二分是一种查询速度为log2n的算法,其使用条件是该数列必须具有单调性
我们把小于x的的第一个位置称为下界lower ,把大于x的第一个称为上界upper
先对STL中的二分函数做个总结
stl二分中查找某个元素使用binary_search(a,a+sizie,所需查询的值)存在返回真 不存在返回假
lower_bound(val): 返回容器中第一个值【大于或等于】val的元素的iterator位置。
lower_bound()在first和last中的前闭后开区间进行二分查找,返回大于或等于val的第一个元素位置。如果所有元素都小于val,则返回last的位置
upper_bound(val): 返回容器中第一个值【大于】val的元素的iterator位置。函数upper_bound()返回的在前闭后开区间查找的关键字的上界,返回大于val的第一个元素位置
若不存在也返回last
lowerbound和upperbound的区间都是左闭右开,并且如果没找到返回的迭代器是越界的
要注意的是判断是否查询成功的条件
int pos = lower_bound(a,a+n,x)-a;
if(a[pos]!=x || pos<0 || pos>=n)///判断值是否一样,并且地址是否在范围内
cout << "-1 << endl;
STL使用起来方便简洁 但是有些过于死板 于是手写版的也是很有必要滴
int findupper(int x)///二分查找上界
{
int m,r=n,l=-1;
while(l+1<r)
{
m=(l+r)/2;
if(s[m]<=x)
{
l=m;
}
else
{
r=m;
}
}
return r;
}
int findlower(int x)//查找下界
{
int m,r=n,l=-1;
while(l+1<r)
{
m=(l+r)/2;
if(s[m]<x)
l=m;
else
r=m;
}
return r;
}
看的出 find_upper与find_lower差别就在于一个等号
下面是查询对照表
查询目标 find_upper_bound的用法 find_lower_bound的用法
大于x的第一个位置 find_upper_bound(x) find_lower_bound(x+1)
x出现的第一个位置 find_upper_bound(x-1) find_lower_bound(x)
小于x的第一个位置 find_upper_bound(x-1)-1 find_lower_bound(x)-1
x出现的最后位置 find_upper_bound(x)-1 find_lower_bound(x+1)-1
由此可以看出对于二分的上下界(对x而言)其区间也是左闭右开的 即下界是可以取到x的 而上界是是在大于x的第一个位置
以下是二分各种常见用法
1.二分的普通单调数组全面查询
#include<stdio.h>
int s[100005],n;
int findupper(int x)
{
int m,r=n,l=-1;
while(l+1<r)
{
m=(l+r)/2;
if(s[m]<=x)
{
l=m;
}
else
{
r=m;
}
}
return r;
}
int findlower(int x)
{
int m,r=n,l=-1;
while(l+1<r)
{
m=(l+r)/2;
if(s[m]<x)
l=m;
else
r=m;
}
return r;
}
main()
{
int i,z,m,a,b,c;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
scanf("%d",&s[i]);
scanf("%d",&m);
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d",&a);
if(a==0)///x出现的最大下标
{
scanf("%d",&b);
z=findupper(b);
if(s[z-1]!=b)
{
printf("-1\n");
}
else
{
printf("%d\n",z-1);
}
}
else if(a==1)///x出现的最小下标
{
scanf("%d",&b);
z=findlower(b);
if(s[z]!=b)
{
printf("-1\n");
}
else
{
printf("%d\n",z);
}
}
else if(a==2)///查询大于等于x且小于等于y的数字个数
{
scanf("%d%d",&b,&c);
int z1=findlower(b);
z=findupper(c);
printf("%d\n",z-z1);
}
else if(a==3)///查询比x大且下标最小的数字的大小
{
scanf("%d",&b);
z=findupper(b);
if(z==n)
{
printf("-1\n");
}
else
{
printf("%d\n",s[z]);
}
}
else///查询比X小且下标最大的数字的大小
{
scanf("%d",&b);
z=findlower(b);
if(z-1==-1)
{
printf("-1\n");
}
else
{
printf("%d\n",s[z-1]);
}
}
}
}
2.根据某种题给条件查询
例如 codeforce 165B
One day a highly important task was commissioned to Vasya — writing a program in a night. The program consists of n lines of code. Vasya is already exhausted, so he works like that: first he writes v lines of code, drinks a cup of tea, then he writes as much as lines, drinks another cup of tea, then he writes lines and so on: , , , …
The expression is regarded as the integral part from dividing number a by number b.
The moment the current value equals 0, Vasya immediately falls asleep and he wakes up only in the morning, when the program should already be finished.
Vasya is wondering, what minimum allowable value v can take to let him write not less than n lines of code before he falls asleep.
Input
The input consists of two integers n and k, separated by spaces — the size of the program in lines and the productivity reduction coefficient, 1 ≤ n ≤ 109, 2 ≤ k ≤ 10.
Output
Print the only integer — the minimum value of v that lets Vasya write the program in one night.
SampleInput 1
7 2
SampleOutput 1
4
SampleInput 2
59 9
SampleOutput 2
54
Note
In the first sample the answer is v = 4. Vasya writes the code in the following portions: first 4 lines, then 2, then 1, and then Vasya falls asleep. Thus, he manages to write 4 + 2 + 1 = 7 lines in a night and complete the task.
In the second sample the answer is v = 54. Vasya writes the code in the following portions: 54, 6. The total sum is 54 + 6 = 60, that’s even more than n = 59.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int check(int v,int k)
{
int sum = 0 ;
while(v)
{
sum += v;
v /= k;
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int n,k;
cin >> n >> k;
int l = 0;
int r = 1e9+5;
while(l+1<r)
{
int mid = l+r >> 1;
if(check(mid,k)<n)
l = mid;
else
r = mid;
}
cout << r << endl;
return 0;
}
3.找出某个方式程的解
终极考验:高智商一定要做一道专业性强的题!
在金融中,我们有时会用内部收益率IRR来评价项目的投资财务效益,它等于使得投资净现值NPV等于0的贴现率。换句话说,给定项目的期数T、初始现金流CF0和项目各期的现金流CF1, CF2, …,CFT,IRR是下面方程的解:
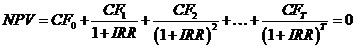
为了简单起见,本题假定:除了项目启动时有一笔投入(即初始现金流CF0 < 0)之外,其余各期均能赚钱(即对于所有i=1,2,…,T,CFi > 0)。根据定义,IRR可以是负数,但必须大于-1。
Input
输入文件最多包含25组测试数据,每个数据占两行,第一行包含一个正整数T(1<=T<=10),表示项目的期数。第二行包含T+1个整数:CF0, CF1, CF2, …, CFT,其中CF0 < 0, 0 < CFi < 10000 (i=1,2,…,T)。T=0表示输入结束,你的程序不应当处理这一行。
Output
对于每组数据,输出仅一行,即项目的IRR,四舍五入保留小数点后两位。如果IRR不存在,输出"No",如果有多个不同IRR满足条件,输出"Too many"(均不含引号)
SampleInput
1
-1 2
2
-8 6 9
0
SampleOutput
1.00
0.50
利用二分来加速查找过程
#include <stdio.h>
int a[15];
int main()
{
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n) && n )
{
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
double l = -1;
double r = 1e8;
double mid , t;
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < 50;i++)
{
sum = 0,t = 1.0;
mid = (l+r)/2;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++)
{
t=t/(1.0+mid);
sum += t*a[i];
}
if(sum+a[0]>0)
l = mid;
else
r = mid;
}
printf("%.2f\n",mid);
}
return 0;
}
POJ 1064
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
double a[100005];
main()
{
int n,k,i,j,b;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%lf",&a[i]);
double l,r,m;
l=0,r=9999999.0;
for(j=0;j<100;j++)
{
b=0;
m=(l+r)/2.0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
b+=(int)(a[i]/m);
if(b>=k)
l=m;
else
r=m;
}
printf("%.2f\n",floor(l*100)/100);
}
4.高精度的二分
HDU2289
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
double pi=acos(-1);
double p(double r,double R,double H,double V)
{
double l=0,r1=100.0,v,m,r2;
while(r1-l>=1e-7)
{
m=(l+r1)/2;
r2=m/H*(R-r)+r;
v=(pi*m*(r2*r2+r*r+r*r2))/3.0;
if(v>V)
r1=m;
else
l=m;
}
return m;
}
int main()
{
double r,R,H,V,h;
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&r,&R,&H,&V);
h=p(r,R,H,V);
printf("%f\n",h);
}
}





















 559
559











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








