上一篇讲了POSIX线程库,是传统的C/C++使用的线程,在C++11中,提供了如下5个头文件来支持。
atomic:该文件主要声明了std::atomic与std::atomic_flag两个类
thread:该文件主要声明了std::thread与std::this_thread两个类
mutex:该文件主要声明了与互斥量(mutex)相关的类,如:std::mutex系列类、std::lock_guard、std::unique_lock以及其他的类型和函数
condition_variable:该文件主要声明了与条件变量相关的类,如:std::condition_variable和std::condition_variable_any
future:该文件主要声明了std::promise和std::package_task这两个Provider类,以及std::future和std::shared_future这两个Future类,另外还有一些与之相关的类型和函数,比如std::async函数。
其中std::thread类是非常重要的类

1、线程的创建
#include <QCorApplication>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <chrono> // std::chrono::seconds
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <thread> // std::thread, std::this_thread::sleep_for
using namespace std;
void thfunc(int n) //线程函数
{
std::cout << "thfunc:" << n <<endl;
}
int main(int aegc, char *argv[])
{
QCorApplication a(argc, argv);
std::thread threads[5]; //批量创建5个thread对象,但此时这些线程并不会执行
std::cout << "creat 5 threads...\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
threads[i] = std::thread(thfunc, i+1);//开始执行线程函数thfunc()
for (auto& t : threads) //等待每一个线程结束
t.join();
std::cout << "All threads joined.\n";
return a.exec();
}
但是创建的5条线程并不会执行需要对该线程进行初始化构造函数。
为了让线程有机会执行,会进行以下操作:
不传入参数
thread t(thfunc); //定义线程对象,并传入线程函数指针,thfunc为要执行的线程函数
sleep(1); //main 线程挂起1s,为了让子线程有机会执行
传入参数/
thread t(thfunc,1); //定义线程对象,并传入线程函数指针,thfunc为要执行的线程函数,1为传入的参数
t.join(); //等待线程对象t的结束这两种方法,sleep函数人为设定一个固定时间去执行,而正常要让设定时间大于运行时间,join函数会一直等到子线程结束后才会去执行后面的代码。
2、线程分离
void detach();
默认创建的线程都是可连接的线程,需要通过调用join()函数来等待该线程的结束并释放其占用的资源。除了通过该方法外,还可以调用detach()函数将可连接的线程分离。变成可分离的线程后,线程结束后就可以由系统自由回收资源,这样就不用等待子线程结束,主线程可以自己先行结束。
void thfunc(int n,int m,int *k,char s[]) //线程函数
{
cout << "in thfunc:n=" <<n<<",m="<<m<<",k="<<*k<<"\nstr="<<s<<endl;
*k=5000;
}
int mian(int argc,char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
int n = 110,m=200,k=5;
char str[] = "hello world";
thread t(thfunc, n,m,&k,str); // 定义线程对象
sleep(1);
t.detach(); //分离线程
cout << "k=" <<k<<endl; //这里输出3
pthread_exit(NULL); //main线程结束,但进程并不会结束,下一句不会执行
cout << "this line will not run"<<endl; // 这一句不会执行
return a.exec();
}最终结果
int func:n=110,m=200,k=5
str=hello world
k=5000
pthread_exit(NULL);在main中执行的时候,将结束main进程,但进程并不会立即退出,要等所有的线程全部结束后进程才会结束,所以能看到线程中函数打印的内容。因为打印k值的时候线程还没有切换,所以主线程会先打印k值。
3、移动(move)构造函数
通过向thread()构造函数中传入一个对象创建线程thread (thread&& x);
调用成功后,x不代表任何thread对象
thread t1(fun, ref(n));
thread t2(move(t1)); //t2执行fun,t1不是threa对象
t2.join(); //等待t2执行完毕t1不会执行,执行的是t2,因为t1的线程函数移给了t2。
4、线程的标识符
获取线程id,只是为了在调试的时候把id打出来看是否相同。
thread::id get_id()
thread::id main_thread_id = this_thread::get_id();//获取主线程id
5、当前线程this_thread
集合了4个有用的函数:get_id()、yield()、sleep_until()、sleep_for()。
(1)void yield();让出CPU时间
调用该函数的线程放弃执行,回到绪态。让出自己的CPU时间,以便其他线程有机会执行。
(2)sleep_until()和sleep_for();用来阻塞线程,会让线程暂停执行一段时间。
void sleep_until()的原型声明如下:
template <class Clock, class Duration>
void sleep_until(const chrono::time_point<Clock,Duration>& abs_time);
其中,参数abs_time表示函数阻塞线程到abs_time这个时间点,然后继续执行。
void sleep_for()的原型声明如下:
template <class Rep, class Period>
void sleep_for(const chrono::time_point<Rep,Period>& rel_time);
其中,参数rel_time表示线程挂起的时间段,在这段时间内线程暂停执行。
6、QThread 类的基本使用
常用成员函数:
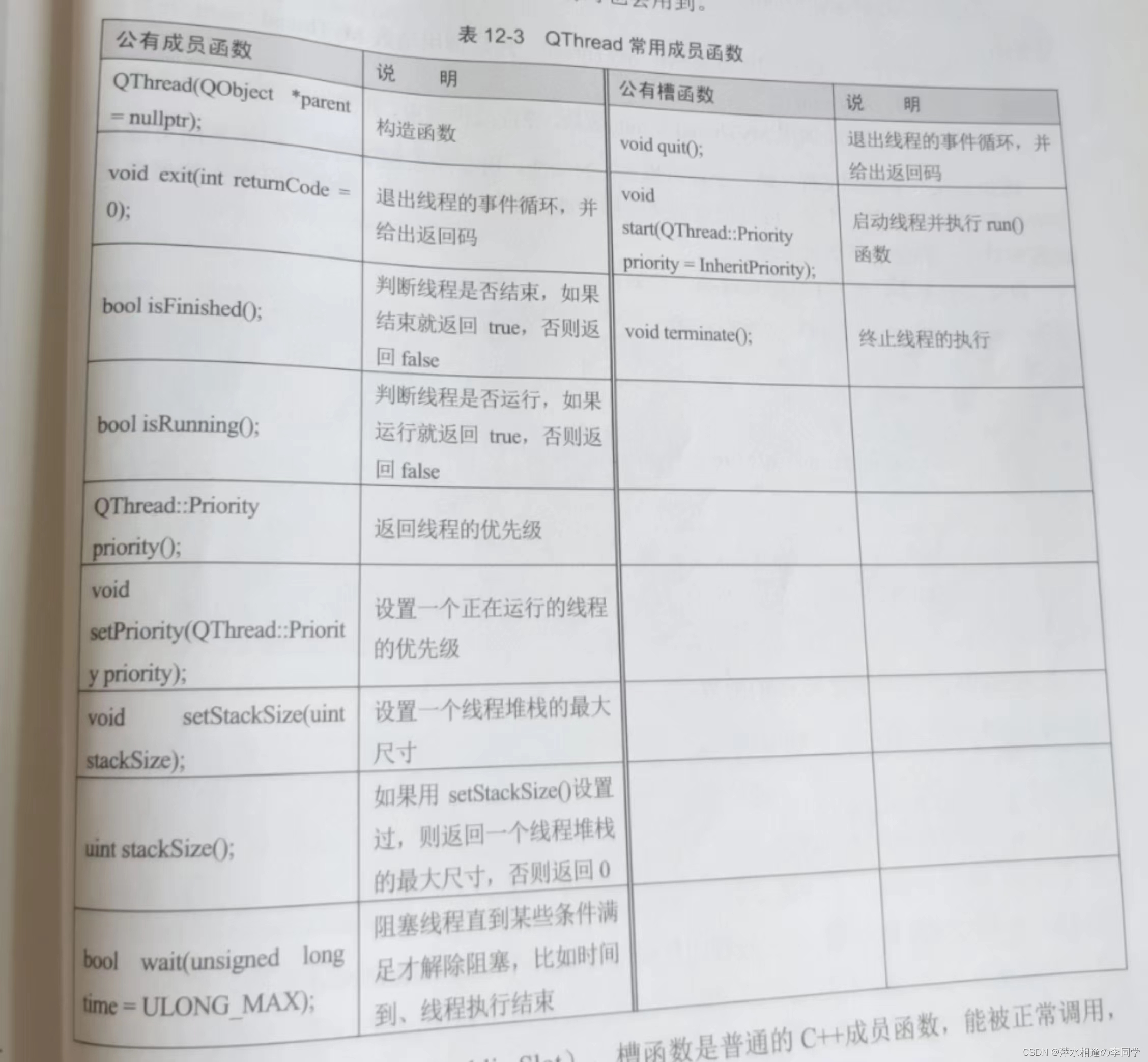
创建多线程的步骤如下:
(1)新建一个MyThread,它的基类为QThread
(2)重写 MyThread类的虚函数run(),即新建一个函数protected void run (),然后对其进行定义
(3)在需要用到多线程的地方进行实例化MyThread,然后调用函数MyThread::start()开启一个线程,自动运行函数run()
(4)当停止线程时,调用MyThread::wait()函数,等待线程结束,并回收线程占用的资源
下面是QThread类的基本使用:
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QThread>
class MyThread :public QThread
{
public:
virtual void run();
};
void MyThread::run()
{
for (int count = 0; count < 10; count++){
sleep(1);//等待1s
qDebug("ping %d", count);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
MyThread thA;
thA.start();//自动调用run()函数,否则即使创建了该线程,也是一开始就挂起
//等待线程a退出
thA.wait();
puts("thread A is over.");
return a.exec();
}7、线程间通信
Qt线程间(数据)通信主要有两种方式:
(1)使用共享内存,也就是使用两个线程都能够共享的变量(如全局变量),这样两个线程都能够访问和修改该变量,从而达到共享数据的目的。
(2)使用信号/槽(Singal/Slot)机制,把数据从一个线程传递到另一个线程中。
注:结束线程可用void terminate();






















 3094
3094











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








