目录
一. 如何使用一张哈希表封装unordered_map和unordered_set
三. unordered_map和unordered_set的实现
附录:哈希表封装unorder_map和unordered_set完整版代码
一. 如何使用一张哈希表封装unordered_map和unordered_set
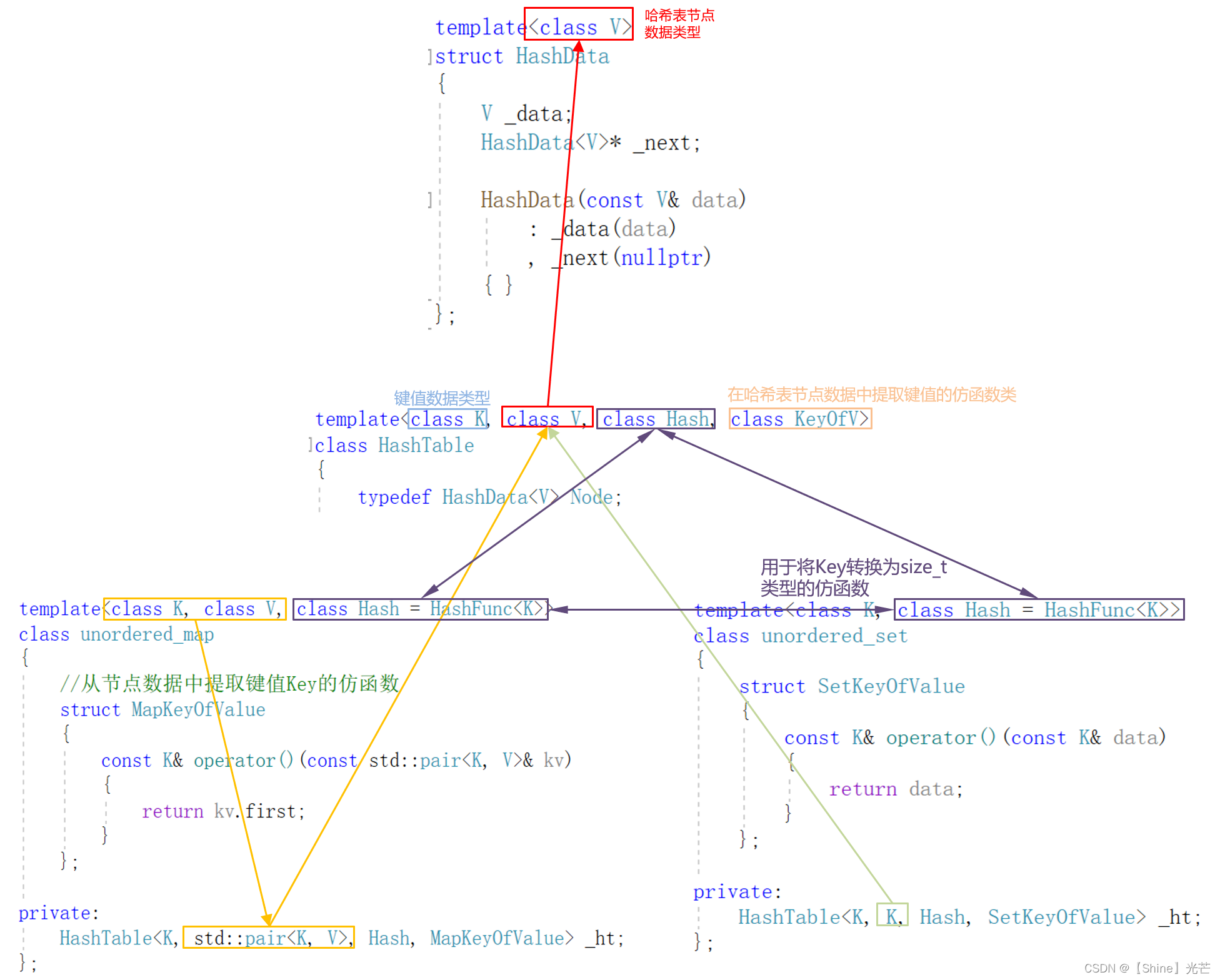
采用一张哈希表封装unordered_map和unordered_set的方法与采用一颗红黑树封装map和set的模型基本完全一样。
哈希表类HashTable有四个模板参数,分别为:键值Key的数据类型K、与键值Key匹配的数据的类型V、哈希仿函数函数类Hash以及用于提取键值的仿函数类KeyOfV。
- 当哈希表封装用于unordered_map时,K-V构成键值对,作为哈希表中存储的数据的类型。当用于封装unordered_set时,V与K相同,哈希表中每个节点存储一个类型为K的数据,此时K和V实例化后的类型相同。
- Hash为哈希仿函数,用于将键值Key转换为size_t(如string类型的键值,就需要相应的算法将其表征为size_t),以便通过哈希函数计算其存储的位置。
- KeyOfV用于在提取键值Key,在unordered_map下,提取键值对的first,在unordered_set下,直接取Key。
二. 哈希表迭代器的实现
2.1 迭代器成员变量及应当实现的功能
应当有两个成员变量:指向当前节点的指针_cur和哈希表类对象指针_ptable。成员函数及所实现的功能应当包括:
- operator++函数:哈希表下一个有效节点的迭代器。
- operator->和operator*,用于访问节点数据_data。
- operator==和operator!=,用于判断两个迭代器是否表示同一个哈希表节点。
2.2 operator++函数
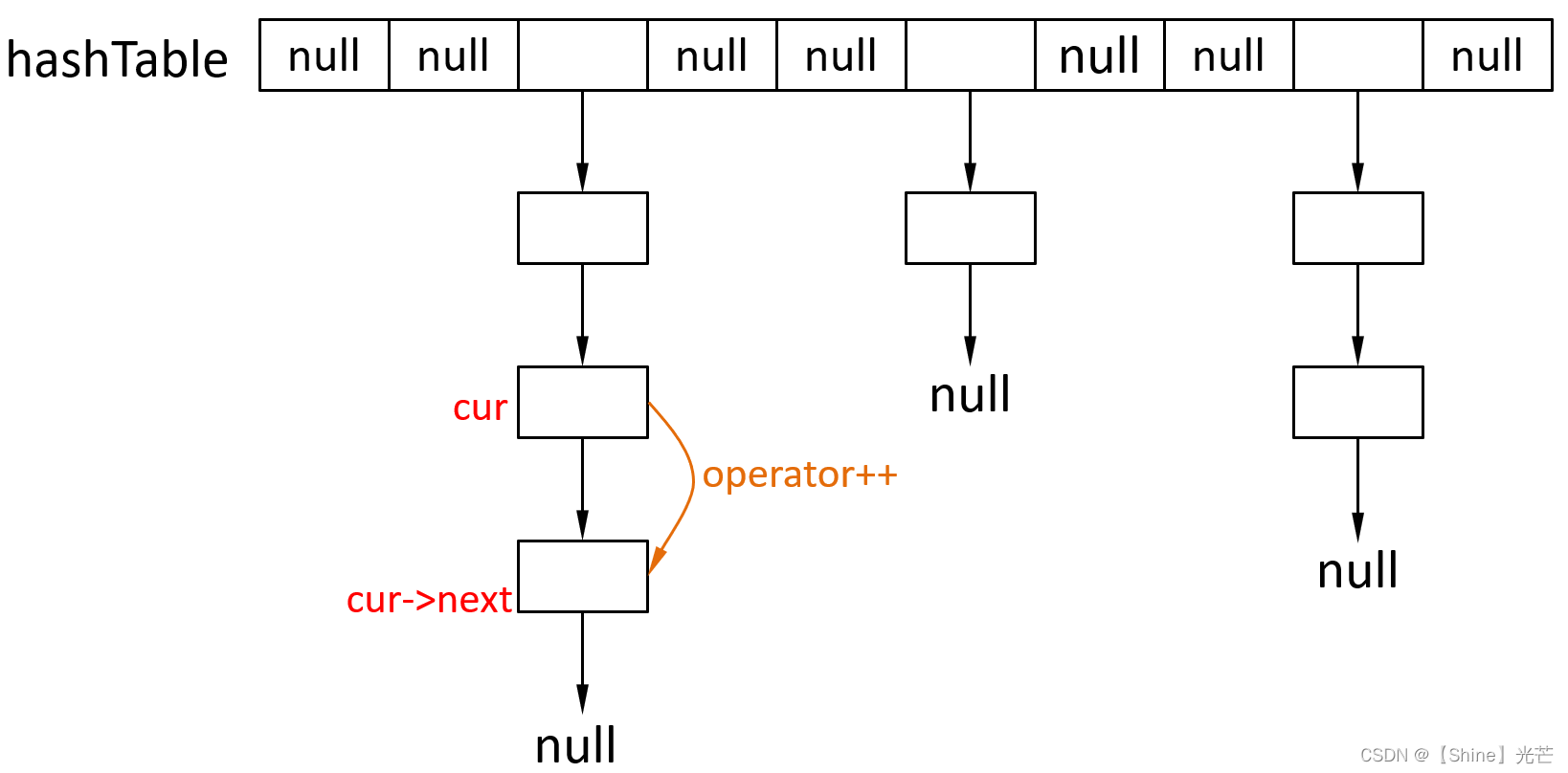
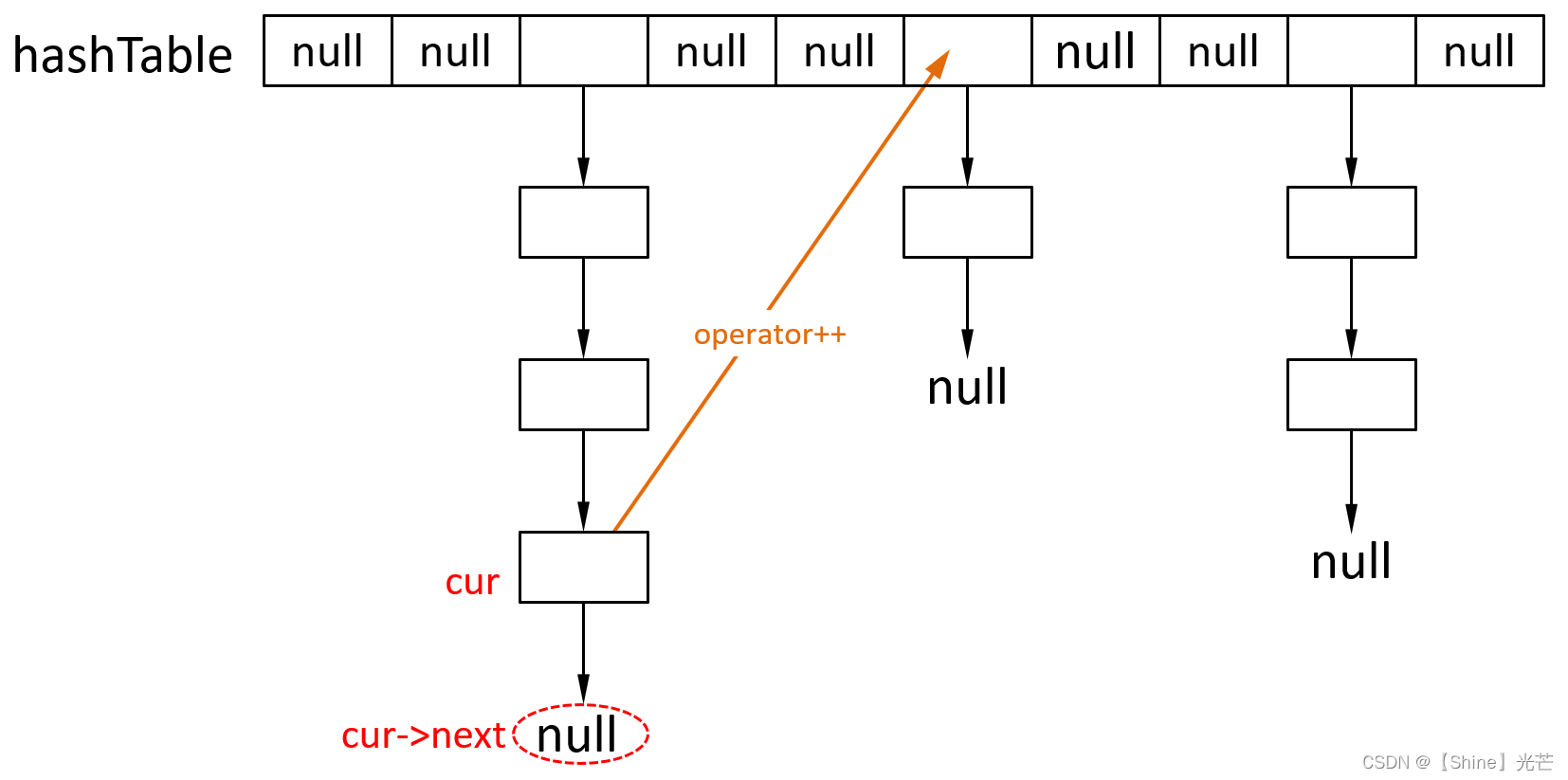
函数功能为找哈希表下一个有效位置,并返回那个位置的迭代器。要分两种情况讨论:
- 如果_cur->_next节点不是nullptr,则表明当前的_cur不是目前桶的最下面的节点,直接将_cur更新为_cur->next,然后返回*this即可。
- 如何_cur->next是nullptr,则表明下一个有效节点不在当前哈希桶,要么没有下一个有效节点,如果有就是_hashTable某个桶最上面位置的节点。因此只需向后遍历_hashTable[i],遇到不为空或结尾即可。
代码2.1:迭代器operator++函数
//Self&表示迭代器本身类型的引用
//迭代器自加函数
Self& operator++()
{
//分两种情况讨论:cur所在的桶的next是否为空
//_cur的下一个节点不为空
if (_cur->_next)
{
_cur = _cur->_next;
return *this;
}
else //_cur的_next节点为空,++要去到其他桶
{
Hash hash;
KeyOfV kofv;
size_t hashi = hash(kofv(_cur->_data)) % _ptable->_hashTable.size();
for (size_t i = hashi + 1; i < _ptable->_hashTable.size(); ++i)
{
_cur = _ptable->_hashTable[i];
if (_cur)
{
return *this;
}
}
return *this;
}
}2.3 operator*和operator->函数
这两个函数都是用于返回节点数据的,不同在于:operator*返回节点数据_data本身的引用,operator->返回_data的地址。
代码2.2:operator*和operator->函数
//V为哈希表存储的数据的类型
V& operator*()
{
return _cur->_data;
}
V* operator->()
{
return &_cur->_data;
}2.4 operator!=和operator==函数
如果两个迭代器表示不用的哈希表类对象的节点位置,那么他们的_cur一定不同,因此,只需要比较两个迭代器的_cur是否相同即可。
代码2.3:operator!=和operator==函数
//迭代器相等判断函数
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _cur == it._cur;
}
//迭代器不等判断函数
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _cur != it._cur;
}2.5 begin()和end()
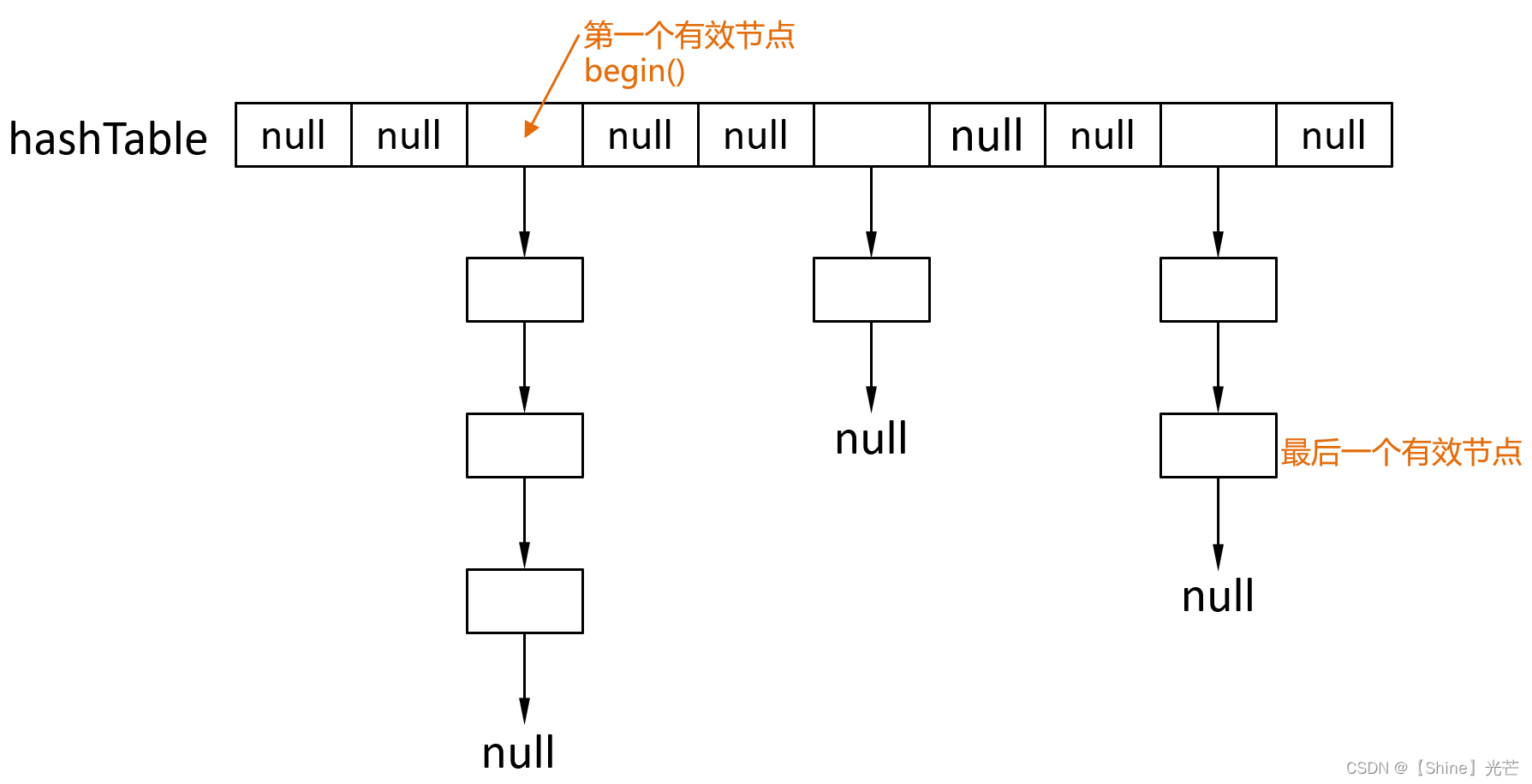
begin()表示第一个有效节点的位置,用nullptr表示最后一个有效节点后面的位置end()。
2.6哈希表迭代器实现代码
//哈希表类的声明
template<class K, class V, class Hash, class KeyOfV>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class V, class Hash, class KeyOfV>
struct __HashIterator
{
typedef HashData<V> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, V, Hash, KeyOfV> Table;
typedef __HashIterator<K, V, Hash, KeyOfV> Self;
Node* _cur;
Table* _ptable;
//迭代器构造函数
__HashIterator(Node* cur, Table* ptable)
: _cur(cur)
, _ptable(ptable)
{ }
//迭代器自加函数
Self& operator++()
{
//分两种情况讨论:cur所在的桶的next是否为空
//_cur的下一个节点不为空
if (_cur->_next)
{
_cur = _cur->_next;
return *this;
}
else //_cur的_next节点为空,++要去到其他桶
{
Hash hash;
KeyOfV kofv;
size_t hashi = hash(kofv(_cur->_data)) % _ptable->_hashTable.size();
for (size_t i = hashi + 1; i < _ptable->_hashTable.size(); ++i)
{
_cur = _ptable->_hashTable[i];
if (_cur)
{
return *this;
}
}
return *this;
}
}
V& operator*()
{
return _cur->_data;
}
V* operator->()
{
return &_cur->_data;
}
//迭代器相等判断函数
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _cur == it._cur;
}
//迭代器不等判断函数
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _cur != it._cur;
}
};三. unordered_map和unordered_set的实现
在unordered_map和unordered_set中,会存储一个自定义类型HashTable的成员变量_ht,_ht是一张哈希表。unordered_map和unordered_set的insert、erase、find、begin、end()函数只需要复用HashTable的对应成员函数即可。
唯一需要注意的是unordered_map中的operator[]函数,其应当返回与Key匹配的Value的引用,或者插入一个键值为Key的数据。operator[]中复用哈希表insert函数,insert函数返回一键值对,这个键值对的first为原有Key的节点位置的迭代器或新插入节点的迭代器位置。
代码3.1:unordered_map的封装
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
//从节点数据中提取键值Key的仿函数
struct MapKeyOfValue
{
const K& operator()(const std::pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename HashTable<K, std::pair<K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfValue>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const std::pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.insert(kv);
}
HashData<V>* find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.find();
}
private:
HashTable<K, std::pair<K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfValue> _ht;
};代码3.2:unordered_set的封装
template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfValue
{
const K& operator()(const K& data)
{
return data;
}
};
public:
typedef typename HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfValue>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& data)
{
return _ht.insert(data);
}
iterator find(const K& data)
{
return _ht.find(data);
}
bool erase(const K& data)
{
return _ht.find(data);
}
private:
HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfValue> _ht;
};附录:哈希表封装unorder_map和unordered_set完整版代码
//hashTable.h文件 -- 哈希表的实现
#pragma once
#include<vector>
template<class V>
struct HashData
{
V _data;
HashData<V>* _next;
HashData(const V& data)
: _data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{ }
};
//仿函数 -- 用于将键值key转换为size_t类型数据
//这样可以带入哈希函数,使不同key值可以映射到不同存储位置
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//哈希表类的声明
template<class K, class V, class Hash, class KeyOfV>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class V, class Hash, class KeyOfV>
struct __HashIterator
{
typedef HashData<V> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, V, Hash, KeyOfV> Table;
typedef __HashIterator<K, V, Hash, KeyOfV> Self;
Node* _cur;
Table* _ptable;
//迭代器构造函数
__HashIterator(Node* cur, Table* ptable)
: _cur(cur)
, _ptable(ptable)
{ }
//迭代器自加函数
Self& operator++()
{
//分两种情况讨论:cur所在的桶的next是否为空
//_cur的下一个节点不为空
if (_cur->_next)
{
_cur = _cur->_next;
return *this;
}
else //_cur的_next节点为空,++要去到其他桶
{
Hash hash;
KeyOfV kofv;
size_t hashi = hash(kofv(_cur->_data)) % _ptable->_hashTable.size();
for (size_t i = hashi + 1; i < _ptable->_hashTable.size(); ++i)
{
_cur = _ptable->_hashTable[i];
if (_cur)
{
return *this;
}
}
return *this;
}
}
V& operator*()
{
return _cur->_data;
}
V* operator->()
{
return &_cur->_data;
}
//迭代器相等判断函数
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _cur == it._cur;
}
//迭代器不等判断函数
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _cur != it._cur;
}
};
template<class K, class V, class Hash, class KeyOfV>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashData<V> Node;
friend struct __HashIterator<K, V, Hash, KeyOfV>;
public:
typedef __HashIterator<K, V, Hash, KeyOfV> iterator;
//哈希表析构函数
~HashTable()
{
//依次释放每个桶(单链表节点)
for (size_t i = 0; i < _hashTable.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _hashTable[i];
//while循环释放每个非空节点
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_hashTable[i] = nullptr;
}
//_hashTable是vector成员,编译器会自动调用其析构函数
}
//查找哈希表第一个有效节点
iterator begin()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _hashTable.size(); ++i)
{
if (_hashTable[i])
{
return iterator(_hashTable[i], this);
}
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
//最后一个节点的下一位置
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
//数据插入函数
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const V& data)
{
//如果哈希表中已经存在kv,那么不插入数据,直接返回
iterator ret = find(_kofv(data));
if (ret != end())
{
return std::make_pair(ret, false);
}
//检查扩容
//当哈希表容量为0(第一次插入数据前),或负载因子在插入数据后会大于1的情况下,对哈希表执行二倍扩容
if (_hashTable.size() == 0 || _size == _hashTable.size())
{
size_t newSize = _hashTable.size() == 0 ? 10 : 2 * _hashTable.size(); //新容量
//建立一个辅助新表(用于让扩容后原哈希表中数据映射到新的位置)
std::vector<Node*> newTable;
newTable.resize(newSize, nullptr); //表中每个哈希桶先初始化为nullptr
//挪动数据 -- 等价于单链表头插操作
for (size_t i = 0; i < _hashTable.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _hashTable[i]; //当前哈希桶头结点
//将原来的每个节点头插到新表的对应位置
while (cur)
{
size_t hashi = _hash(_kofv(cur->_data)) % newSize;
//头插
Node* next = cur->_next;
cur->_next = newTable[hashi];
newTable[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
_hashTable.swap(newTable);
}
Node* insertNode = new Node(data); //新插入的节点
size_t hashi = _hash(_kofv(data)) % _hashTable.size(); //计算新节点在哪个哈希桶
//节点插入
insertNode->_next = _hashTable[hashi];
_hashTable[hashi] = insertNode;
++_size;
return std::make_pair(iterator(insertNode, this), true);
}
//数据查找函数
iterator find(const K& key)
{
//表容量为0时,一定找不到任何数据
//为了避免除0错误,直接返回
if (_hashTable.size() == 0)
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
size_t hashi = _hash(key) % _hashTable.size(); //确定key应该在哪个哈希桶
Node* cur = _hashTable[hashi];
//查找hashi对应的哈希桶是否存在key
while (cur)
{
if (_kofv(cur->_data) == key)
{
return iterator(cur, this);
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
//数据删除函数
bool erase(const K& key)
{
//避免除0错误
if (_hashTable.size() == 0)
{
return false;
}
size_t hashi = _hash(key) % _hashTable.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _hashTable[hashi];
//找到键值为key的节点删除
//等价于单链表节点删除操作 -- 分删除头结点和中间节点两种情况来讨论
while (cur)
{
//找到了要删除的节点
if (_kofv(cur->_data) == key)
{
//删除头结点
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_hashTable[hashi] = cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur = nullptr;
}
else //删除中间节点
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur = nullptr;
}
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
private:
size_t _size = 0;
Hash _hash;
KeyOfV _kofv;
std::vector<Node*> _hashTable;
};
//UnorderedMap.h文件 -- unordered_map的封装
#pragma once
#include "hashTable.h"
namespace zhang
{
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
//从节点数据中提取键值Key的仿函数
struct MapKeyOfValue
{
const K& operator()(const std::pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename HashTable<K, std::pair<K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfValue>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const std::pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.insert(kv);
}
HashData<V>* find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.find();
}
private:
HashTable<K, std::pair<K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfValue> _ht;
};
}
//UnorderedSet.h文件 -- unordered_set的封装
#pragma once
#include "hashTable.h"
namespace zhang
{
template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfValue
{
const K& operator()(const K& data)
{
return data;
}
};
public:
typedef typename HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfValue>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& data)
{
return _ht.insert(data);
}
iterator find(const K& data)
{
return _ht.find(data);
}
bool erase(const K& data)
{
return _ht.find(data);
}
private:
HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfValue> _ht;
};
}




















 319
319











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








