让同一块物理内存被映射到进程A、B各自的进程地址空间。进程A可以即时看到进程B对共享内存中数据的更新;
共享内存的使用步骤
1、进程调用shmget函数创建新的或获取已有共享内存
2、进程调用shmat函数,将物理内存映射到自己的进程空间
3、shmdt函数,取消映射
4、调用shmctl函数释放开辟的那片物理内存空间
创建共享内存:
有亲缘关系的两个进程通信:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#define SHM_NAME "./shm_file"
#define SHM_SIZE 4096
int shmid;
void *addr;
void my_exit(int sig)
{
if (sig == SIGINT)
{
shmdt(addr);
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL); // ipcrm -M + (shmid)
exit(1);
}
else if (sig == SIGUSR1)
{
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
signal(SIGINT, my_exit);
key_t key;
pid_t pid;
key = ftok(SHM_NAME, 's');
// int shmget(key_t key, size_t size, int shmflg);
shmid = shmget(key, SHM_SIZE, 0655 | IPC_CREAT);
if (shmid < 0)
{
perror("shm get error!");
exit(1);
}
/**
* semflg:与消息队列一样
* 指定原始权限和IPC_CREAT,比如0664|IPC_CREAT。
* 只有在创建一个新的共享内存时才会用到,否者不会用到
*/
printf("key = %x\n", key);
printf("shmid = %d\n", shmid);
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
perror("fork error:");
exit(1);
}
if (pid == 0)
{
char buffer[1024];
// void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg);
addr = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if (addr == (void *)-1)
{
perror("shm error:\n");
exit(1);
}
/**
* 将shmid所指向的共享内存空间映射到进程空间(虚拟内存空间),并返回影射后的起始地址(虚拟地址)。
* 有了这个地址后,就可以通过这个地址对共享内存进行读写操作
* shmaddr:指定映射的起始地址有两种设置方式
* 自己指定映射的起始地址(虚拟地址)。
* 我们一般不会这么做,因为我们自己都搞不清哪些虚拟地址被用了,哪些没被用。
* NULL:表示由内核自己来选择映射的起始地址(虚拟地址)。
* 这是最常见的方式,也是最合理的方式,因为只有内核自己才知道哪些虚拟地址可用,哪些不可用。
* shmflg:指定映射条件。
* 0:以可读可写的方式映射共享内存也就是说映射后,可以读、也可以写共享内存。
* SHM_RDONLY:以只读方式映射共享内存也就是说映射后,只能读共享内存,不能写。
*/
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
scanf("%s", buffer);
memcpy(addr, buffer, strlen(buffer));
kill(getppid(), SIGUSR1);
}
}
else if (pid > 0)
{
char buffer[1024];
signal(SIGUSR1, my_exit);
addr = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0); // 获得映射的地址
if (addr == (void *)-1)
{
perror("shm error:\n");
exit(1);
}
while (1)
{
#if 0 // 非阻塞 -- 浪费CPU资源
if (strlen((char *)addr) != 0)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
memcpy(buffer, addr, strlen((char *)addr));
printf("recv data = %s\n", buffer);
memset(addr, 0, SHM_SIZE);
}
#endif
// 阻塞
pause(); // 没有数据的时候先挂起
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
memcpy(buffer, addr, strlen((char *)addr));
printf("recv data = %s\n", buffer);
memset(addr, 0, SHM_SIZE);
sleep(1);
}
}
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
superlan@GodFather:~/C_Language/interprocess_communication$ ./a.out
key = ffffffff
shmid = 33
xiaobai
recv data = xiaobai
super
recv data = super---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
两个没有亲缘关系的进程通信:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#define SHM_NAME "./shm_file"
#define FIFO_NAME "./fifo_file"
#define SHM_SIZE 4096
int shmid;
void *addr;
pid_t recv_pid() // 接受管道文件
{
int fd = open(FIFO_NAME, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open fifo error:");
exit(1);
}
pid_t pid;
if (read(fd, &pid, sizeof(pid)) < 0) // 获得 pid 的值
{
perror("send pid error:");
exit(1);
}
return pid;
}
void my_exit(int sig)
{
if (sig == SIGINT)
{
shmdt(addr);
// int shmdt(const void *shmaddr);
/**
* 功能:取消建立的映射。
* 返回值:调用成功返回0,失败返回-1,且errno被设置。
* 参数:shmaddr:映射的起始地址(虚拟地址)
**/
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL);
// 调用shmctl函数释放开辟的那片物理内存空间
remove(FIFO_NAME);
exit(1);
}
else if (sig == SIGUSR1)
{
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
key_t key;
char buffer[1024];
key = ftok(SHM_NAME, 's');
shmid = shmget(key, SHM_SIZE, 0655 | IPC_CREAT);
if (shmid < 0)
{
perror("shm get error!");
exit(1);
}
printf("key = %x\n", key);
printf("shmid = %d\n", shmid);
signal(SIGINT, my_exit);
signal(SIGUSR1, my_exit);
addr = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if (addr == (void *)-1)
{
perror("shn error:\n");
exit(1);
}
pid_t pid = recv_pid();
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
scanf("%s", buffer);
memcpy(addr, buffer, strlen(buffer));
kill(pid, SIGUSR1);
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#define SHM_NAME "./shm_file"
#define FIFO_NAME "./fifo_file"
#define SHM_SIZE 4096
int shmid;
void *addr;
void my_exit(int sig)
{
if (sig == SIGINT)
{
shmdt(addr);
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL);
exit(1);
}
else if (sig == SIGUSR1) // 空处理
{
}
}
void send_pid()
{
if (mkfifo(FIFO_NAME, 0655 | IPC_CREAT) < 0) // 创建管道文件
{
perror("mkfifo error:");
exit(1);
}
int fd = open(FIFO_NAME, O_WRONLY); // 以只读的方式打开
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open fifo error:");
exit(1);
}
pid_t pid = getpid();
if (write(fd, &pid, sizeof(pid)) < 0) // 发送这个Pid
{
perror("send pid error:");
exit(1);
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
key_t key;
pid_t pid;
char buffer[1024];
key = ftok(SHM_NAME, 's');
shmid = shmget(key, SHM_SIZE, 0655 | IPC_CREAT);
if (shmid < 0)
{
perror("shm get error!");
exit(1);
}
printf("key = %x\n", key);
printf("shmid = %d\n", shmid);
send_pid();
signal(SIGINT, my_exit);
signal(SIGUSR1, my_exit);
addr = shmat(shmid, NULL, 0);
if (addr == (void *)-1)
{
perror("shn error:\n");
exit(1);
}
while (1)
{
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
/*void
if (strlen((char *)addr) != 0)
{
memcpy(buffer, addr, strlen((char *)addr));
printf("recv data = %s\n", buffer);
memset(addr, 0, SHM_SIZE);
}
*/
pause();
memcpy(buffer, addr, strlen((char *)addr));
printf("recv data = %s\n", buffer);
memset(addr, 0, SHM_SIZE);
}
return 0;
}
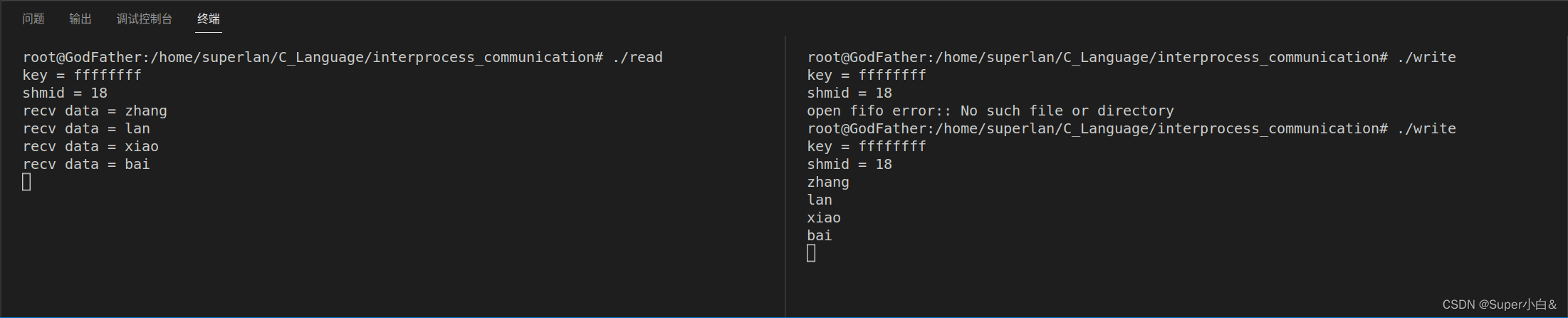
运行结果如下:
共享内存的特点:
1、减少进入内核空间的次数
2、直接使用地址来读写缓存时,效率会更高,适用于大数据量的通信






















 2496
2496











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








