NIO三大核心原理示意图

- 每个channel(通道)都会对应一个buffer(缓冲区)
- Selector(选择器)对应一个线程,一个线程对应多个channel(连接)
- 程序切换到那个channel是由事件决定的,==Event(事件)==是一个非常重要概念
- Selector会根据不同的事件,在各个通道上切换
- Buffer就是一个内存块,底层是一个数组
- 数据的读写是通过Buffer,这个和BIO不同的。BIO中要么是输入流或者是输出流,不可能是双向流动的,但是NIO中的Buffer是可以读也可以写,需要用flip()方法切换
- channel是双向的,可以返回底层操作系统情况,比如Linux系统的底层操作通道就是双向的
NIO核心之一Buffer
- Buffer基本介绍:缓冲区本质上是一个可以读写数据的内存块。可以理解为一个容器对象(含数组),该对象提供一组方法,可以轻松地使用内存块,缓冲区对象内置了一些机制,能够跟踪和记录缓冲区的状态变化情况。Channel提供从文件、网络读取数据渠道,但是读取和写入数据必须经过Buffer
- 基本使用代码
package com.dd.nio;
import java.nio.IntBuffer;
public class BasicBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//举例说明buffer的使用
//创建一个buffer,大小为5,既可以存放5个int
IntBuffer intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5);
//向buffer,存放数据
for (int i = 0; i < intBuffer.capacity(); i++) {
intBuffer.put(i*2);
}
//如何从buffer读取数据
//将buffer转换,读写切换.不转换读不出数据
intBuffer.flip();
while (intBuffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(intBuffer.get());
}
}
}
-
Buffer类定义了所有的缓存区都具有的四个属性来提供关于其包含数据元素信息
- Capacity:容量,即可以容纳的最大数据量;在缓冲区创建时被设定并且不能该变
- Limit:表示缓冲区的当前终点,不能对缓冲区超过极限的位置经行读写操作。且极限是可以修改的
- Position:位置,下一个要被读或写的元素的索引,每次读写缓冲区数据时都会改变值,为下次读写准备
- Mark:标记
-
Buffer及其子类常用API


NIO核心之一Channel
- 基本介绍:通道可以同时进行读写,而流只能读或者只能写;通道可以实现异步读写数据;通道可以从缓冲读数据,也可以写数据到缓冲
- BIO中的stream是单向的,例如FileInputStream对象只能进行读取数据操作,而NIO中的通道(channel)是双向的,可以读操作,也可以写操作
- Channel在NIO中是一个接口
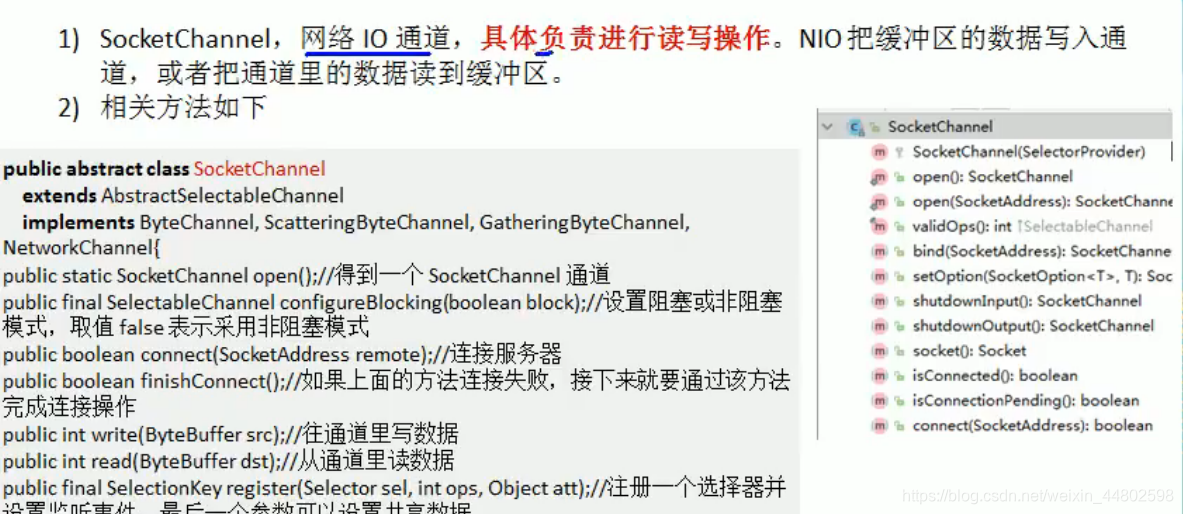
- 常用的Channel类有:FileChannel、DatagramChannel、ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel
- FileChannel用于文件的数据读写,DataGramChannel用于UDP的数据读写,ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel用于TCP的数据读写
- 通道写文件实例
package com.dd.nio;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str = "hello word";
//创建一个输出流->channel
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\file.txt");
//通过fileOutputStream获取对应的FileChannel
//这个fileChannel的真实类型为filechannelImpl
FileChannel channel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//创建一个缓冲区byteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8 * 1024);
//将 str 放入到
buffer.put(str.getBytes());
//对byteBuffer经行反转
buffer.flip();
//将byteBuffer数据写入到channel中
channel.write(buffer);
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
- 相关API解释

- 使用buffer完成文件的拷贝实例
package com.dd.nio;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannelCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("1.txt");
FileChannel inChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("2.txt");
FileChannel outChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8 * 1024);
while (true){//循环读取
//重要操作,重置标志位,必须有
/*
public final Buffer clear() {
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
*/
buffer.clear();
int read = inChannel.read(buffer);
if (read == -1 ){
break;
}
//将buffer中的数据写入到outChannel中
buffer.flip();
outChannel.write(buffer);
}
}
}
-
关于Buffer和channel的注意事项和细节
1.ByteBuffer支持类型化的put和get,放入的是什么数据类型,get就应该使用相应的数据类型取出来,否则可能BufferUnderflowException异常
2.可以将一个普通的Buffer,转换成只读(asReadOnlyBuffer()方法)
3.NIO还提供了MappedByteBuffer,可以让文件直接在内存(堆外内存)中进行修改,而如何同步到文件由NIO完成
4.NIO还支持通过多个Buffer完成读写操作,即Scattering(分散)和Gathering(聚合)
package com.dd.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/*
1.MappedByteBuffer可以让文件直接在内存(堆外内存)修改,操作系统不需要拷贝依次
*/
public class MappedByteBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("1.txt", "rw");
//获取对应的通道
FileChannel channel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
/*
* 参数1:表示使用的是读写模式
* 参数2:代表可以修改的起始位
* 参数3:表示映射到内存的大小,即1.txt的多少个字节映射到内存
* 可以修改的范围为0-5,不包含5
* 实际类型为DirectByteBuffer
*/
java.nio.MappedByteBuffer map = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 5);
map.put(0,(byte)'h');
map.put(3,(byte)'8');
randomAccessFile.close();
}
}
package com.dd.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Arrays;
/*
scattering:将数据写入到buffer时,可以采用buffer数组,依次写入
gathering:从buffer读取数据时,亦可以采用buffer数组,依次读
*/
public class ScatteringAndGathering {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用serverSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel open = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(7000);
//绑定端口到socket,并启动
open.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);
//创建buffer数组
ByteBuffer[] byteBuffers = new ByteBuffer[2];
byteBuffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
byteBuffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(2);
//等待客户端连接(telnet)
SocketChannel socketChannel = open.accept();
int messageLength = 7; //假定接受7个字节
//循环的读取
while (true){
int byteRead = 0;
while (byteRead<messageLength){
long read = socketChannel.read(byteBuffers);
byteRead += read;
System.out.println("累计读取的字节数"+byteRead);
//使用流打印,看看当前的buffer的position和limit
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).stream().map(buffer -> "postion="+buffer.position()+","
+buffer.limit()).forEach(System.out::println);
}
//将所有的buffer经行flip
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(buffer -> buffer.flip());
long byteWrite = 0;
//将数据读出显示到客户端
while(byteWrite < messageLength){
long write = socketChannel.write(byteBuffers);
byteWrite += write;
}
//将所有的buffer 进行clear
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(buffer -> buffer.clear());
System.out.println("byteRead="+byteRead+"byteWrite="+byteWrite);
}
}
}
NIO核心之一Selector(选择器)
-
基本介绍:Selector能够检测多个注册的通道上是否是事件发生(注意:多个channel以事件的方式可以注册到同一个selector)。如果有事件发生,便获取事件然后针对每个事件进行相应的处理,这样就可以只有一个单线程去管理多个通道,也就是管理多个连接和请求。只有在 连接/通道 真正有读写事件发生时,才会读写,大大减少了系统开销,并且不必每一个连接都创建一个线程,不用去维护多个线程,减少了多线程之间的上下文切换导致的开销
-
相关方法

-
注意
1.NIO中的ServerSocketChannel功能类似ServerSocket,SocketChannel功能类似Socket
2.Selector.select()//阻塞,只有至少一个事件发生返回
Selector.select(1000)//阻塞1000毫秒,在1000毫秒后返回,如果没有事件,也会返回
Selector.wakeup()//唤醒selector阻塞时候使用
Selector.selectNow()//不阻塞,立马返还 -
Selector、SelectionKey、ServerScoketChannel和SocketChannel关系梳理图

说明:1.当客户端连接时,会通过ServerSocketChannel得到对应的SocketChannel; 2.将SocketChannel注册到Selector上,register(Selector sel,int ops),一个selector上可以注册多个socketChannel 3.注册后返回一个SelectionKey,会和该Selector以集合的方式关联 4.Sekector通过select()方法进行监听,会返回有事件产生的通道的个数 5.进一步得到各个SelectorKey(事件发生的) 6.再通过SelectorKey,反向获取socketChannel 7.通过channel,完成业务处理 -
通过代码解读上面模型代码
客户端
package com.dd.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//得到一个网络通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//设置非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//提供服务器端的ip和端口
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 6666);
//连接服务器
if (!socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress)){
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()){
System.out.println("因为连接需要时间,客户端不会阻塞,可以做其他工作");
}
}
//如果连接成功就发送数据
String srt ="hello word 哈塞给";
//这个方法根据字节数组的大小生成buffer 相当于
//ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(srt.length());
//allocate.put(srt.getBytes());
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(srt.getBytes());
//发送数据,将buffer数据写入到channel
socketChannel.write(buffer);
//让代码停在这里
System.in.read();
}
}
服务端
package com.dd.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建servserSocketChannel -> serverSocket
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//创建一个sekector对象
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(6666));
//设置为非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//把serverSocketChannel 注册到 selector 上 关心事件为op_accept
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//循环等待客户端连接
while(true){
//这里的等待一秒,如果没有事件发生就继续
if (selector.select(1000) == 0){//没有事件发生
System.out.println("服务器等待一秒,无连接");
continue;
}
//如果返回>0,获取到相关的selectionKey集合
//通过这个方法返回关注事件的集合,然后反向获取通道
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
//遍历
Iterator<SelectionKey> Keyiterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (Keyiterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = Keyiterator.next();
//根据key 对应通道发生事件做相应的处理
if (key.isAcceptable()){//如果时OP_ACCEPT ,有新的客户端连接
//该客户端分配一个SocketChannel
//注意,accept()方法不是阻塞的吗?
//其实BIO中accept阻塞是因为不知道客户端连接,而NIO是由事件驱动的,咱们上面已经判断是连接事件,所以并不会阻塞
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
//将socketChannel设置成非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将SocketChannel注册到 seletor上 , 关注事件为OP_READ
//同时给socketChannel关联一个buffer
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
//从2,3,4.。。。
System.out.println("注册后的selectionKey 数量="+selector.keys().size());
}
if (key.isReadable()){//发生了OP_READ事件
//通过key 反向获取到对应的channel
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
//获取到该channel关联的buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("客户端发送的数据是:"+new String(buffer.array()));
}
//手动从集合中移除当前的selectionKey,防止重复操作
Keyiterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
SelectionKey说明
- SelectionKey表示Selector和网络通道的注册关系,共四种
























 398
398

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








