一。概念
管道的概念
管道在Unix和Linux中一般用于将当前命令的输出结果作为下一个命令的参数。
MongoDB的聚合管道将MongoDB文档在一个管道处理完毕后将结果传递给下一个管道处理。管道操作是可以重复的。
聚合框架
MongoDB中聚合(aggregate)主要用于处理数据(诸如统计平均值,求和等),并返回计算后的数据结果。
聚合框架是MongoDB的高级查询语言,它允许我们通过转换和合并多个文档中的数据来生成新的单个文档中不存在的信息。
聚合管道操作主要包含下面几个部分:
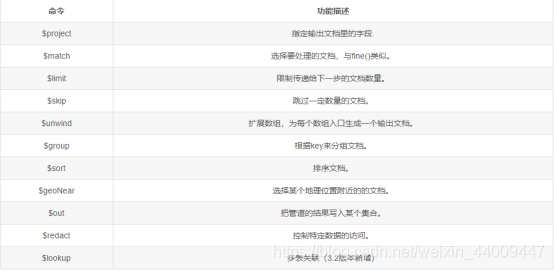
二。集合示例准备
假设有学生、班级以及学科集合,批量添加语句如下:
1.学生集合批量插入:
//student批量插入
db.student.insertMany([{
"id": "1",
"name": "小明",
"age": NumberInt(12),
"sex": "男",
"course": ["数学", "语文", "英语"]
}, {
"id": "2",
"name": "小章",
"age": NumberInt(13),
"sex": "男",
"course": ["数学", "语文"]
}, {
"id": "3",
"name": "小九",
"age": NumberInt(12),
"sex": "女",
"course": ["数学"]
}]);

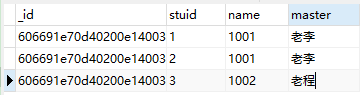
2.班级的批量插入:
//class批量插入
db.class.insertMany([{
"stuid": "1",
"name": "1001",
"master":"老李"
}, {
"stuid": "2",
"name": "1001",
"master":"老李"
}, {
"stuid": "3",
"name": "1002",
"master":"老程"
}]);
3.课程的批量插入:
//course批量插入
db.course.insertMany([{
"name": "数学",
"master":"老李"
}, {
"name": "语文",
"master":"老程"
}, {
"name": "英语",
"master":"老梁"
}]);

三。各个操作符的用法
1.$lookup
主要功能:
是将每个输入待处理的文档,经过$lookup 阶段的处理,输出的新文档中会包含一个新生成的数组列(户名可根据需要命名新key的名字 )。
数组列存放的数据是来自被Join 集合的适配文档,如果没有,集合为空(即 为[ ])
基本语法:
{
$lookup:
{
from: <collection to join>,
localField: <field from the input documents>,
foreignField: <field from the documents of the "from" collection>,
as: <output array field>
}
}
参数说明
- from:同一个数据库下等待被Join的集合。
- localField: 源集合中的match值,如果输入的集合中,某文档没有localField,这个Key(Field),在处理的过程中,会默认为此文档含有 localField:null的键值对。
- foreignField:待Join的集合的match值,如果待Join的集合中,文档没有foreignField值,在处理的过程中,会默认为此文档含有
foreignField:null的键值对。 - as:为输出文档的新增值命名。如果输入的集合中已存在该值,则会覆盖掉。
示例:
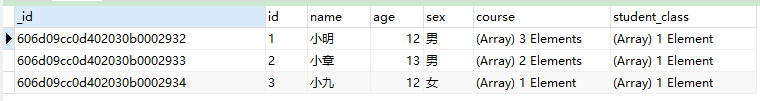
使用$lookup联合student集合以及class集合查询学生的个人信息以及班级信息:
//管道查询,联合查询
db.getCollection("student").aggregate([{
$lookup: {
from: "class",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "stuid",
as: "student_class"
}
}])
2.$match
$match用于过滤数据,只输出符合条件的文档
示例:
1.再使用$match过滤进行条件查询,查询小明的信息:
//管道查询,联合查询,$match过滤条件查询
db.getCollection("student").aggregate([{
$lookup: {
from: "class",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "stuid",
as: "student_class"
}
}, {
$match: {
name: "小明"
}
}])

2.联表查询,两张表都含有过滤条件:
//两表关联,每个表都有条件
db.getCollection('student').aggregate([
{
$match: {
name: "小明"
}
},
{
$lookup: {
from: "class",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "stuid",
as: "student_class"
}
},
{
$match: {
"student_class.master": "老李"
}
}
])

3.$unwind
$unwind是将文档中的某一个数组类型字段拆分成多条,每条包含数组中的一个值。
示例:
1.使用$unwind便利学生信息中的课程数组
//便利数组数据
db.getCollection('student').aggregate([
{
$unwind: "$course"
}
])

2.使用$unwind便利学生信息中的课程数组,再进行联表查询:
//管道查询,联合查询,$unwind数组便利
db.getCollection('student').aggregate([
{
$unwind: "$course"
},
{
$lookup: {
from: "class",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "stuid",
as: "student_class"
}
}
])

3.使用$unwind便利学生信息中的课程数组,再进行联表查询,最后加上过滤条件:
//管道查询,联合查询,$unwind数组便利,$match过滤条件查询
db.getCollection('student').aggregate([
{
$unwind: "$course"
},
{
$lookup: {
from: "class",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "stuid",
as: "student_class"
}
},
{
$match: {
name: "小明"
}
}
])

4.$project
$project可以用来提取想要的字段,1表示要该字段,0表示不要该字段,也可以对返回的字段进行重命名:
//管道查询,联合查询,$unwind数组便利,$match过滤条件查询,$project设置需要返回的字段属性
db.getCollection('student').aggregate([
{
$unwind: "$course"
},
{
$lookup: {
from: "class",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "stuid",
as: "student_class"
}
},
{
$match: {
name: "小明"
}
},
{
$project: {
name: 1,
age: 1
}
}
])

5.$limit
限制聚合管道返回的文档数。
示例:
返回前两条数据:
//返回前两条数据
db.getCollection("student").aggregate([{
$lookup: {
from: "class",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "stuid",
as: "student_class"
}
}, {
$limit: 2
}])

6.$skip
跳过指定数量的文档,并返回余下的文档。
示例:
跳过第一个文档并返回两个文档,一般适用于做分页处理:
//跳过第一个文档并返回两个文档
db.getCollection("student").aggregate([{
$lookup: {
from: "class",
localField: "id",
foreignField: "stuid",
as: "student_class"
}
}, {
$skip: 1
}, {
$limit: 2
}])
注意:$skip语句应该在$limit之前。
7.$group
分组查询,相当于mysql的group by语句。
示例:
班级分组查询:
//分组查询
db.getCollection("class").aggregate([{
$group: {
_id: "$master",
count: {
$sum: 1
}
}
}])

提示:$sum函数为求和函数。
8.$sort
将查询结果按照某个字段进行排序,相当于mysql的order by语句,1表示升序,-1表示降序,默认为升序显示。
示例:
将学生集合按照id号降序排序:
//排序
db.getCollection("student").aggregate([{
$sort: {
id: -1
}
}])








 本文详细介绍MongoDB聚合框架中的关键操作符如$lookup、$match、$unwind等,通过实例演示如何在学生、班级和课程集合间进行数据查询、联接和筛选,帮助读者理解聚合管道在数据处理中的强大功能。
本文详细介绍MongoDB聚合框架中的关键操作符如$lookup、$match、$unwind等,通过实例演示如何在学生、班级和课程集合间进行数据查询、联接和筛选,帮助读者理解聚合管道在数据处理中的强大功能。


















 646
646

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










