2. Resource Description Framework (RDF)
Graph
Directed vs. undirected
Labeled vs. unlabeled
Homogenous vs. heterogeneous nodes
Cyclic vs. acyclic
Knowledge Graphs are Graphs
Directed, labeled graph, Heterogeneous node types (and edges), Need not be cycle free
Node types (“classes”) and edge types (“properties”) are also referred to the “schema” of the graph (aka “ontology”) e.g. an edge of type “author” links a publication to a person
Metadata on the Web
Goal: more effective rating and ranking of web contents
Metadata on the Web: Dublin Core

2.1 What is RDF?
RDF = Resource Description Framework
Description of arbitrary things
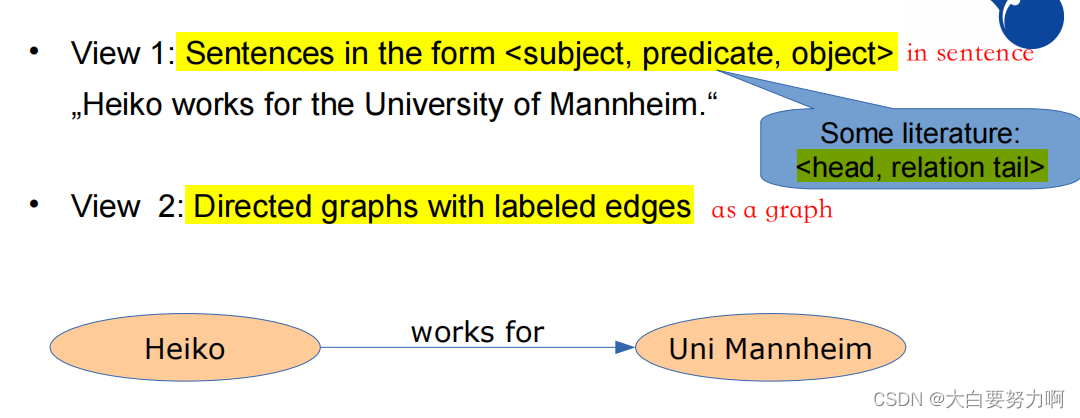
A knowledge graph consists of multiple sentences
We usually think of knowledge graphs as densely connected graphs (Objects of one statement become subjects of another)
2.2 Basic Building Blocks of RDF
2.2.1 Resources
- denote things
- are identified by a URI
- can have one or multiple types
- A resource can be a subject itself
Types: All resources (not literals) can have a type. Types can be arbitrarily defined. The predefined predicate rdf:type* defines the type of a resource.
2.2.2 Literals
- are values like strings or integers,;
- A literal is an atomic value, can only be objects, not subjects or predicates(graph view: they can only have ingoing edges)【和resource的不同点】
- can have a datatype or a language tag (but not both)
Datatypes for Literals
(Almost) all XML Schema datatypes may be used, Exception: XML specific types, The underspecified type “duration”, and sequence types.
There are no default datatypes (not even “string”!)
Language Tags for Literals
Literals may be defined in different natural languages: “München”@de, “Munich”@en
Those can be marked
Knowledge Graphs can be multilingual!
Example:
:Munich :hasName “München”@de .
:Munich :hasName “Munich”@en .
:Munich :hasPopulation "1356594 "^^xsd:integer .
:Munich :hasFoundingYear “1158-01-01”^^xsd:date .
以下是3种不同的literal
– “München”
– “München”@de
– “München”^^xsd:string .
2.2.3 Properties (Predicates)
- Link resources to other resources and to literals
2.3 Triple Notation
Triples consist of a subject, predicate, and object.
An RDF document is an unordered set of triples.
Example:
Literal with language tag:
http://www.dws.informatik.uni-mannheim.de/teaching/semantic-web
http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/subject
“Semantic Web”@en .
Type literal:








 本文介绍了ResourceDescriptionFramework(RDF)的基本概念,包括资源、literal、属性、三元组表示法(如TurtleNotation),以及RDFS(RDFSchema)的使用,展示了如何通过RDF和相关技术如HTML、RDFa和Microdata在网页上添加结构化数据。同时讨论了RDF的语义原则和限制,如非负性和RDFS的推理能力。
本文介绍了ResourceDescriptionFramework(RDF)的基本概念,包括资源、literal、属性、三元组表示法(如TurtleNotation),以及RDFS(RDFSchema)的使用,展示了如何通过RDF和相关技术如HTML、RDFa和Microdata在网页上添加结构化数据。同时讨论了RDF的语义原则和限制,如非负性和RDFS的推理能力。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 6万+
6万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








