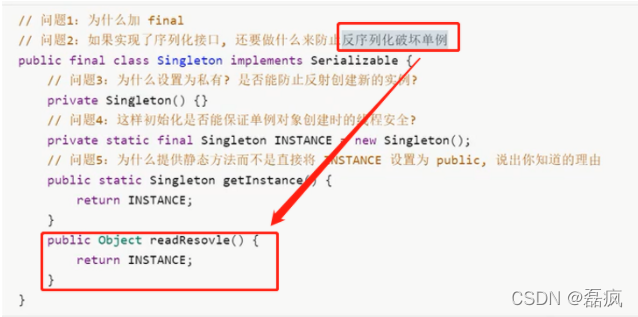
1.饿汉式问题
2. 哲学家就餐问题——死锁
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Chopstick c1 = new Chopstick("1");
Chopstick c2 = new Chopstick("2");
Chopstick c3 = new Chopstick("3");
Chopstick c4 = new Chopstick("4");
Chopstick c5 = new Chopstick("5");
new Philosopher("苏格拉底",1,c1,c2).start();
new Philosopher("柏拉图",2,c2,c3).start();
new Philosopher("亚里士多德",3,c3,c4).start();
new Philosopher("赫拉克利特",4,c4,c5).start();
new Philosopher("阿基米德",5,c5,c1).start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Philosopher")
class Philosopher extends Thread{
private Chopstick left;
private Chopstick right;
private int index;
public Philosopher(String name, int index , Chopstick left, Chopstick right){
super(name);
this.index = index;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if(index %2 == 0){
synchronized (left){
SleepHelper.sleepSeconds(1 + index);
log.debug(left.toString() + "左");
synchronized (right){
log.debug(left.toString() + "右");
eat();
}
}
}else {
synchronized (right){
log.debug(left.toString() + "右");
synchronized (left){
log.debug(left.toString() + "左");
eat();
}
}
}
}
}
private void eat(){
log.debug("eating...");
SleepHelper.sleepSeconds(1);
}
}
class Chopstick{
String name;
public Chopstick(String name){
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "筷子{" + name + '}';
}
}
class SleepHelper{
public static void sleepSeconds(long seconds){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.交替输出
方法一:LockSupport
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
@Slf4j
public class Test02 {
static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] ai = "123456".toCharArray();
char[] ac = "ABCDEF".toCharArray();
t1 = new Thread(()->{
for (char c : ai){
log.debug("{}",c);
LockSupport.unpark(t2);
LockSupport.park();
}
},"t1");
t2 = new Thread(()->{
for (char c : ac){
LockSupport.park();
log.debug("{}",c);
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
}
},"t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
方法二:synchronized 、wait 、 notify
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
@Slf4j
public class Test03 {
static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null;
public static void main(String[] args){
final Object o = new Object();
char[] ai = "123456".toCharArray();
char[] ac = "ABCDEF".toCharArray();
t1 = new Thread(()->{
synchronized (o){
for (char c : ai){
log.debug("{}",c);
o.notify();
try {
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify();
}
},"t1");
t2 = new Thread(()->{
synchronized (o){
for (char c : ac){
o.notify();
log.debug("{}",c);
try {
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify();
}
},"t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
方法三:reentrantLock方式
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
@Slf4j
public class Test04 {
static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null;
public static void main(String[] args){
char[] ai = "123456".toCharArray();
char[] ac = "ABCDEF".toCharArray();
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
t1 = new Thread(()->{
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
lock.lock();
try{
for (char c : ai){
log.debug("{}",c);
condition2.signal();
condition1.await();
}
condition2.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
},"t1");
t2 = new Thread(()->{
lock.lock();
try{
for (char c : ac){
log.debug("{}",c);
latch.countDown();
condition1.signal();
condition2.await();
}
condition1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
},"t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
交替输入ABC
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
@Slf4j
public class Test05 {
static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null, t3 = null;
public static void main(String[] args){
int num = 3;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
CountDownLatch latch1 = new CountDownLatch(1);
CountDownLatch latch2 = new CountDownLatch(1);
t1 = new Thread(()->{
lock.lock();
try{
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if(i == 0) latch1.countDown();
log.debug("A");
condition2.signal();
condition1.await();
}
condition2.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
},"t1");
t2 = new Thread(()->{
try {
latch1.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
lock.lock();
try{
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if(i == 0) latch2.countDown();
log.debug("B");
condition3.signal();
condition2.await();
}
condition3.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
},"t2");
t3 = new Thread(()->{
try {
latch1.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
lock.lock();
try{
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if(i == 0) latch2.countDown();
log.debug("C");
condition1.signal();
condition3.await();
}
condition1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
},"t3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}






















 588
588











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








