const PENDDING = 'pending'
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const REJECTED = 'rejected'
class MyPromise {
constructor(executor) {
//初始状态
this.status = PENDDING
//存放成功的值
this.value = undefined
//存放失败的原因
this.reason = undefined
//成功存放成功的回调
this.onResolvedCallbacks = []
//失败存放失败的回调
this.onRejectedCallbacks = []
const resolve = (data) => {
//状态是pending才能修改状态
if (this.status === PENDDING) {
this.status = FULFILLED
this.value = data
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => fn())
}
}
const reject = (reason) => {
//状态是pending才能修改状态
if (this.status === PENDDING) {
this.status = REJECTED
this.reason = reason
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => fn())
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
resolvedPromise(promise, result, resolve, reject) {
if (promise === result) reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise'))
// 在 JavaScript 中,函数也是一种对象,因此也可以具有 then 方法。如果 result 是一个函数并且具有 then 方法,那么就会按照 Promise/A+ 规范来处理它,调用它的 then 方法,并根据其返回值来决定当前 Promise 的状态和值。
if ((result && typeof result === 'object') || typeof result === 'function') {
//处理嵌套的Promise对象思路是使用递归
//如果传入的 result 是一个对象或者一个函数的话,令 then = result.then。
//然后判断 then 是否是一个函数,如果是就说明 result 是一个 promise 对象,那就调用 then,并且 把 result 作为 this,然后在成功回调中继续调用 resolvedPromise 并且把拿到的值作为新的 result 传入,其他不变。
//如果 then 不是一个函数,那就说明 result 是一个函数或者是一个普通对象,那就直接 resolve。
//如果传入的 result 不是一个对象且不是一个函数,就直接 resolve 即可,同时这也是该递归的最终状态。
//为了保证成功和失败只能调用其中一个,声明变量 called 来作为标记。
//使用 try...catch 来进行异常处理。
let called
try {
let then = result.then
if (typeof then === 'function') {
then.call(
result,
(value) => {
if (called) return
called = true
this.resolvedPromise(promise, value, resolve, reject)
},
(reason) => {
if (called) return
called = true
reject(reason)
}
)
} else {
if (called) return
called = true
resolve(result)
}
} catch (error) {
if (called) return
called = true
reject(error)
}
} else {
resolve(result)
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
//处理then的参数,如果参数不是函数,那么忽略它
if (typeof onFulfilled !== 'function')
onFulfilled = (value) => {
return value
}
if (typeof onRejected !== 'function')
onRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason
}
let promise = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
//使用settimeout处理then方法的异步执行
setTimeout(() => {
try {
this.resolvedPromise(promise, onFulfilled(this.value), resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
this.resolvedPromise(promise, onRejected(this.reason), resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
}
if (this.status === PENDDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() =>
setTimeout(() => {
try {
this.resolvedPromise(promise, onFulfilled(this.value), resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
)
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() =>
setTimeout(() => {
try {
this.resolvedPromise(promise, onRejected(this.reason), resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
)
}
})
return promise
}
catch(err) {
return this.then(null, err)
}
static resolve(value) {
let promise = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
promise.resolvedPromise(promise, value, resolve, reject)
})
})
return promise
}
static reject(reason) {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(reason)
})
}
static all(promises) {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
let results = []
let count = 0
let index = 0
for (let promise of promises) {
let resultIndex = index
index += 1
MyPromise.resolve(promise).then(
(e) => {
count += 1
results[resultIndex] = e
if (count === index) resolve(results)
},
(reason) => {
reject(reason)
}
)
}
if (index === 0) resolve(results)
})
}
static race(promises) {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
promises.forEach((promise) => {
MyPromise.resolve(promise).then(resolve, reject)
})
})
}
}
//以下是用于测试的代码
MyPromise.defer = MyPromise.deferred = function () {
let dfd = {}
dfd.promise = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
dfd.resolve = resolve
dfd.reject = reject
})
return dfd
}
module.exports = MyPromise安装测试脚本
npm install -g promises-aplus-tests然后在 MyPromise 所在文件 (promise.js) 的目录下执行:
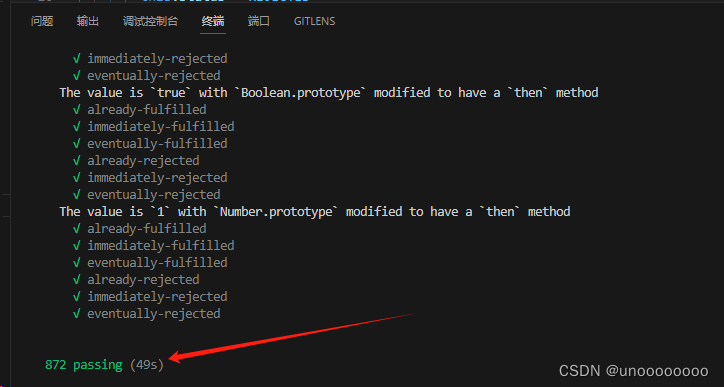
promises-aplus-tests promise.js





















 1208
1208

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








