Java Clone
使用clone方法复制一个对象,clone对象拥有独立的地址。
实现clone的方式:
@Data
@ToString
class Father implements Cloneable { //1.clone的对象需要实现Cloneable接口
private String name;
private int age;
public Father(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { //2.重写父类的clone()方法
return super.clone();
}
}
通常我们实现接口的时候会一并实现接口的方法,可是当我们 implements Cloneable 接口的时候,会发现Cloneable接口根本没有方法。
Q:clone方法是从哪里来的?
A:通过源码可以看到,clone()是基类Object的方法,所有对象默认继承Object,也就是说只要是对象就有clone方法。
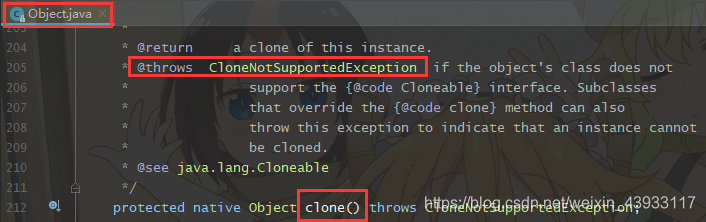
那么,问题来了,既然基类有 clone() 方法,
Q:为什么要实现 Cloneable 接口?
A:从源码 clone() 注释可以看到,如果不实现 Cloneable 接口,则会抛出 CloneNotSupportedException 异常,那注释含义是否可以理解为,Cloneable 接口是作为可以clone对象的标识,标志着只有实现了Cloneable 接口的对象才可以克隆对象。
Q:克隆对象跟引用对象的区别?
A:
引用对象:通过对象A赋值得到一个引用对象B,A和B指向的是同一个地址,所以当改变任意一个的值,另一个也会随着改变。
克隆对象:A对象克隆一个对象B,A和B拥有独立的地址,任意改变一个值,另一个对象不会受影响。
测试 clone() 对象:
public class CloneTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//引用对象
Father a = new Father("a", 40); //初始化a对象
Father b = a; //通过a赋值得到一个引用对象b
b.setName("b"); //b对象改变name值为b
System.out.println("a : " + a.toString() + " b : " + b.toString());
//打印结果:a : Father(name=b, age=40) b : Father(name=b, age=40)
//通过结果发现,b对象改变name值,影响了a对象的name值,说明a和b指向同一地址
//克隆对象
a = new Father("a", 40); //初始化a对象
b = (Father) a.clone(); //a克隆对象b
b.setName("b"); //b对象改变name值为b
System.out.println("a : " + a.toString() + " b : " + b.toString());
//打印结果:a : Father(name=a, age=40) b : Father(name=b, age=40)
//通过结果发现,b对象改变name值,没有影响a对象,说明a和b拥有独立的地址
}
}
Q:浅拷贝和深拷贝的区别?
A:
浅拷贝:对象无法clone包含的引用对象,clone() 默认浅拷贝。
@Data
@ToString
class Father implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private int age;
private Child child; //新增child
public Father(String name, int age, Child child) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.child = child;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
@Data
@ToString
class Child {
private String childName;
public Child(String childName) {
this.childName = childName;
}
}
Father对象里面新增了一个Child对象。
浅拷贝代码测试:
public class CloneTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Father a = new Father("a", 40, new Child("a.a"));
Father b = (Father) a.clone();
b.getChild().setChildName("b.b");
System.out.println("a == b : " + (a == b));
//打印结果:a == b : false
//结果表明实现了Cloneable的Father对象,拥有不同的地址
System.out.println("a.child == b.child : " + (a.getChild() == b.getChild()));
//打印结果:a.child == b.child : true
//结果表明未实现Cloneable的Father.Child对象,即使父类实现了Cloneable,但是Father.Child对象指向的是同一个地址
System.out.println("a : " + a.toString() + " \nb : " + b.toString());
//打印结果:a : Father(name=a, age=40, child=Child(childName=b.b))
// b : Father(name=a, age=40, child=Child(childName=b.b))
}
}
深拷贝:对象包含的引用对象同步clone。
@Data
@ToString
class Father implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private int age;
private Child child; //1.新增child
public Father(String name, int age, Child child) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.child = child;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Father father = (Father) super.clone();
father.child = (Child) child.clone(); //3.Father接收Clone的Child对象
return father;
}
}
@Data
@ToString
class Child implements Cloneable { //2.Child实现Cloneable
private String childName;
public Child(String childName) {
this.childName = childName;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
Child对象实现了Cloneable,Father对象里面新增了一个Child对象,Father继承的clone方法接收了clone对象。
深拷贝代码测试:
public class CloneTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Father a = new Father("a", 40, new Child("a.a"));
Father b = (Father) a.clone();
b.getChild().setChildName("b.b");
System.out.println("a == b : " + (a == b));
//打印结果:a == b : false
System.out.println("a.child == b.child : " + (a.getChild() == b.getChild()));
//打印结果:a.child == b.child : false
//结果表明Father.Child对象也被clone
System.out.println("a : " + a.toString() + " \nb : " + b.toString());
}
}





















 3860
3860











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








