平台缓存管理器 -->
<property name="cacheManager" ref="shiroCacheManager"/>
</bean>
<bean id="bosRealm" class="com.example.realm.MyRealm"/>
<!-- shiro整合echcache的缓存配置 -->
<!-- 配置Shiro的平台缓存管理 -->
<bean id="shiroCacheManager" class="org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManager">
<!-- 注入ehcache的对象 -->
<property name="cacheManager" ref="ehCacheManager"/>
</bean>
我们再次访问,只登陆一次对账号所拥有的权限角色进行查询,其余都走缓存
开启shiro的注解开发:
理由:每次都在xml中配置比较麻烦
解决:
在 springMvc-servlet.xml 添加shiro注解支持
<!-- 开启aop,对类代理 -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true"></aop:config>
<!-- 开启shiro注解支持 -->
<bean class="org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor.AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor">
<property name="securityManager" ref="securityManager"/>
</bean>
在controller类中的方法上使用:@RequiresPermissions(“所需的权限”)
@RequiresRoles(“所需要的角色”)























 797
797











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








