目录
1.哈希概念
顺序结构以及平衡二叉搜索树结构中,在查找一个元素时需要经过比较。顺序查找时间复杂度为O(N),平衡二叉搜索树查找时间复杂度为O(log_2N)。
理想的搜索方法便是不经过任何比较,通过常数次的操作从表中得到搜索的元素。如果构造一种存储结构,如果某种函数使元素的存储位置与它存储的元素之间形成一种映射关系,那么在查找中可以通过该函数很快找到搜索元素。
该方式称为哈希(散列)方法,哈希方法使用的转换函数称为哈希函数, 构造出来的数据结构称为哈希表。
1.1哈希函数
常用的哈希函数有多种,这里介绍一种:除留余数法。即将元素转换成数字再模上容器的大小,得到的数字便是该元素的存储位置。
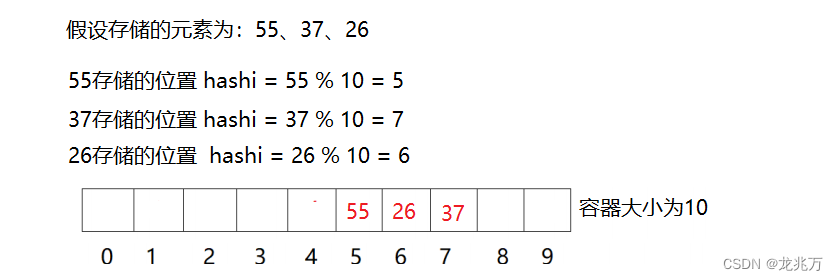
1.2哈希冲突
哈希冲突是避免不了的。如果我们使用上述哈希函数,存储26、36、46三个元素时,它们的位置将会重合,这样的行为称为哈希冲突/哈希碰撞。解决这种冲突的办法有两个:闭散列和开散列。
闭散列(开放定址法):当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有空位,那么可以把当前元素存储到冲突位置的下一个空位。
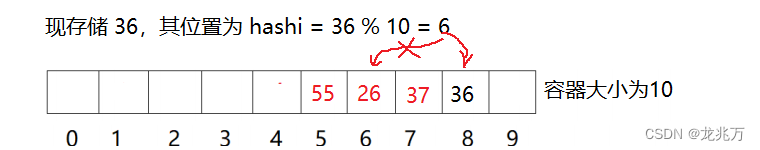
闭散列又有多种寻找空位的方法。通常使用线性探测法和二次探测法。线性探测法是指在冲突位置上一个一个位置向后寻找空位;二次探测则是先看后一个位置、后两个位置、后四个位置、后八个位置......
开散列(链地址法):哈希表中不直接存储元素,而是存放指针。这个指针指向链表的某个节点。如果发生哈希冲突,就把当前元素链到冲突位置的链表当中去。

2.闭散列实现
enum Status
{
//空 存在 删除
EMPTY,EXIST,DELETE
};
template <class K,class V>
struct HashData
{
pair<K,V> _kv;
Status _st;
};
// 仿函数
template <class K>
struct HashFunc
{
//如果是数字类型,直接转化为size_t类型即可
size_t operator()(const K& k)
{
return (size_t)k;
}
};
//如果不是数字类型,例如string,就需要特化单独处理
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& k)
{
size_t hash = 0;//返回值
for (auto& e : k)
{
hash *= 131;//每次累加之前,先乘等131
hash += e;
}
return hash;
}
};
template <class K,class V>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashData<K, V> Data;
typedef HashFunc<K> Func;
public:
HashTable()
:_n(0)//一开始的有效数据个数为0
{
_tables.resize(10);//一开始确保表的大小为10
//通过resize可以确保size == capacity
}
Data* find(const K& k)
{
Func f;
size_t hashi = f(k) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._st == EXIST)//只有存在才说明可能有这个数据存在
{
//因为我们删除数据不是彻底删除数据
//而是将其状态改变
//所以比较的时候需要确保当前位置的数据不能是删除状态
if (_tables[hashi]._st != DELETE && _tables[hashi]._kv.first == k)
{
return &_tables[hashi];
}
++hashi;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
return nullptr;
}
bool insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
//如果新插入的数据已经存在,就不需要插入了
if (find(kv.first))
{
return false;
}
//首先需要确保负载因子不大于0.7才进行插入
// 否则就要对表进行扩容
//double lf = _n / _tables.size();
//if(lf >= 0.7)
//{ }
if (_n * 10 / _tables.size() >= 7)
{
HashTable<K, V> newHash;//创建一个新的对象
//这个对象的表的容量是当前表容量的2倍
newHash._tables.resize(_tables.size() * 2);
//将旧表的内容拷贝至新表
for (auto& e : _tables)
{
newHash.insert(kv);
}
//最后交换这两个表
//新对象出了此作用域后自动销毁
swap(_tables, newHash._tables);
}
//不管是否已经扩容,这里都进行新数据的插入操作
//当然,key不可能永远为数字类型
//size_t hashi = kv.first % _tables.size();
Func f;
size_t hashi = f(kv.first) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._st == EXIST)//如果映射位置已经存在数据
{
++hashi;//就到下一个位置去
hashi %= _tables.size();//确保不越界
}
// 此时就找到了状态为EMPTY DELETE的位置
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;//插入
_tables[hashi]._st = EXIST;//设置状态
++_n;//递增有效数据个数
return true;
}
bool erase(const K& k)//通过key值来删除
{
Data* del = find(k);
if (del)
{
del->_st = DELETE;
--_n;
return true;
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Data> _tables;//存储数据的表
size_t _n;//有效数据个数
};3.开散列实现
namespace ly
{
template <class T>
struct Func
{
size_t operator()(const T& t)
{
return (size_t)t;
}
};
template<>
struct Func<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto& e : s)
{
hash *= 131;
hash += e;
}
return hash;
}
};
template <class K, class V>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_kv(kv), _next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class HashBucket
{
public:
typedef Func<K> Func;
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
HashBucket()
:_n(0)
{
_tables.resize(10);//默认大小为10
}
~HashBucket()
{
clear();
}
void clear()
{
for (auto cur : _tables)
{
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
}
}
bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (find(kv.first))
{
return false;
}
if (_n == _tables.size())//当负载因子等于1时
{
vector<Node*> newTables;
newTables.resize(_tables.size() * 2, nullptr);
for (auto cur : _tables)
{
while (cur)//把cur看成新节点
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
//size_t hashi = cur->_kv.first % newTables.size();
size_t hashi = Func()(cur->_kv.first) % newTables.size();
cur->_next = newTables[hashi];
newTables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
_tables.swap(newTables);
}
//不需要扩容时,头插
//size_t hashi = kv.first % _tables.size();//不能确保每个K都是数字类型
size_t hashi = Func()(kv.first) % _tables.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;//增加有效数据个数
return true;
}
Node* find(const K& k)
{
size_t hashi = Func()(k) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == k)
{
return cur;
}
else
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool erase(const K& k)
{
size_t hashi = Func()(k) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
Node* prev = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == k)
{
if (prev != nullptr)
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
}
else
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
delete cur;
}
--_n;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n;//有效数据个数
};
}4.容器的封装
4.1unordered_map
//HashBucket.h
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using std::string;
using std::vector;
using std::make_pair;
namespace ly
{
template <class T>
struct Func
{
size_t operator()(const T& t)
{
return (size_t)t;
}
};
template<>
struct Func<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto& e : s)
{
hash *= 131;
hash += e;
}
return hash;
}
};
template <class KV>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode<KV>* _next;
KV _data;
HashNode(const KV& data)
:_data(data),_next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class K, class KV, class KOfKV, class HashFunc>
class HashBucket;//声明
//template<class KV>
template<class K, class KV, class KOfKV, class HashFunc>
struct HashIterator
{
typedef HashNode<KV> Node;
typedef HashIterator<K, KV, KOfKV, HashFunc> Self;
typedef HashBucket<K, KV, KOfKV, HashFunc> Tables;
typedef Func<K> Func;
Node* _node;
Tables* _ht;
/*如果const对象,传参是传不进来的
就算加上const兼容,那么成员的定义是非const,也不能转换
所以const迭代器不能在一个模板上实现
必须单独实现*/
HashIterator(Node* _node,Tables* ht)
:_node(_node),_ht(ht)
{}
KV& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
KV* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)//如果下一个节点不为空
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
//如果下一个节点为空,就要想办法跳到下一个有效位置
KOfKV kof;
size_t hashi = Func()(kof(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();
++hashi;
while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[hashi])
{
_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
else
{
++hashi;
}
}
if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
};
template<class K, class KV, class KOfKV, class HashFunc>
struct HashConstIterator
{
typedef HashNode<KV> Node;
typedef HashConstIterator<K, KV, KOfKV, HashFunc> Self;
typedef HashBucket<K, KV, KOfKV, HashFunc> Tables;
typedef HashIterator<K, KV, KOfKV, HashFunc> iterator;
typedef Func<K> Func;
const Node* _node;
const Tables* _ht;
HashConstIterator(const Node* _node, const Tables* ht)
:_node(_node), _ht(ht)
{}
/*与set同样的问题,支持普通迭代器向const迭代器的转换*/
HashConstIterator(const iterator& it)
:_node(it._node), _ht(it._ht)
{}
const KV& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
const KV* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)//如果下一个节点不为空
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
//如果下一个节点为空,就要想办法跳到下一个有效位置
KOfKV kof;
size_t hashi = Func()(kof(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();
++hashi;
while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[hashi])
{
_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
else
{
++hashi;
}
}
if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
};
template<class K,class KV,class KOfKV,class HashFunc>
class HashBucket
{
public:
typedef Func<K> Func;
typedef HashNode<KV> Node;
template<class K, class KV, class KOfKV, class HashFunc>
friend struct HashIterator;
template<class K, class KV, class KOfKV, class HashFunc>
friend struct HashConstIterator;
typedef HashIterator<K, KV, KOfKV, HashFunc> iterator;
typedef HashConstIterator<K, KV, KOfKV, HashFunc> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
//begin应该指向第一个有效位置
for (auto cur : _tables)
{
if (cur)
{
return iterator(cur, this);
}
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
//begin应该指向第一个有效位置
for (auto cur : _tables)
{
if (cur)
{
return const_iterator(cur, this);
}
}
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
HashBucket()
:_n(0)
{
_tables.resize(10);//默认大小为10
}
~HashBucket()
{
clear();
}
void clear()
{
for (auto cur : _tables)
{
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
}
}
std::pair<iterator,bool> insert(const KV& data)
{
KOfKV kof;
auto ret = find(kof(data));
if (ret != end())
{
return make_pair(ret, false);
}
if (_n == _tables.size())//当负载因子等于1时
{
vector<Node*> newTables;
newTables.resize(_tables.size() * 2, nullptr);
for (auto cur : _tables)
{
while (cur)//把cur看成新节点
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
//size_t hashi = cur->_kv.first % newTables.size();
size_t hashi = Func()(kof(cur->_data)) % newTables.size();
cur->_next = newTables[hashi];
newTables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
_tables.swap(newTables);
}
//不需要扩容时,头插
//size_t hashi = kv.first % _tables.size();//不能确保每个K都是数字类型
size_t hashi = Func()(kof(data)) % _tables.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(data);
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;//增加有效数据个数
return make_pair(iterator(newnode,this), true);
}
iterator find(const K& k)
{
KOfKV kof;
size_t hashi = Func()(k) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kof(cur->_data) == k)
{
return iterator(cur,this);
}
else
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return iterator(nullptr,this);
}
bool erase(const K& k)
{
size_t hashi = Func()(k) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
Node* prev = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == k)
{
if (prev != nullptr)
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
}
else
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
delete cur;
}
--_n;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
vector<Node*>& get_tables()
{
return _tables;
}
size_t& get_n()
{
return _n;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n;//有效数据个数
};
}//unordered_map.h
#pragma once
#include "HashBucket.h"
#include <map>
using std::pair;
namespace ly
{
// 通常这个函数由上层提供
template <class K,class V,class HashFunc = Func<K>>
class unordered_map
{
public:
struct KeyOfMap
{
K operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
typedef typename HashBucket<K, pair<K, V>, KeyOfMap, HashFunc>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename HashBucket<K, pair<K, V>, KeyOfMap, HashFunc>::const_iterator const_iterator;
template<class Iterator>
unordered_map(Iterator begin, Iterator end)
{
while (begin != end)
{
insert(make_pair(begin->first, begin->second));
++begin;
}
}
unordered_map(const unordered_map& um)
{
unordered_map tmp(um.begin(), um.end());
swap(tmp);
}
unordered_map()
{}
void swap(unordered_map& um)
{
std::swap(_hb.get_tables(), um._hb.get_tables());
std::swap(_hb.get_n(), um._hb.get_n());
}
iterator begin()
{
return _hb.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _hb.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _hb.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _hb.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _hb.insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& k)
{
pair<iterator, bool> p = insert(make_pair(k, V()));
return p.first->second;
}
private:
HashBucket<K, pair<K, V>,KeyOfMap,HashFunc> _hb;
};
}4.2unordered_set
#pragma once
#include "HashBucket.h"
#include <map>
using std::pair;
namespace ly
{
// 通常这个函数由上层提供
template <class K,class HashFunc = Func<K>>
class unordered_set
{
public:
struct KeyOfSet
{
K operator()(const K& k)
{
return k;
}
};
typedef typename HashBucket<K,K, KeyOfSet, HashFunc>::const_iterator iterator;
template<class Iterator>
unordered_set(Iterator begin, Iterator end)
{
while (begin != end)
{
insert(*begin);
++begin;
}
}
unordered_set(const unordered_set& um)
{
unordered_set tmp(um.begin(), um.end());
swap(tmp);
}
unordered_set()
{}
void swap(unordered_set& um)
{
std::swap(_hb.get_tables(), um._hb.get_tables());
std::swap(_hb.get_n(), um._hb.get_n());
}
iterator begin() const
{
return _hb.begin();
}
iterator end() const
{
return _hb.end();
}
/*与set同样的问题,需要支持普通迭代器向const迭代器的转换*/
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& k)
{
pair<typename HashBucket<K, K, KeyOfSet, HashFunc>::iterator, bool> p = _hb.insert(k);
return pair<iterator, bool>(p.first, p.second);
}
private:
HashBucket<K, K, KeyOfSet, HashFunc> _hb;
};
}4.3封装过程中遇到的问题
首先便是迭代器的问题。只用哈希表中的链表指针封装出迭代器是不够的,因为我们要保证链表走到空之后还能够走到下一个哈希表中的下一个有效位置的链表位置。所以还需要还需要指向哈希表本身的指针,用来辅助迭代器的计算。
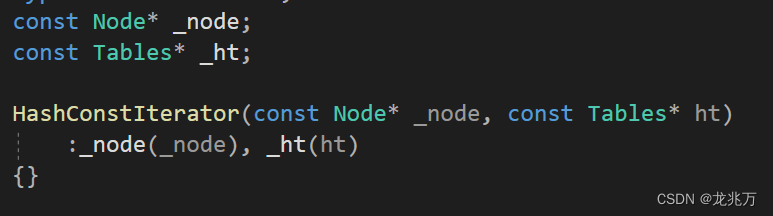
const迭代器为何不能像其他容器一样使用同一个类模板?因为我们需要照顾迭代器中的两个成员。

如箭头所指,cur和this都将是被const修饰的,保护了指向的内容。而要将const成员赋值给非const成员会造成权限放大,是不合理的。























 2161
2161











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










