概述
克鲁斯卡尔算法是求连通网的最小生成树的另一种方法。与普里姆算法不同,它的时间复杂度为O(eloge)(e为网中的边数),所以,适合于求边稀疏的网的最小生成树 。
克鲁斯卡尔(Kruskal)算法从另一途径求网的最小生成树。其基本思想是:假设连通网G=(V,E),令最小生成树的初始状态为只有n个顶点而无边的非连通图T=(V,{}),图中每个顶点自成一个连通分量。在E中选择代价最小的边,若该边依附的顶点分别在T中不同的连通分量上,则将此边加入到T中;否则,舍去此边而选择下一条代价最小的边。依此类推,直至T中所有顶点构成一个连通分量为止 。
图解
1.此算法需要对边集合从小到大排序。
在下面的图解中,红色的边表示已经被淘汰了,绿色的代表选中了。
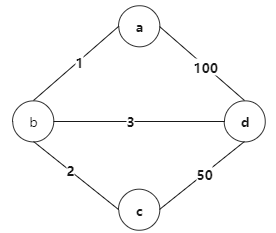
题目初始状态
{a} {b} {c} {d}
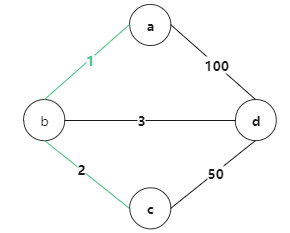
现在最小的边是1
因为a,b 没有联通起来,所以要 边长为1 的边,变绿色 {a,b} {c} {d}
现在最小的边是2
因为b,c 没有联通起来,所以要 边长为2 的边,变绿色 {a,b,c} {d}
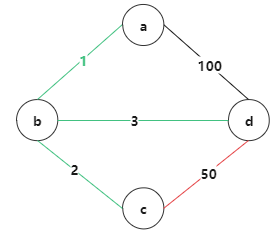
现在最小的边是3
因为b,d 没有联通起来,所以要 边长为3 的边,变绿色 {a,b,c, d}
现在最小的边是50
因为c,d 联通起来了,所以不需要边长为50 的边,变红色 {a,b,c, d}
现在最小的边是100
因为a,d 联通起来了,所以不需要边长为100 的边,变红色 {a,b,c, d}
代码
Edge .java
public class Edge {
public int weight;//边的权重
public Node from;//边的起始点
public Node to;//边的结束点
public Edge(int weight, Node from, Node to) {
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
}
Node.java
public class Node {
public int value;//节点号
public int in;//入度
public int out;//初度
public ArrayList<Node> nexts;//相邻点
public ArrayList<Edge> edges;//边
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
in = 0;
out = 0;
nexts = new ArrayList<>();
edges = new ArrayList<com.algorithm.图.Edge>();
}
}
Graph .java
public class Graph {
public HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes;//点和节点号
public HashSet<Edge> edges;//边
public Graph() {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
edges = new HashSet<>();
}
}
克鲁斯卡尔算法需要判断集合是否联通,所以要用到并查集的知识。
Kruskal.java
public class Kruskal {
// Union-Find Set
public static class UnionFind {
// key 某一个节点, value key节点往上的节点
private HashMap<Node, Node> fatherMap;
// key 某一个集合的代表节点, value key所在集合的节点个数
private HashMap<Node, Integer> sizeMap;
public UnionFind() {
fatherMap = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
sizeMap = new HashMap<Node, Integer>();
}
public void makeSets(Collection<Node> nodes) {
fatherMap.clear();
sizeMap.clear();
for (Node node : nodes) {
fatherMap.put(node, node);
sizeMap.put(node, 1);
}
}
private Node findFather(Node n) {
Stack<Node> path = new Stack<>();
while(n != fatherMap.get(n)) {
path.add(n);
n = fatherMap.get(n);
}
while(!path.isEmpty()) {
fatherMap.put(path.pop(), n);
}
return n;
}
public boolean isSameSet(Node a, Node b) {
return findFather(a) == findFather(b);
}
public void union(Node a, Node b) {
if (a == null || b == null) {
return;
}
Node aDai = findFather(a);
Node bDai = findFather(b);
if (aDai != bDai) {
int aSetSize = sizeMap.get(aDai);
int bSetSize = sizeMap.get(bDai);
if (aSetSize <= bSetSize) {
fatherMap.put(aDai, bDai);
sizeMap.put(bDai, aSetSize + bSetSize);
sizeMap.remove(aDai);
} else {
fatherMap.put(bDai, aDai);
sizeMap.put(aDai, aSetSize + bSetSize);
sizeMap.remove(bDai);
}
}
}
}
public static class EdgeComparator implements Comparator<Edge> {
@Override
public int compare(Edge o1, Edge o2) {
return o1.weight - o2.weight;
}
}
public static Set<Edge> kruskalMST(Graph graph) {
UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind();
unionFind.makeSets(graph.nodes.values());
// 从小的边到大的边,依次弹出,小根堆!
PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new EdgeComparator());
for (Edge edge : graph.edges) { // M 条边
priorityQueue.add(edge); // O(logM)
}
Set<Edge> result = new HashSet<>();
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) { // M 条边
Edge edge = priorityQueue.poll(); // O(logM)
if (!unionFind.isSameSet(edge.from, edge.to)) { // O(1)
result.add(edge);
unionFind.union(edge.from, edge.to);
}
}
return result;
}
}
























 3809
3809











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








