case … esac 与其他语言中的 switch … case 语句类似,是一种多分枝选择结构。
case 值 in
模式1)
command1
command2
command3
;;
模式2)
command1
command2
command3
;;
*)
command1
command2
command3
;;
esac
示例:
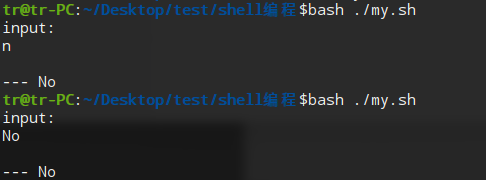
#!/bin/bash
echo "input:"
read line
# 初探case 语句
case "$line" in
yes | Yes | y) echo -e "\n--- Yes" ;;
no | No | n) echo -e "\n--- No" ;;
*) echo -e "\ninput="$line ;;
esac
exit 0

使用正则表达式
# 用正则表达式进行匹配
case "$line" in
[Yy][Ee][Ss] | [Yy]) echo "this is Yes" ;;
[Nn][Oo] | [Nn]) echo "this is No" ;;
*) ;;
esac
函数
# 函数
# 没有申明,需要写在执行之前,无返回值类型和参数列表
# 有返回值,可以传参
# 程序以第一行非函数语句执行
fun()
{
echo "fun run"
echo "fun \$#=$#" #参数个数
echo "fun \$1=$1"
echo "fun \$2=$2"
echo "fun \${10}=${10}"
}
# 函数名调用函数
fun 123 hello 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
函数返回值
#!/bin/bash
# 函数的返回值
my_add()
{
if [ "$#" -ne 2 ] #参数的个数
then
echo "arg error"
return -1
fi
a=$1
b=$2
res=`expr $a + $b`
return "$res"
}
my_add $1 $2
echo $? # $? 紧跟着的函数(或语句)的返回值
exit 0

局部变量
#!/bin/bash
# shell脚本不区分临时变量与全局变量
# 不论变量定义在函数内还是函数外,都是定义在解释器中
# 如果不想临时变量占用资源,可以使用 unset var 命令撤销一个已定义的变量
# 或者使用 local 定义变量,在变量离开时会自动撤销
# 因此shell脚本不强调返回值,返回值可以由一个变量保存带出
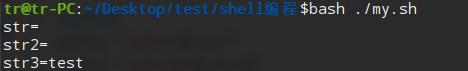
myfun()
{
local str="hello"
str2="world"
str3="test"
unset str2
}
myfun
echo "str=$str"
echo "str2=$str2"
echo "str3=$str3"
exit 0
























 444
444











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










