1.栈(Stack)
1.1 概念
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据在栈顶。
1.2 顺序表实现栈代码实例:
public class MyStack<T> {
public T[] elem;
public int top;//下标
public MyStack() {
this.elem = (T[]) new Object[10];
this.top = 0;
}
private boolean isFull() {
return this.top == this.elem.length;
}
public void push(T val) {
if(isFull()) {
return;
}
this.elem[this.top] = val;
this.top++;
}
private boolean isEmpty() {
return this.top == 0;
}
//出栈
public T pop() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
T tmp = this.elem[top-1];//保存你出栈的数据
this.top--;//真正的出栈
return tmp;
}
//得到栈顶元素,但是不出栈 peek
public T getTop() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return this.elem[top-1];
}
}
测试代码:
public static void main1(String[] args) {
MyStack<Integer> myStack = new MyStack<>();
myStack.push(10);
myStack.push(20);
myStack.push(30);
myStack.push(40);
System.out.println(myStack.pop());//40
System.out.println(myStack.getTop());//30
2.队列(Queue)
2.1 概念
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(FirstIn First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(Tail/Rear) 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头(Head/Front)。
2.2 链表实现队列代码实例:
public class MyListQueue {
static class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public Node front;
public Node rear;
public int usedSize;
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
//入队
public void offer(int data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
if(isEmpty()) {
this.front = node;
this.rear = front;
}else {
this.rear.next = node;
this.rear = node;
}
this.usedSize++;
}
public int poll() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("队列为空");
}
int val = this.front.data;
this.front = this.front.next;
this.usedSize--;
return val;
}
public int peek() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("队列为空");
}
return this.front.data;
}
}
测试代码:
public static void main2(String[] args) {
MyListQueue myListQueue = new MyListQueue();
myListQueue.offer(1);
myListQueue.offer(2);
myListQueue.offer(3);
myListQueue.offer(4);
System.out.println(myListQueue.poll());//1
System.out.println(myListQueue.peek());//2
}
2.3 循环队列
实际中我们有时还会使用一种队列叫循环队列。如操作系统课程讲解生产者消费者模型时可以就会使用循环队列。环形队列通常使用数组实现。
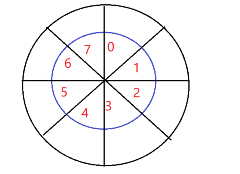
同一般队列一样,也有队头元素front下标和rear队尾下标。
2.4 代码实例:
public class MyCircularQueue {
public int[] elem;
public int front;
public int rear;
public int usedSize;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.elem = new int[k];
this.front = 0;
this.rear = 0;
this.usedSize = 0;
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()) {
return false;
}
this.elem[this.rear] = value;
this.rear = (this.rear+1)%this.elem.length;
this.usedSize++;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
this.front = (this.front+1)%this.elem.length;
this.usedSize--;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return this.elem[this.front];
}
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int index = this.rear == 0 ?
this.elem.length-1 : this.rear-1;
return this.elem[index];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.front == this.rear;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (this.rear+1)%this.elem.length == this.front;
}
}
测试代码:
public class Soultion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCircularQueue myCircularQueue=new MyCircularQueue(5);
myCircularQueue.enQueue(2);
myCircularQueue.enQueue(3);
myCircularQueue.enQueue(4);
myCircularQueue.enQueue(5);
myCircularQueue.enQueue(6);
myCircularQueue.enQueue(7);
System.out.println(myCircularQueue.isFull());
System.out.println(myCircularQueue.Front());
System.out.println(myCircularQueue.Rear());
}
}
运行结果:true 2 5
代码解释:
在得到队尾元素时,有可能下标大于其数组的长度,则这段代码: int index = this.rear == 0 ? this.elem.length-1 : this.rear-1;代表的时如果队尾下标不等于0为真的情况下,则返回数组长度减一,否则返回队尾元素下标减1.
在删除队列中的某一个元素时,如果对头元素下标等于数组长度减1时,则应使用this.front = (this.front+1)%this.elem.length,经过计算后其this.front则到达下标为0的位置。
在向队列中增加一个元素时,如果添加的元素的位置在队列长度减1的下标时,则应使用 this.rear = (this.rear+1)%this.elem.length ,计算后this.rear则到达下标为0的位置。
在判断队列是否满时,当循环队列中数组的最后一个位置不放元素时,为了与空进行区别,则使用(this.rear+1)%this.elem.length=this.front时,则可认为队列已满。





















 271
271











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








