
简介
👨💻个人主页:@云边牧风
👨🎓小编介绍:欢迎来到云边牧风破烂的小星球🌝
📋专栏:Java基础知识
🔑本章内容:Java常用实用类
记得 评论📝 +点赞👍 +收藏😽 +关注💞哦~
接着上一节时间与日期的处理,这节主要是Java的
Math类、提供任意精度整数运算的BigInteger类、Random类、数字格式化
一、Math类
Math类提供了很多静态方法用来进行数学运算,如:求平方根、绝对值、获取随机数等。
位于 java.lang 包中
常用方法(静态方法)👇:
public static long abs(double a) // 求绝对值
public static double max(double a,double b) // 求最大值
public static double min (double a,double b) // 求最小值
public static double random() // 产生一个 0 到 1 之间的随机数 [0.0, 1.0 )
public static double pow(double a,double b) // 求 a 的 b 次幂
public static double sqrt(double a) // 求平方根
public static double log(double a) // 求对数
public static double sin(double a) // 求正弦值
public static double asin (double a) // 求反正弦值
二、BigInteger类
BigInteger类提供任意精度的整数运算。
位于 java.math 包中。
构造方法:
public BigInteger (String value)
注:当value字符串参数中含有非数字字符时会发生NumberFormatException异常。
常用方法👇:
public BigInteger add( BigIngeger value) // 加运算
public BigInteger subtract( BigIngeger value) // 减运算
public BigInteger multiply( BigIngeger value) // 乘运算
public BigInteger divide( BigIngeger value) // 除运算
public BigInteger remainder( BigIngeger value) // 取余运算
public int compareTo ( BigIngeger value) // 比较运算,返回 1 、 -1 或 0
public BigInteger abs() // 求绝对值运算
public BigInteger pow(int a) // 幂运算
public String toString () // 转换成字符串对象
例如:
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
double a=5.0;
double st=Math.sqrt(a);
System.out.println(a+"的平方跟:"+st);
BigInteger result=new BigInteger("0");
BigInteger one=new BigInteger("123456789");
BigInteger two=new BigInteger("987654321");
result=one.add(two);
System.out.println("和:"+result);
result=one.multiply(two);
System.out.println("积:"+result);
}
}输出为:
5.0的平方跟:2.23606797749979
和:1111111110
积:121932631112635269
三、Random类
👉获取随机数
位于java.util包中,比Math.random()灵活 (建议直接使用random 而不是Math.random)
构造方法:
public Random(); // 用当前机器时间作为种子创建对象,随机性更强public Random( long seed ); // 用 seed 指定的种子创建对象,伪随机,可预见性好
常用方法:
public XXX nextXXX (); // 获取某种类型的随机数
如:
Random random=new Random(); //开头先声明
random.nextInt(); //返回一个随机整数值
random.nextInt(100); //返回一个[0, 100)之间的随机数
random.nextBoolean(); //返回一个随机boolean值四、数字格式化
犹记得初学C和C++的时候最常遇见的就是各种输出格式了,比如“保留n位有效数字”、“日期时间个位数的前面补零”、“上下对应平行”等等
同样的。Java也需要这些类型的输出,为此我们需要掌握数字格式化的常用方法👇:
String类的format静态方法,可以对数字进行格式化
①格式化整数:
格式符: %d, %o, %x 和 %X
String s=String.format(“%d,%o,%x”,20,20,20);
如:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
String s=String.format("%d,%o,%x",20,20,20);
System.out.println(s);
}
}输出:20,24,14
修饰符:“ + ” ( 强制添加上正号 ) 和“ , ” ( 按千分组 )
按千分组: %,d (在%d之间加上个逗号)
加上正号: %+d (在%d之间加上个加号)
按千分组&加正号:%+,d (+和,的先后不影响)
String s=String.format(“%,d, %+,d”,12345678,1234);//输出: 12,345,678, +1,234
输出宽度:“ % m d ” 或 “ % -m d ”
String s= String.format (“%8d”,1234);String s= String.format (“%-8d”,1234);String s= String.format (“%08d”,1234);
%md : 输出宽度为m位的数字(默认右对齐)
%-md : 输出宽度为m位的数字(改为左对齐)
%0md : 输出宽度为m位的数字(不够的补零)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
String s = String.format("%8d",1234);
String s1 = String.format("%-8d",1234);
String s2 = String.format("%08d",1234);
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
}
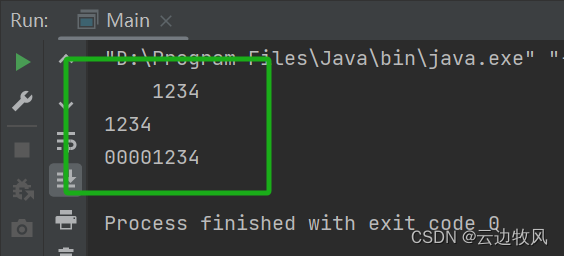
}1234
1234
00001234
②格式化浮点数:
格式符: %f, %e(%E), %g(%G) 和 %a(%A)
String s= String.format (“%f, %e”,13579.98,13579.98);//13579.980000, 1.357998e+04
修饰符:“ + ” ( 强制添加上正号 ) 和“ , ” ( 按千分组 )
按千分组: %,f (在%f之间加上个逗号)
加上正号: %+f (在%f之间加上个加号)
按千分组&加正号:%+,f (+和,的先后不影响)
String s=String.format("%+,f",12345678.9876);//+12,345,678.987600
输出宽度:“ % m.n f ” 或 “ % -m.n f ”
String s=String.format("%12.3f",12345678.9876);
String s1=String.format ("%-12.2f",12345678.9876);
String s2=String.format ("%012.2f",12345678.9876);
%m.nf : 输出宽度为m位的浮点(保留小数点后n位)(默认右对齐)
%-m.nf : 输出宽度为m位的浮点(保留小数点后n位)(改为左对齐)
%0m.nf : 输出宽度为m位的浮点(保留小数点后n位)(不够的补零)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
String s=String.format("%12.3f",12345678.9876);
String s1=String.format ("%-12.2f",12345678.9876);
String s2=String.format ("%012.2f",12345678.9876);
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
}
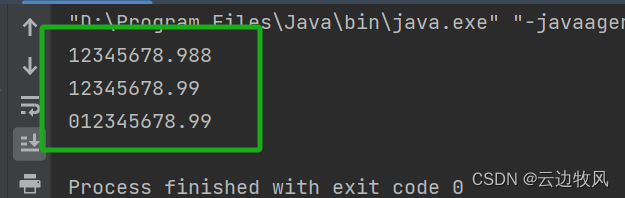
}12345678.988
12345678.99
012345678.99
五、Pattern类与Matcher类
模式匹配就是检索与指定模式匹配的字符序列。JAVA提供了专门用于模式匹配的Pattern类和Matcher类。
位于java.util.regex包中。
①建立Pattern模式对象:
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile ( regex );String regex = “good”;Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile ( regex );
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile ( regex , flags );
flags取值为以下常量之一:
②获取Matcher匹配对象:
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher ( input );String input = “ hello,good morning,this is a good idea”;Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher ( input );
③通过matcher匹配对象,调用各种方法检索input字符串
public boolean find() :查找匹配对象中和模式对象匹配的子串
public String group() :返回 find() 找到的子串
public int start() :返回 find() 找到的子串起始位置
public int end() :返回 find() 找到的子串结束位置
public boolean matches() :判断字符串和匹配串是否完全一致
如:
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "hello,good morning,this is a good idea";
String regex = "good";
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(regex);
Matcher m = p.matcher(input);
while (m.find()) {
String s = m.group();
System.out.println(s);
int n1 = m.start();
int n2 = m.end();
System.out.println(n1 + "," + n2);
}
}
}good
6,10
good
29,33
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input="话费清单:市话费76.89元,长途话费167.38元,短信费12.68元";
String regex="[0-9.]+";
Pattern p=Pattern.compile(regex);
Matcher m=p.matcher(input);
double count=0;
while(m.find()){
String s=m.group();
System.out.println(s);
count+=Double.parseDouble(s);
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}76.89
167.38
12.68
256.95
练习:
检索简历
简历的内容如下:
“姓名:张三 出生时间:1989.10.16。个人网站:http://www.zhangsan.com。身高:185cm,体重:72kg”
编写一个java应用程序,判断简历中的姓名是否姓“张”,单独输出简历中的出生日期和个人网站,并判断简历中的身高是否大于180cm,体重是否小于75kg。
(代码可在评论区求)
结束语:
以上4节是Jav第五章的全部内容:
希望大家喜欢
下一节开始讲第六章输入输出流
喜欢的可以点赞+关注哈 ❤























 205
205

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










