C++17future类+可变参模板实现线程池
基于C++17提供的future类实现,不再需要我们自己写Any类和Result类,实现时只需打包一个异步执行的函数对象即可。
可变参模板实现,不在需要自己定义一个类来继承task类重写run方法,只需传入一个函数和它所需的参数,或者一个函数对象,甚至一个lambda表达式即可,用一个future类的get方法来异步获取任务返回值。
实现可变参模板线程池的重难点在于submitTask任务提交函数的实现,因为要接收可变参数返回类型不定的任务,会使用到C++的一些高级语法和一些比较高级技巧。
submitTask函数的声明:
template<typename Func, typename... Args>
auto submitTask(Func&& func, Args&&... args) -> std::future<decltype(func(args...))>
用到模板的引用折叠原理,比如给Func传入一个int&时,会替换成int&&&,Func类型会自动推导成int&;Func传入一个int&&时,会替换成int&&&&,Func类型会自动推导成int&&;
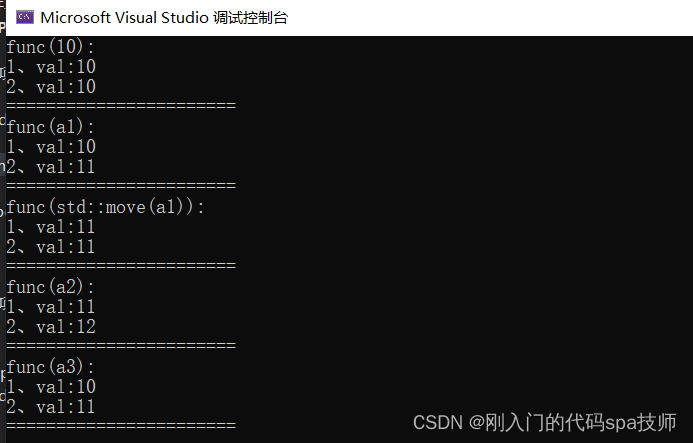
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
void func(T&& val)
{
cout << "1、val:" << val << endl;
T tmp = val;
tmp++;
cout << "2、val:" << val << endl;
cout << "=======================" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a1 = 10;
int& a2 = a1;
int&& a3 = 10;
cout << "func(10):" << endl;
func(10);// 10是右值,引用类型是int&&,T&&推导过程是int&&+&&折叠成int&&,所以T是int,下同
cout << "func(a1):" << endl;
func(a1);// a是左值,不可能用右值引用来引用,所以func推导T为int&,那么T&&->int&+&&折叠成int&
cout << "func(std::move(a1)):" << endl;
func(std::move(a1)); // std::move(a1)是把a转成右值类型,右值引用类型是int&&,所以func推导T为int
cout << "func(a2):" << endl;
func(a2);// a2是左值,不可能用右值引用来引用,所以func推导T为int&,那么T&&->int&+&&折叠成int&
cout << "func(a3):" << endl;
func(a3);// a3是左值,不可能用右值引用来引用,所以func推导T为int&,那么T&&->int&+&&折叠成int&
}
submitTask函数的声明:
template<typename Func, typename... Args>
auto submitTask(Func&& func, Args&&... args) -> std::future<decltype(func(args...))>
decltype是C++的操作符,用于查询表达式的数据类型,在C++11标准制定时引入,主要是为泛型编程而设计,以解决泛型编程中,由于某些类型由模板参数决定,而不好表达的问题。
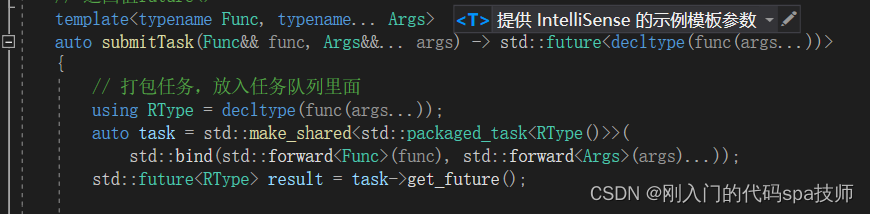
packaged_task可以包装一个函数对象,可以异步的调用这个函数对象,简单来说就是把一个普通的函数对象转换成异步执行的任务。
因为任务实际的执行线程肯定不在submitTask所在的线程,所有需要使用forward类型完美转发。
因为核心代码都在模板函数中实现,就把所有实现过程都写在头文件中,使用时只需包含头文件即可。
threadpool.h:
#pragma once
#ifndef THREADPOOL_H
#define THREADPOOL_H
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <memory>
#include <atomic>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <functional>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <thread>
#include <future>
const int TASK_MAX_THRESHHOLD = INT32_MAX; // INT32_MAX;
const int THREAD_MAX_THRESHHOLD = 1024;
const int THREAD_MAX_IDLE_TIME = 60; // 单位:秒
enum class PoolMode
{
MODE_FIXED, //固定数量的线程
MODE_CACHED //线程可动态增长
};
//线程类型
class Thread
{
public:
//线程 函数对象 类型
using ThreadFunc = std::function<void(int)>;
Thread(ThreadFunc func) : func_(func)
, threadId_(generateId_++)
{ }
~Thread() = default;
//启动线程
void start()
{
// 创建一个线程来执行一个线程函数 pthread_create
std::thread t(func_, threadId_); // C++11来说 线程对象t 和线程函数func_
t.detach(); // 设置分离线程 pthread_detach pthread_t设置成分离线程
}
//获取线程ID
int getId()const
{
return threadId_;
}
private:
ThreadFunc func_;
static int generateId_;
int threadId_; //保存线程id
};
int Thread::generateId_ = 0;
//线程池类型
class ThreadPool
{
public:
ThreadPool()
: initThreadSize_(0)
, taskSize_(0)
, idleThreadSize_(0)
, curThreadSize_(0)
, taskQueMaxThreshHold_(TASK_MAX_THRESHHOLD)
, threadSizeThreshHold_(THREAD_MAX_THRESHHOLD)
, poolMode_(PoolMode::MODE_FIXED)
, isPoolRunning_(false)
{}
~ThreadPool()
{
isPoolRunning_ = false;
// 等待线程池里面所有的线程返回 有两种状态:阻塞 & 正在执行任务中
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(taskQueMtx_);
notEmpty_.notify_all();
exitCond_.wait(lock, [&]()->bool {return threads_.size() == 0; });
}
ThreadPool(const ThreadPool&) = delete;
ThreadPool& operator=(const ThreadPool&) = delete;
//设置线程池工作模式
void setMode(PoolMode mode)
{
if (checkRunningState())
return;
poolMode_ = mode;
}
//设置task任务队列上限阈值
void setTaskQueMaxThreadHold(int threshhold)
{
if (checkRunningState())
return;
taskQueMaxThreshHold_ = threshhold;
}
//设置线程池cache模式下线程阈值
void setThreadMaxThreshHold(int threshhold)
{
if (checkRunningState())
return;
if (poolMode_ == PoolMode::MODE_CACHED)
{
threadSizeThreshHold_ = threshhold;
}
}
// 给线程池提交任务
// 使用可变参模板编程,让submitTask可以接收任意任务函数和任意数量的参数
// pool.submitTask(sum1, 10, 20); 引用折叠原理
// 返回值future<>
template<typename Func, typename... Args>
auto submitTask(Func&& func, Args&&... args) -> std::future<decltype(func(args...))>
{
// 打包任务,放入任务队列里面
using RType = decltype(func(args...));
auto task = std::make_shared<std::packaged_task<RType()>>(
std::bind(std::forward<Func>(func), std::forward<Args>(args)...));
std::future<RType> result = task->get_future();
// 获取锁
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(taskQueMtx_);
// 用户提交任务,最长不能阻塞超过1s,否则判断提交任务失败,返回
if (!notFull_.wait_for(lock, std::chrono::seconds(1),
[&]()->bool { return taskQue_.size() < (size_t)taskQueMaxThreshHold_; }))
{
// 表示notFull_等待1s种,条件依然没有满足
std::cerr << "task queue is full, submit task fail." << std::endl;
auto task = std::make_shared<std::packaged_task<RType()>>(
[]()->RType { return RType(); });
(*task)();
return task->get_future();
}
// 如果有空余,把任务放入任务队列中
// taskQue_.emplace(sp);
// using Task = std::function<void()>;
taskQue_.emplace([task]() {(*task)(); });
taskSize_++;
// 因为新放了任务,任务队列肯定不空了,在notEmpty_上进行通知,赶快分配线程执行任务
notEmpty_.notify_all();
// cached模式 任务处理比较紧急 场景:小而快的任务 需要根据任务数量和空闲线程的数量,判断是否需要创建新的线程出来
if (poolMode_ == PoolMode::MODE_CACHED
&& taskSize_ > idleThreadSize_
&& curThreadSize_ < threadSizeThreshHold_)
{
std::cout << ">>> create new thread..." << std::endl;
// 创建新的线程对象
auto ptr = std::make_unique<Thread>(std::bind(&ThreadPool::threadFunc, this, std::placeholders::_1));
int threadId = ptr->getId();
threads_.emplace(threadId, std::move(ptr));
// 启动线程
threads_[threadId]->start();
// 修改线程个数相关的变量
curThreadSize_++;
idleThreadSize_++;
}
// 返回任务的Result对象
return result;
}
// 开启线程池
void start(int initThreadSize = std::thread::hardware_concurrency())
{
// 设置线程池的运行状态
isPoolRunning_ = true;
// 记录初始线程个数
initThreadSize_ = initThreadSize;
curThreadSize_ = initThreadSize;
// 创建线程对象
for (int i = 0; i < initThreadSize_; i++)
{
// 创建thread线程对象的时候,把线程函数给到thread线程对象
auto ptr = std::make_unique<Thread>(std::bind(&ThreadPool::threadFunc, this, std::placeholders::_1));
int threadId = ptr->getId();
threads_.emplace(threadId, std::move(ptr));
// threads_.emplace_back(std::move(ptr));
}
// 启动所有线程 std::vector<Thread*> threads_;
for (int i = 0; i < initThreadSize_; i++)
{
threads_[i]->start(); // 需要去执行一个线程函数
idleThreadSize_++; // 记录初始空闲线程的数量
}
}
private:
// 定义线程函数
void threadFunc(int threadid)
{
auto lastTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock().now();
// 所有任务必须执行完成,线程池才可以回收所有线程资源
for (;;)
{
Task task;
{
// 先获取锁
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(taskQueMtx_);
std::cout << "tid:" << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< "尝试获取任务..." << std::endl;
// cached模式下,有可能已经创建了很多的线程,但是空闲时间超过60s,应该把多余的线程
// 结束回收掉(超过initThreadSize_数量的线程要进行回收)
// 当前时间 - 上一次线程执行的时间 > 60s
// 每一秒中返回一次 怎么区分:超时返回?还是有任务待执行返回
// 锁 + 双重判断
while (taskQue_.size() == 0)
{
// 线程池要结束,回收线程资源
if (!isPoolRunning_)
{
threads_.erase(threadid); // std::this_thread::getid()
std::cout << "threadid:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " exit!"
<< std::endl;
exitCond_.notify_all();
return; // 线程函数结束,线程结束
}
if (poolMode_ == PoolMode::MODE_CACHED)
{
// 条件变量,超时返回了
if (std::cv_status::timeout ==
notEmpty_.wait_for(lock, std::chrono::seconds(1)))
{
auto now = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock().now();
auto dur = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(now - lastTime);
if (dur.count() >= THREAD_MAX_IDLE_TIME
&& curThreadSize_ > initThreadSize_)
{
// 开始回收当前线程
// 记录线程数量的相关变量的值修改
// 把线程对象从线程列表容器中删除 没有办法 threadFunc《=》thread对象
// threadid => thread对象 => 删除
threads_.erase(threadid); // std::this_thread::getid()
curThreadSize_--;
idleThreadSize_--;
std::cout << "threadid:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " exit!"
<< std::endl;
return;
}
}
}
else
{
// 等待notEmpty条件
notEmpty_.wait(lock);
}
}
idleThreadSize_--;
std::cout << "tid:" << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< "获取任务成功..." << std::endl;
// 从任务队列种取一个任务出来
task = taskQue_.front();
taskQue_.pop();
taskSize_--;
// 如果依然有剩余任务,继续通知其它得线程执行任务
if (taskQue_.size() > 0)
{
notEmpty_.notify_all();
}
// 取出一个任务,进行通知,通知可以继续提交生产任务
notFull_.notify_all();
} // 就应该把锁释放掉
// 当前线程负责执行这个任务
if (task != nullptr)
{
task(); // 执行function<void()>
}
idleThreadSize_++;
lastTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock().now(); // 更新线程执行完任务的时间
}
}
//检查pool运行状态
bool checkRunningState() const
{
return isPoolRunning_;
}
private:
//std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Thread>> threads_; //线程列表
std::unordered_map<int, std::unique_ptr<Thread>> threads_; //线程列表
int initThreadSize_; //初始的线程数量
int threadSizeThreshHold_; //线程数量上限阈值
std::atomic_int curThreadSize_; //当前线程池里线程的总数量
std::atomic_int idleThreadSize_; //记录空闲线程的数量
// Task => 函数对象
using Task = std::function<void()>;
std::queue<Task> taskQue_; //任务队列
std::atomic_int taskSize_; //任务的数量
int taskQueMaxThreshHold_; //任务队列数量上限阈值
std::mutex taskQueMtx_; //保证任务队列的线程安全
std::condition_variable notFull_; //表示任务队列不满
std::condition_variable notEmpty_; //表示任务队列不空
std::condition_variable exitCond_; //等到线程资源全部回收
PoolMode poolMode_; //当前线程池的工作模式
std::atomic_bool isPoolRunning_; //表示当前线程池的启动状态
};
#endif // !THREADPOOL_H
使用示例:
//
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <thread>
#include <future>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
#include "threadpool.h"
int sum1(int a, int b)
{
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(2));
// 比较耗时
return a + b;
}
int sum2(int a, int b, int c)
{
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(2));
return a + b + c;
}
// io线程
void io_thread(int listenfd)
{
}
// worker线程
void worker_thread(int clientfd)
{
}
int main()
{
ThreadPool pool;
// pool.setMode(PoolMode::MODE_CACHED);
pool.start(2);
future<int> r1 = pool.submitTask(sum1, 1, 2);
future<int> r2 = pool.submitTask(sum2, 1, 2, 3);
future<int> r3 = pool.submitTask([](int b, int e)->int {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = b; i <= e; i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
}, 1, 100);
future<int> r4 = pool.submitTask([](int b, int e)->int {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = b; i <= e; i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
}, 1, 100);
future<int> r5 = pool.submitTask([](int b, int e)->int {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = b; i <= e; i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
}, 1, 100);
//future<int> r4 = pool.submitTask(sum1, 1, 2);
cout << r1.get() << endl;
cout << r2.get() << endl;
cout << r3.get() << endl;
cout << r4.get() << endl;
cout << r5.get() << endl;
//packaged_task<int(int, int)> task(sum1);
future <=> Result
//future<int> res = task.get_future();
task(10, 20);
//thread t(std::move(task), 10, 20);
//t.detach();
//cout << res.get() << endl;
/*thread t1(sum1, 10, 20);
thread t2(sum2, 1, 2, 3);
t1.join();
t2.join();*/
}























 924
924











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










