String
1. 非可变类
2. 实现可对比接口
3. 实现字符序列接口
成员变量
- char value[] 不可变的char数组
- int hash 字符串的hash值
构造方法
随机选取一个比较长的构造方法讲解:
public String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= codePoints.length) {
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > codePoints.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
final int end = offset + count;
// Pass 1: Compute precise size of char[]
int n = count;
for (int i = offset; i < end; i++) {
int c = codePoints[i];
if (Character.isBmpCodePoint(c))
continue;
else if (Character.isValidCodePoint(c))
n++;
else throw new IllegalArgumentException(Integer.toString(c));
}
// Pass 2: Allocate and fill in char[]
final char[] v = new char[n];
for (int i = offset, j = 0; i < end; i++, j++) {
int c = codePoints[i];
if (Character.isBmpCodePoint(c))
v[j] = (char)c;
else
Character.toSurrogates(c, v, j++);
}
this.value = v;
}
-
codePoints 字符数组
-
offset 起始位置
-
count 字符个数
1.先判断offset是否越界 (最小界为0,为什么没有判断最大界?)
2.判断字符个数是否越界,在字符个数 等于 0 的情况下,判断起始值是否判断超越最大界(这里判断最大界可以省略一次判断操作,从而优化代码),没有超过直接返回空字符
3.判断 起始位置 + 字符个数是否超过 字符数组长度
4. isBmpCodePoint(char) 用于判断字符是否 在Basic Multilingual Plane中,BMP其实就是UTF的一个编码平面
5. isValidCodePoint(char) 判断字符是否为一个有效的UTF编码
6.n++ ,因为如果字符是有效的UTF编码,又超出了长度,所以要++占位
7. 开始创建String
常用方法:
checkBounds(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length) 用于判断越界
getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin) 将字符串指定字串赋值给字符数组
contentEquals(StringBuffer sb) 同步判断字符串是否相等,因为传递的是StringBuffer,所以有可能发生错误
nonSyncContentEquals(AbstractStringBuilder sb) 非同步判断字符串是否相等
equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) 忽略大小写比较
regionMatches(int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len) 判断两个字符串区域是否相等
equals(Object anObject) 比较对象是否相等
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
1.this == anObject 判断引用地址是否相等
2. 判断类型
3. 判断长度
4. 循环判断字符是否相等
compareTo(String anotherString) Comparable的实现方法 排序方法
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int k = 0;
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
return len1 - len2;
}
- 拿到两个字符串的最小长度
- 循环进行对比,如果字符不相等则直接返回
- 第二步骤没有得到结果证明两个字符前面都是相等的,比较长度
compare(String s1, String s2) Comparator的实现方法 对比方法 ,该方法忽略大小写
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
int n1 = s1.length();
int n2 = s2.length();
int min = Math.min(n1, n2);
for (int i = 0; i < min; i++) {
char c1 = s1.charAt(i);
char c2 = s2.charAt(i);
if (c1 != c2) {
c1 = Character.toUpperCase(c1);
c2 = Character.toUpperCase(c2);
if (c1 != c2) {
c1 = Character.toLowerCase(c1);
c2 = Character.toLowerCase(c2);
if (c1 != c2) {
// No overflow because of numeric promotion
return c1 - c2;
}
}
}
}
return n1 - n2;
}
1.获取最小长度
2.转换大写比较
3.转换小写比较
4. 循环重复 2 -3 步骤,没有结果直接返回长度差
int hashCode() 获取字符串的hash码
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value;
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
h = 31 * h + val[i];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
- 先判断hash 是否有值
- h = 31 * h + val[i]; 选择31是因为 31是个素数,31= 11111【二进制】,只占5bits,不容易发生hash冲突。
- 返回
indexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount,
int fromIndex) 判断是否包含字串
static int indexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,
char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount,
int fromIndex) {
if (fromIndex >= sourceCount) {
return (targetCount == 0 ? sourceCount : -1);
}
if (fromIndex < 0) {
fromIndex = 0;
}
if (targetCount == 0) {
return fromIndex;
}
char first = target[targetOffset];
int max = sourceOffset + (sourceCount - targetCount);
for (int i = sourceOffset + fromIndex; i <= max; i++) {
/* Look for first character. */
if (source[i] != first) {
while (++i <= max && source[i] != first);
}
/* Found first character, now look at the rest of v2 */
if (i <= max) {
int j = i + 1;
int end = j + targetCount - 1;
for (int k = targetOffset + 1; j < end && source[j]
== target[k]; j++, k++);
if (j == end) {
/* Found whole string. */
return i - sourceOffset;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
source: 源数组
sourceOffset: 源数组的起始位置
sourceCount: 源数组的字符个数
target: 目标数组
targetOffset: 目标数组的起始位置
targetCount: 目标数组的长度
fromIndex: 从那个位置开始判断
1.先判断判断位置是否大于源数组长度,如果大于判断目标数组是否为空,空则返回长度位置,否则返回不包含
2.判断起始位置是否越界,为什么设置成0?
3.如果目标数组是空串,则返回0 (这就是为什么任意字符串都有一个空的字符子串)
4.拿到目标串的起始位置,并计算出最大循环次数
5.设定好对比字符,开始循环, (++i <= max && source[i] != first) 找到与目标串起始位置的相同的字符,减少循环次数
6.开始一一对比,直到对比长度等于目标串的长度 ,返回位置,否则返回 -1
lastIndexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount,int fromIndex) 判断字串最后出现的位置,倒序查找
static int lastIndexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,
char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount,
int fromIndex) {
/*
* Check arguments; return immediately where possible. For
* consistency, don't check for null str.
*/
int rightIndex = sourceCount - targetCount;
if (fromIndex < 0) {
return -1;
}
if (fromIndex > rightIndex) {
fromIndex = rightIndex;
}
/* Empty string always matches. */
if (targetCount == 0) {
return fromIndex;
}
int strLastIndex = targetOffset + targetCount - 1;
char strLastChar = target[strLastIndex];
int min = sourceOffset + targetCount - 1;
int i = min + fromIndex;
startSearchForLastChar:
while (true) {
while (i >= min && source[i] != strLastChar) {
i--;
}
if (i < min) {
return -1;
}
int j = i - 1;
int start = j - (targetCount - 1);
int k = strLastIndex - 1;
while (j > start) {
if (source[j--] != target[k--]) {
i--;
continue startSearchForLastChar;
}
}
return start - sourceOffset + 1;
}
}
source: 源数组
sourceOffset: 源数组的起始位置
sourceCount: 源数组的字符个数
target: 目标数组
targetOffset: 目标数组的起始位置
targetCount: 目标数组的长度
fromIndex: 从那个位置开始判断
1.先得到倒叙的位置,判断开始位置是否越界,是直接返回 ?
2.将开始位置设定好,并且判断目标数组长度是否为0,是的话直接返回倒序位置(和Indexof最大区别),空串indexof返回0,而lastIndexof返回数组长度的位置
3.获取目标串的最后一个对比字串,得到对比长度
4.(i >= min && source[i] != strLastChar) 找到与目标串起始位置的相同的字符,减少循环次数
5.startSearchForLastChar代表一个标签跳转,循环对比,直到找到长度结束或者找到位置
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) 获取指定位置的字串
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
if (endIndex > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex);
}
int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == value.length)) ? this
: new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}
- 判断起始位置 和 结束位置 是否越界
- 判断长度是否溢出
- 根据条件返回对象
String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) 更换匹配的字符
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) {
if (oldChar != newChar) {
int len = value.length;
int i = -1;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
while (++i < len) {
if (val[i] == oldChar) {
break;
}
}
if (i < len) {
char buf[] = new char[len];
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
buf[j] = val[j];
}
while (i < len) {
char c = val[i];
buf[i] = (c == oldChar) ? newChar : c;
i++;
}
return new String(buf, true);
}
}
return this;
}
1.找到第一次匹配的位置
2.将匹配位置之前的字符赋值,循环开始匹配替换,返回新的字符
3.如果找不到匹配的字符,返回旧的字符串
String[] split(String regex, int limit) 代码分片
public String[] split(String regex, int limit) {
/* fastpath if the regex is a
(1)one-char String and this character is not one of the
RegEx's meta characters ".$|()[{^?*+\\", or
(2)two-char String and the first char is the backslash and
the second is not the ascii digit or ascii letter.
*/
char ch = 0;
if (((regex.value.length == 1 &&
".$|()[{^?*+\\".indexOf(ch = regex.charAt(0)) == -1) ||
(regex.length() == 2 &&
regex.charAt(0) == '\\' &&
(((ch = regex.charAt(1))-'0')|('9'-ch)) < 0 &&
((ch-'a')|('z'-ch)) < 0 &&
((ch-'A')|('Z'-ch)) < 0)) &&
(ch < Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE ||
ch > Character.MAX_LOW_SURROGATE))
{
int off = 0;
int next = 0;
boolean limited = limit > 0;
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
while ((next = indexOf(ch, off)) != -1) {
if (!limited || list.size() < limit - 1) {
list.add(substring(off, next));
off = next + 1;
} else { // last one
//assert (list.size() == limit - 1);
list.add(substring(off, value.length));
off = value.length;
break;
}
}
// If no match was found, return this
if (off == 0)
return new String[]{this};
// Add remaining segment
if (!limited || list.size() < limit)
list.add(substring(off, value.length));
// Construct result
int resultSize = list.size();
if (limit == 0) {
while (resultSize > 0 && list.get(resultSize - 1).length() == 0) {
resultSize--;
}
}
String[] result = new String[resultSize];
return list.subList(0, resultSize).toArray(result);
}
return Pattern.compile(regex).split(this, limit);
}
regex: 分割标志
limit: 分割片段 0:根据分割片段分割,其他数字则按照数字总量分割
1.判断标志是否符合条件,不符合直接调用正则分割返回
2.初始化开始,分割位置和分割数量
3. 循环分割有以下三种情况:
1.分割数量为0,则不会走else分支 ,循环分割完后,如果末尾刚好是个分割字符,则分割多出一个空格,此时 (!limited || list.size() < limit) 会为true,将最后的分割字符添加到list,而在 (resultSize > 0 && list.get(resultSize - 1).length() == 0) 的时候会将最后一个空格字符删除,返回前面分割的list。
2.分割数量不为0,则循环最后一次走else分支,将剩余的字符子串作为一个新的字符串添加到list。此时末尾是没有多余的空格字符。直接返回list。
3.分割数量为负数,则不会将末尾的空格删除。
intern() 本人认为String最大的更新方法
native String intern();
由于intern涉及到jvm的版本变动,对于intern的探索就说大概,以后有机会会在别的文章中再讲 ,下面以jdk1.7为例子。
String str1 = "s";
String str2 = "d";
String str3 = "sd";
String str4 = str1 + str2;
String str5 = new String("sd");
String str6 = str3.intern();
System.out.println(str5.equals(str3));
System.out.println(str5 == str3);
System.out.println(str6 == str3);
System.out.println(str5.intern() == str3);
System.out.println(str5.intern() == str4);
结果如下:
true
false
true
true
false
首先jdk1.7之前常量池是在方法区内的,而jdk1.7将常量池移出了方法区(这里不详述方法区和常量池)。
1.str1 是直接放进常量池的,没有创建对象。s2和s3也同理。
2. s4会在堆创建一个对象,这里就涉及到堆的知识和jvm的字节码解析。附一张图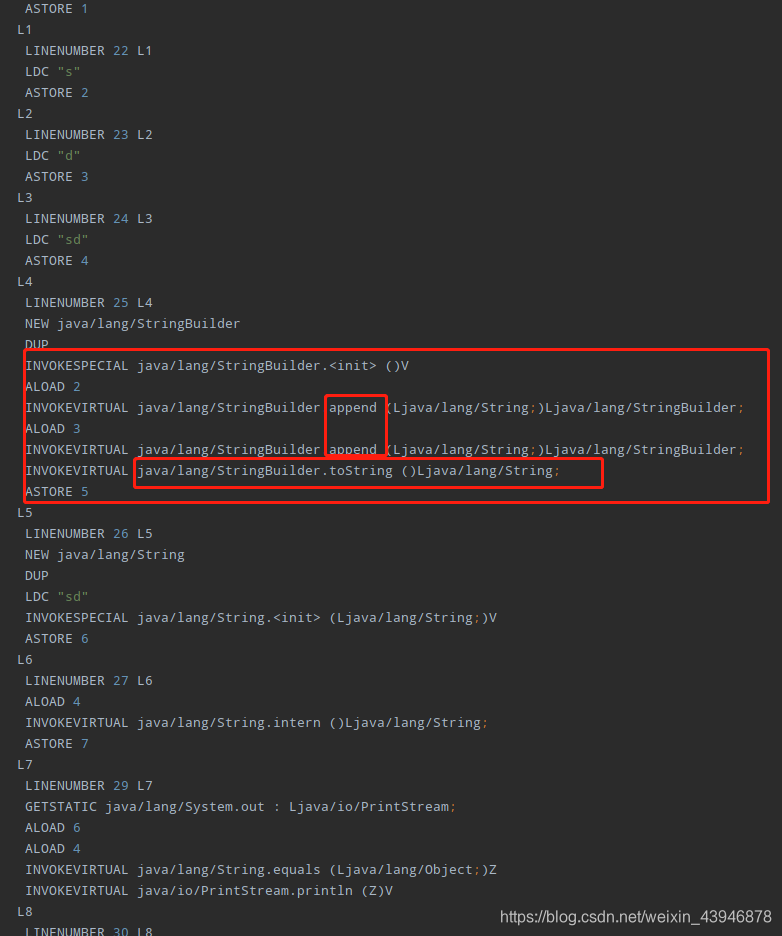
StringBuilder.toString的时候方法会产生一个String对象(StringBuilder会在以后的文章详细讲到)。现在只要知道S4会创建一个对象,S5也同理,而S6却不会,为什么?
4.因为字符串常量默认去常量池里面寻找有没有已经被初始化,如果被初始化了,直接就返回。
那这里有人会问为什么s4不等于s5? 首先 == 对比是比对地址,而s4和s5都在堆创建了对象,
所以对比的时候直接比对了堆地址。而intern方法的作用就是找到常量池的字符地址,把该引用直接返回给栈变量。
从而缩小了内存使用。
如果有讲解错误,请留言联系作者及时删除,避免引导错误。





















 699
699











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








