import pandas as pd

(1)Series类型

1.Series类型的创建方法
#series类型的创建方法:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
a=pd.Series([9,8,7,6])
b=pd.Series([9,8,7,6],index=['a','b','c','d'])
c=pd.Series(25,index=['a','b','c'])
d=pd.Series({'a':9,'b':8,'c':7})
e=pd.Series({'a':9,'b':8,'c':7},index=['c','a','b','d'])
f=pd.Series(np.arange(5))
g=pd.Series(np.arange(5),index=np.arange(9,4,-1))
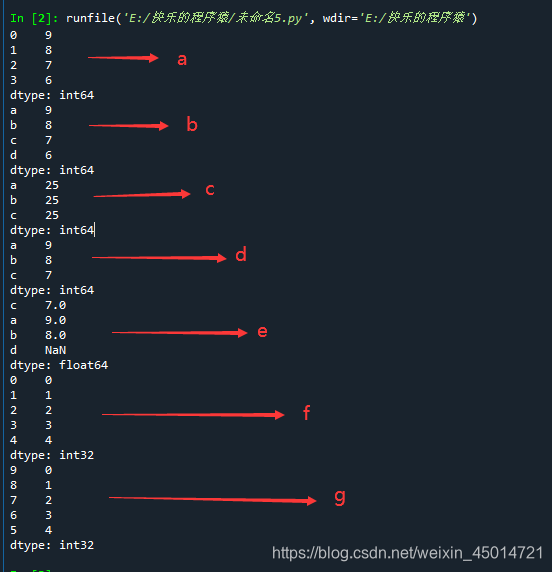
总之,创建Series要么是pd.Series([列表1],index=[列表二]);
要么是pd.Series({'a':9,'b':8,'c':7,'d':6})这种的。
这里的列表既可以是np.arange(9,4,-1),也可以是[9,8,7,6]这种的。
2.Series类型的基本操作
import pandas as pd
b=pd.Series([9,8,7,6],['a','b','c','d'])
b
b.values
b.index
b[1]
b['b']
b[['c','d','a']]
b[['c','d','a']] = 10
b[3]
b[:3]
b[b>b.median()]
np.exp(b) #exp(a)就是e的a次方
b.get('f',100) #如果f在b里面,返回索引f对应的值;如果f不在b里面,那就返回100
import pandas as pd
b=pd.Series([9,8,7,6],['a','b','c','d'])
b.name='Series对象'
b.index.name='索引列'
'''
索引列
a 9
b 8
c 7
d 6
Name: Series对象, dtype: int64
'''
import pandas as pd
a=pd.Series([1,2,3],['c','d','e'])
b=pd.Series([9,8,7,6],['a','b','c','d'])
>>> b
a 9
b 8
c 7
d 6
dtype: int64
>>> a
c 1
d 2
e 3
dtype: int64
>>> a + b #只有a和b都有的才能相加,有一个没有那就是NaN
a NaN
b NaN
c 8.0
d 8.0
e NaN
dtype: float64
上面操作的具体输出如下:(可看可不看)
import pandas as pd
b=pd.Series([9,8,7,6],['a','b','c','d'])
>>> b
a 9
b 8
c 7
d 6
dtype: int64
>>> b.index # Series内部建立的类型
Index(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], dtype='object')
>>> b.values
array([9, 8, 7, 6], dtype=int64)
>>> b['b']
8
>>> b[1] # 即使指定索引,自动索引仍然存在
8
# b[['c', 'd', 0]] 目前已经不再支持这种混合使用的用法
>>> b[['c', 'd', 'a']]
c 7
d 6
a 9
dtype: int64
>>> b[3]
6
>>> b[:3]
a 9
b 8
c 7
dtype: int64
>>> b[b>b.median()]
a 9
b 8
dtype: int64
>>> np.exp(b)
a 8103.083928
b 2980.957987
c 1096.633158
d 403.428793
dtype: float64
>>> b.get('f', 100)
100
2.DataFrame类型
DataFrame类型和series类型是兄弟

1.DataFrame类型的创建方法
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
a=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(10).reshape(2,5))
'''
0 1 2 3 4
0 0 1 2 3 4
1 5 6 7 8 9
'''
dt={
'one':pd.Series([1,2,3],index=['a','b','c']),
'two':pd.Series([9,8,7,6],index=['a','b','c','d'])
}
b=pd.DataFrame(dt)
c=pd.DataFrame(dt,index=['b','c','d'],columns=['two','three'])
'''
dt就是一个普通的字典: 而b就是一个DataFrame: c也是一个DataFrame:
{'one' one two two three
a 1 a 1.0 9 b 8 NaN
b 2 b 2.0 8 c 7 NaN
c 3 c 3.0 7 d 6 NaN
dtype: int64, d NaN 6
'two':
a 9
b 8
c 7
d 6
dtype: int64}
'''
dt2={'one':[1,2,3,4],'two':[9,8,7,6]}
d=pd.DataFrame(dt2,index=['a','b','c','d'])
'''
dt2就是一个普通的字典:{'one': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'two': [9, 8, 7, 6]}
而d就是:
one two
a 1 9
b 2 8
c 3 7
d 4 6
'''
2.DataFrame可以直接输出来的属性

import pandas as pd
d1={'城市':['北京','上海','广州','深圳','沈阳'],
'环比':[101.5,101.2,101.3,102.0,100.1],
'同比':[120.7,127.3,119.4,140.9,101.4],
'定基':[121.4,127.8,120.0,145.5,101.6]}
d=pd.DataFrame(d1,index=['c1','c2','c3','c4','c5'])
d.index
'''Index(['c1', 'c2', 'c3', 'c4', 'c5'], dtype='object')'''
d.columns
'''Index(['城市', '环比', '同比', '定基'], dtype='object')'''
d.values
'''
array([['北京', 101.5, 120.7, 121.4],
['上海', 101.2, 127.3, 127.8],
['广州', 101.3, 119.4, 120.0],
['深圳', 102.0, 140.9, 145.5],
['沈阳', 100.1, 101.4, 101.6]], dtype=object)
'''
d
'''
城市 环比 同比 定基
c1 北京 101.5 120.7 121.4
c2 上海 101.2 127.3 127.8
c3 广州 101.3 119.4 120.0
c4 深圳 102.0 140.9 145.5
c5 沈阳 100.1 101.4 101.6
'''
import pandas as pd
d1={'城市':['北京','上海','广州','深圳','沈阳'],
'环比':[101.5,101.2,101.3,102.0,100.1],
'同比':[120.7,127.3,119.4,140.9,101.4],
'定基':[121.4,127.8,120.0,145.5,101.6]}
frame=pd.DataFrame(d1,index=['c1','c2','c3','c4','c5'])
'''
城市 环比 同比 定基
c1 北京 101.5 120.7 121.4
c2 上海 101.2 127.3 127.8
c3 广州 101.3 119.4 120.0
c4 深圳 102.0 140.9 145.5
c5 沈阳 100.1 101.4 101.6
'''
print(frame['同比'][0:2]) #找到某一行某一列
print(frame[0:2]['同比']) #找到某一行某一列
print(frame['城市']) #找到某一列
print(frame[['城市','环比']] ) #找到某一列(这里必须是两个[])
print(frame[0:2]) #找到某一行
print(frame['c2']) #这个输出会报错!!!c2是索引,frame[]不能通过索引查询指定行
print(frame[ frame['环比']>101.3 ])
print(frame['环比']>101.3)

import pandas as pd
d1={'城市':['北京','上海','广州','深圳','沈阳'],
'环比':[101.5,101.2,101.3,102.0,100.1],
'同比':[120.7,127.3,119.4,140.9,101.4],
'定基':[121.4,127.8,120.0,145.5,101.6]}
frame=pd.DataFrame(d1,index=['c1','c2','c3','c4','c5'])
'''
城市 环比 同比 定基
c1 北京 101.5 120.7 121.4
c2 上海 101.2 127.3 127.8
c3 广州 101.3 119.4 120.0
c4 深圳 102.0 140.9 145.5
c5 沈阳 100.1 101.4 101.6
'''
print(frame.loc[['c1','c3'],['城市','环比']]) #输出指定行指定列
print(frame.loc[['城市','环比']]) ##这个输出会报错!!!frame.loc[]专门针对行索引设定的,不能查询指定列的数据
print(frame.loc[['c1','c3']]) #通过索引输出指定行的数据
print(frame[['c1','c3']]) #这个输出会报错!!!frame[]不能通过索引查询指定行
总之,
frame[]这种可以查询指定列的数据,但不能通过索引查询指定行的数据(如frame['c2']是错误的)
frame.loc[]专门针对行索引设定的,可以通过索引查询指定行的数据,但不能查询指定列的数据(如frame.loc[['城市','环比']]是错误的)

3.pandas库的数据类型操作(适用于DataFrame和Series)
(再强调一遍:同时适用于DataFrame和Series)
①重排(重新索引 reindex)
.reindex(index=None,columns=None,…)的参数
- index行自定义索引
- columns列自定义索引
- fill_value用于填充缺失值的值(fill_value=200就是把NaN替换为200)
- method填充方法(ffill向前填充也就是克隆前一行的数据,bfill向后填充也就是克隆后一行的数据)
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({"A": [1, 2, 3], "B": [4, 5, 6]})
df
Out[1]:
A B
0 1 4
1 2 5
2 3 6
df.reindex(index=(1,2,3)) #重新给行索引命名
Out[2]:
A B
1 2.0 5.0
2 3.0 6.0
3 NaN NaN
df.reindex(columns=("B","C")) #重新给列索引命名
Out[3]:
B C
0 4 NaN
1 5 NaN
2 6 NaN
1.reindex调整行列顺序
import pandas as pd
d1={'城市':['北京','上海','广州','深圳','沈阳'],
'环比':[101.5,101.2,101.3,102.0,100.1],
'同比':[120.7,127.3,119.4,140.9,101.4],
'定基':[121.4,127.8,120.0,145.5,101.6]}
d=pd.DataFrame(d1,index=['c1','c2','c3','c4','c5'])
'''
城市 环比 同比 定基
c1 北京 101.5 120.7 121.4
c2 上海 101.2 127.3 127.8
c3 广州 101.3 119.4 120.0
c4 深圳 102.0 140.9 145.5
c5 沈阳 100.1 101.4 101.6
'''
d=d.reindex(index=['c5','c4','c3','c2','c1'])
'''
城市 环比 同比 定基
c5 沈阳 100.1 101.4 101.6
c4 深圳 102.0 140.9 145.5
c3 广州 101.3 119.4 120.0
c2 上海 101.2 127.3 127.8
c1 北京 101.5 120.7 121.4
'''
d=d.reindex(columns=['城市','同比','环比','定基'])
'''
城市 同比 环比 定基
c5 沈阳 101.4 100.1 101.6
c4 深圳 140.9 102.0 145.5
c3 广州 119.4 101.3 120.0
c2 上海 127.3 101.2 127.8
c1 北京 120.7 101.5 121.4
'''
2.插入行列元素
reindex可以插入行和列,而且优点是可以批量填充数值
#coding:utf-8
import pandas as pd
from pandas import DataFrame
data={'ID':['000001','000002','000003','000004','000005','000006','000007'],
'name':['黎明','赵春怡','张福平','百利','牛玉德','姚华','李楠'],
'gender':[True,False,True,False,True,False,True],
'age':[16,20,18,18,17,18,16],
'height':[1.88,1.78,1.81,1.86,1.74,1.75,1.76]
}
frame=pd.DataFrame(data,index=['c1','c2','c3','c4','c5','c6','c7'])
print(frame)
newc = frame.columns.insert(2,'新增') #在第2列的位置添加一个"新增的列标题"
newd = frame.reindex(columns=newc,fill_value=200) #在NaN处填充200
print(newd)
nl=frame.index.insert(7,'c0')
#print(nl) #Index(['c1', 'c2', 'c3', 'c4', 'c5', 'c6', 'c7', 'c0']
nd=frame.reindex(index=nl,columns=newc,fill_value=200)
print(nd)
#值得注意的是把columns=newc改成columns=newd是错误的,因为newc是frame.columns,而newd是frame

②drop删除行列元素
#coding:utf-8
import pandas as pd
from pandas import DataFrame
data={'ID':['000001','000002','000003','000004','000005','000006','000007'],
'name':['黎明','赵春怡','张福平','百利','牛玉德','姚华','李楠'],
'gender':[True,False,True,False,True,False,True],
'age':[16,20,18,18,17,18,16],
'height':[1.88,1.78,1.81,1.86,1.74,1.75,1.76]
}
frame=pd.DataFrame(data,index=['c1','c2','c3','c4','c5','c6','c7'])
frame=frame.drop('c2',axis=0) #值得注意的是在drop中axis=0是删除行,axis=1是删除列
print(frame)
frame=frame.drop(['c5','c3'],axis=0) #删除行;axis=0写与不写都可以,axis是默认为0的
print(frame)
frame=frame.drop('name',axis=1) #删除列
print(frame)
frame=frame.drop( index=( frame.loc[(frame['gender']==True)].index ) ) #删除性别为True的行;axis是默认为0的
print(frame)

③索引类型
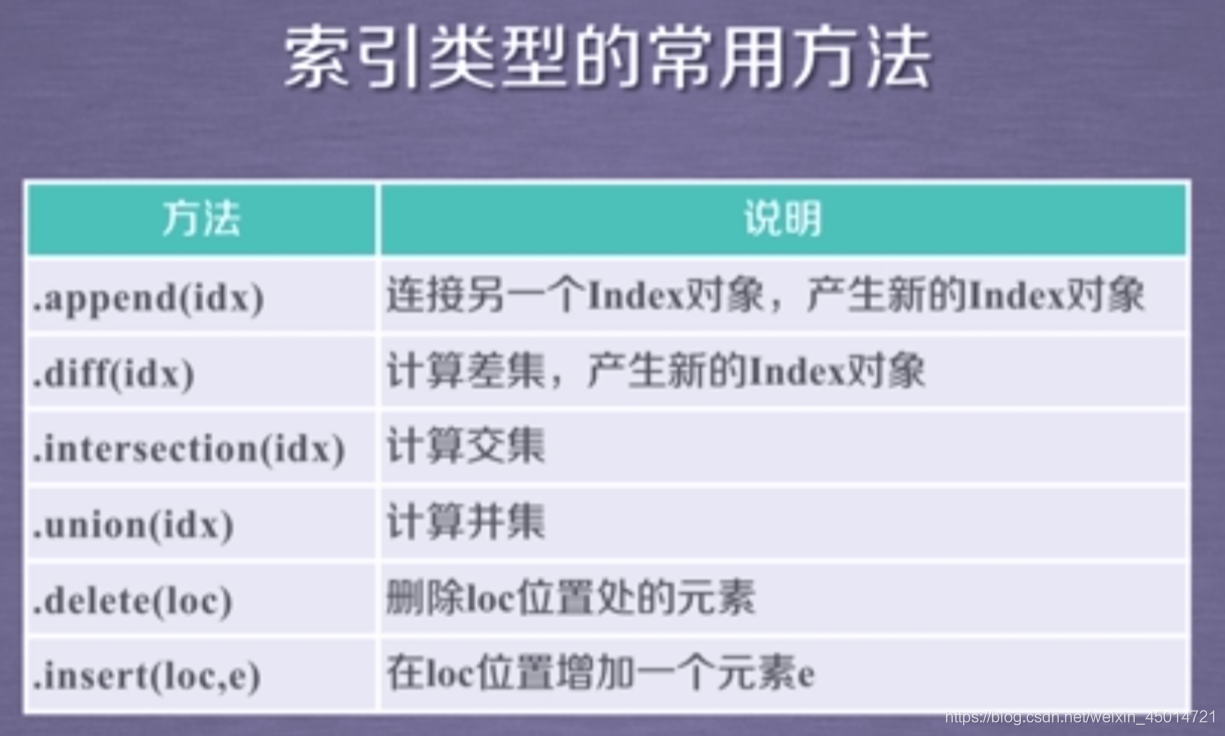
④算术运算

import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
a = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4))
'''
0 1 2 3
0 0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6 7
2 8 9 10 11
'''
b=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5))
'''
0 1 2 3 4
0 0 1 2 3 4
1 5 6 7 8 9
2 10 11 12 13 14
3 15 16 17 18 19
'''
a+b
'''
0 1 2 3 4
0 0.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 NaN
1 9.0 11.0 13.0 15.0 NaN
2 18.0 20.0 22.0 24.0 NaN
3 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
'''
a*b
'''
0 1 2 3 4
0 0.0 1.0 4.0 9.0 NaN
1 20.0 30.0 42.0 56.0 NaN
2 80.0 99.0 120.0 143.0 NaN
3 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
'''

import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
a = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4))
'''
0 1 2 3
0 0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6 7
2 8 9 10 11
'''
b=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5))
'''
0 1 2 3 4
0 0 1 2 3 4
1 5 6 7 8 9
2 10 11 12 13 14
3 15 16 17 18 19
'''
m=b.add(a,fill_value=100) # 缺值用100补
'''
0 1 2 3 4
0 0.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 104.0
1 9.0 11.0 13.0 15.0 109.0
2 18.0 20.0 22.0 24.0 114.0
3 115.0 116.0 117.0 118.0 119.0
'''
mm=a.mul(b,fill_value=0) #相乘
'''
0 1 2 3 4
0 0.0 1.0 4.0 9.0 0.0
1 20.0 30.0 42.0 56.0 0.0
2 80.0 99.0 120.0 143.0 0.0
3 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
'''

import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
b= pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5))
'''
0 1 2 3 4
0 0 1 2 3 4
1 5 6 7 8 9
2 10 11 12 13 14
3 15 16 17 18 19
'''
c = pd.Series(np.arange(4))
'''
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 3
dtype: int32
'''
b-c
'''
0 1 2 3 4
0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 NaN
1 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 NaN
2 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 NaN
3 15.0 15.0 15.0 15.0 NaN
二维与一维运算时是二维的所有轴1(横行)与一维的数据进行运算
也就是b的每一行都减去一下c
'''
b.sub(c,axis=0)
'''
使用这种运算方法便可以使得轴0参与运算
0 1 2 3 4
0 0 1 2 3 4
1 4 5 6 7 8
2 8 9 10 11 12
3 12 13 14 15 16
'''
⑤比较运算
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
a = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4))
'''
0 1 2 3
0 0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6 7
2 8 9 10 11
'''
d=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12,0,-1).reshape(3,4))
'''
0 1 2 3
0 12 11 10 9
1 8 7 6 5
2 4 3 2 1
'''
a>d
'''
0 1 2 3
0 False False False False
1 False False False True
2 True True True True
'''
a==d
'''
0 1 2 3
0 False False False False
1 False False True False
2 False False False False
'''
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
a = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4))
'''
0 1 2 3
0 0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6 7
2 8 9 10 11
'''
c=pd.Series(np.arange(4))
'''
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 3
dtype: int32
'''
a>c
'''
不同维度,广播运算,默认在1轴
0 1 2 3
0 False False False False
1 True True True True
2 True True True True
'''
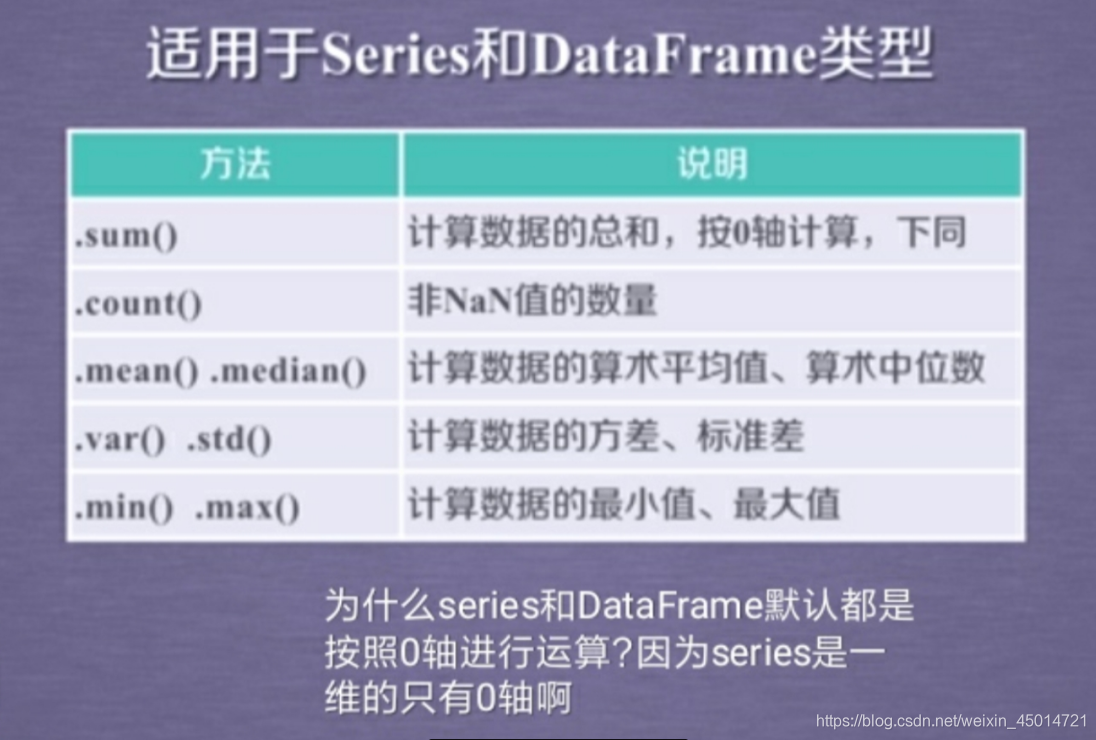
4.pandas数据特征分析(适用于DataFrame和Series)

①对数据的排序
1、sort_index()方法
.sort_index() 方法在指定轴上根据索引进行排序,默认为零轴,升序。.sort_index(axis=0,ascending=True) 为默认
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
a = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5), index = 'c','a','d','b'])
a
0 1 2 3 4
c 0 1 2 3 4
a 5 6 7 8 9
d 10 11 12 13 14
b 15 16 17 18 19
# 默认按照0轴索引升序排序
a.sort_index()
0 1 2 3 4
a 5 6 7 8 9
b 15 16 17 18 19
c 0 1 2 3 4
d 10 11 12 13 14
# 规定按照降序排序
a.sort_index(ascending=False)
0 1 2 3 4
d 10 11 12 13 14
c 0 1 2 3 4
b 15 16 17 18 19
a 5 6 7 8 9
# 规定在1轴上按照降序排序
a.sort_index(axis=1, ascending=False)
4 3 2 1 0
c 4 3 2 1 0
a 9 8 7 6 5
d 14 13 12 11 10
b 19 18 17 16 15
2、sort_values()方法
.sort_values() 方法在指定轴上根据数值进行排序,默认为零轴,升序
Series.sort_values(axis=0, ascending=True)
DataFrame.sort_values(by, axis=0, ascending=True)
by: axis 轴上的某个索引或索引列表
b = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5), index = 'a','b','c','d'])
b
0 1 2 3 4
a 0 1 2 3 4
b 5 6 7 8 9
c 10 11 12 13 14
d 15 16 17 18 19
# 默认在0轴上,指定对索引为2的那一列按照降序排序
b.sort_values(2, ascending=False)
0 1 2 3 4
d 15 16 17 18 19
c 10 11 12 13 14
b 5 6 7 8 9
a 0 1 2 3 4
# 指定在1轴上,对索引为‘c’的那一行进行降序排序
b.sort_values('c',axis=1, ascending=False)
4 3 2 1 0
a 4 3 2 1 0
b 9 8 7 6 5
c 14 13 12 11 10
d 19 18 17 16 15
3、对排序时 空值 的处理
NaN 统一放到排序末尾
b = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5), index = 'a','b','c','d'])
a = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4), index = 'a','b','c'])
c = b-a
c
0 1 2 3 4
a 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 NaN
b 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 NaN
c 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 NaN
d NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
c.sort_values(2, ascending = False)
0 1 2 3 4
c 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 NaN
b 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 NaN
a 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 NaN
d NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
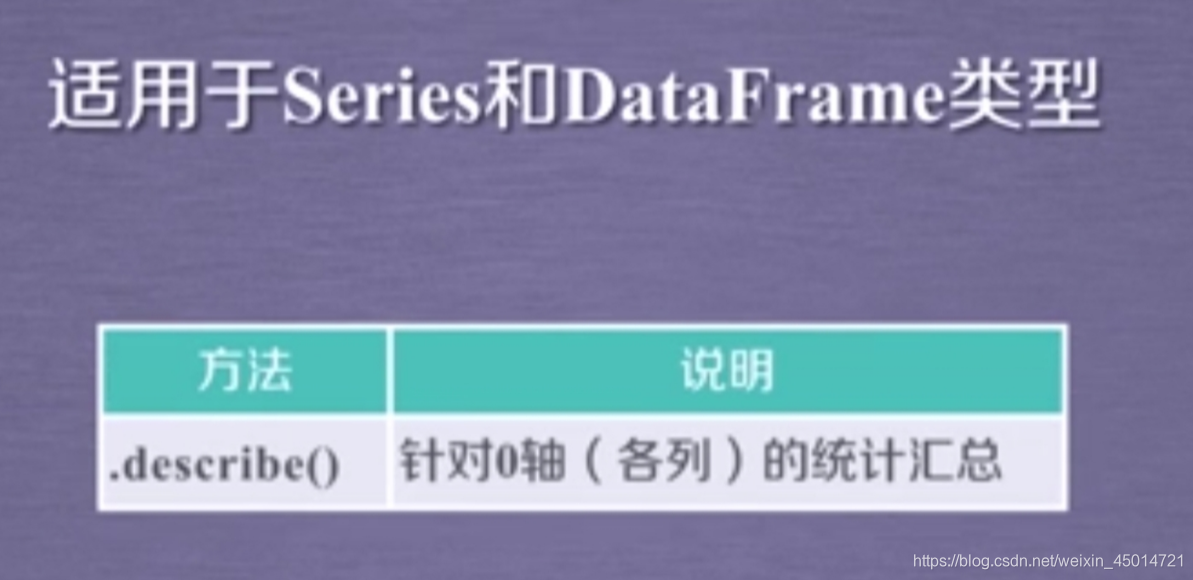
②对数据做统计

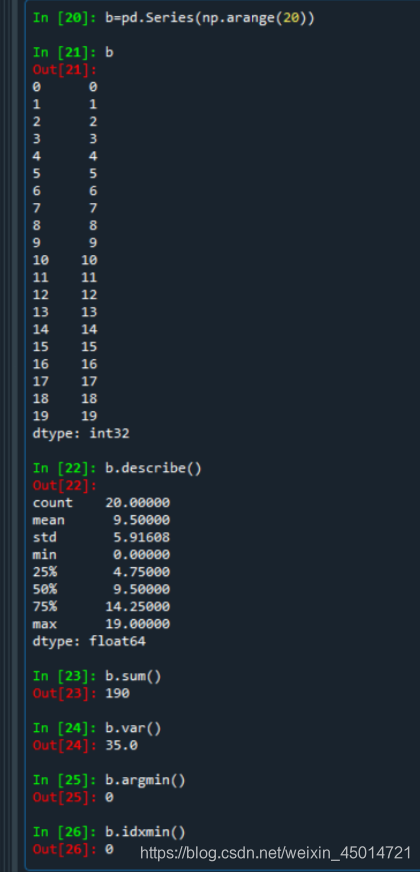
a = pd.Series([9,8,7,6], index=['a','b','c','d'])
a
a 9
b 8
c 7
d 6
dtype: int64
# describe()把统计值一次性输出出来
a.describe()
count 4.000000
mean 7.500000
std 1.290994
min 6.000000
25% 6.750000
50% 7.500000
75% 8.250000
max 9.000000
dtype: float64
# describe()输出的为Series类型,可以对其使用Series类型的方法。
type(a.describe())
<class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
a.describe()['count']
4.0
a.describe()['min']
6.0
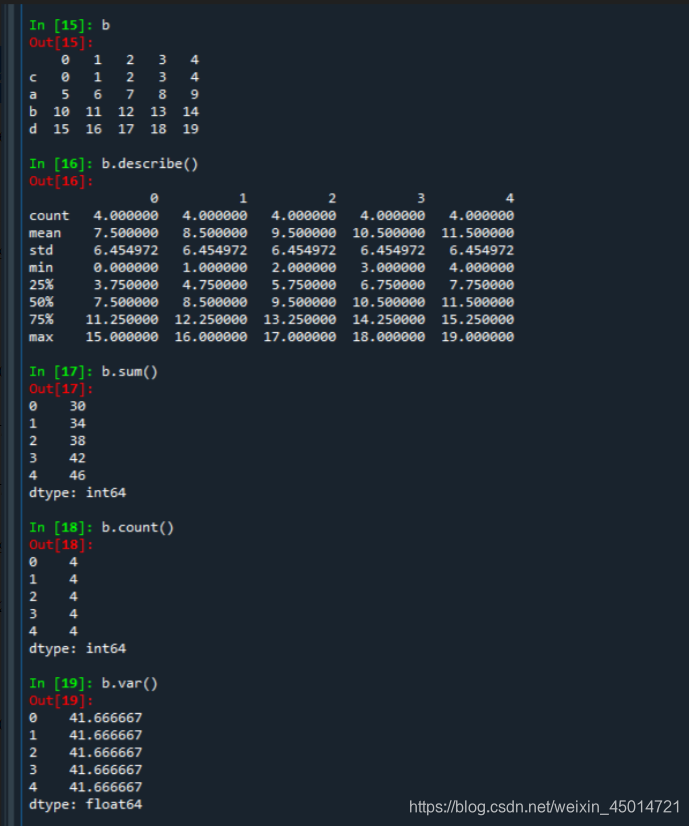
b = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape(4,5), index = 'c','a','d','b'])
b.describe()
0 1 2 3 4
count 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000
mean 7.500000 8.500000 9.500000 10.500000 11.500000
std 6.454972 6.454972 6.454972 6.454972 6.454972
min 0.000000 1.000000 2.000000 3.000000 4.000000
25% 3.750000 4.750000 5.750000 6.750000 7.750000
50% 7.500000 8.500000 9.500000 10.500000 11.500000
75% 11.250000 12.250000 13.250000 14.250000 15.250000
max 15.000000 16.000000 17.000000 18.000000 19.000000
# describe()输出的为DataFrame类型,可以对其使用DataFrame类型的方法。
type(b.describe())
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
b.describe()[2]
count 4.000000
mean 9.500000
std 6.454972
min 2.000000
25% 5.750000
50% 9.500000
75% 13.250000
max 17.000000
Name: 2, dtype: float64
# 这里注意一下DataFrame获取某一行数据时的方法
b.describe().ix['max']
0 15.0
1 16.0
2 17.0
3 18.0
4 19.0
Name: max, dtype: float64
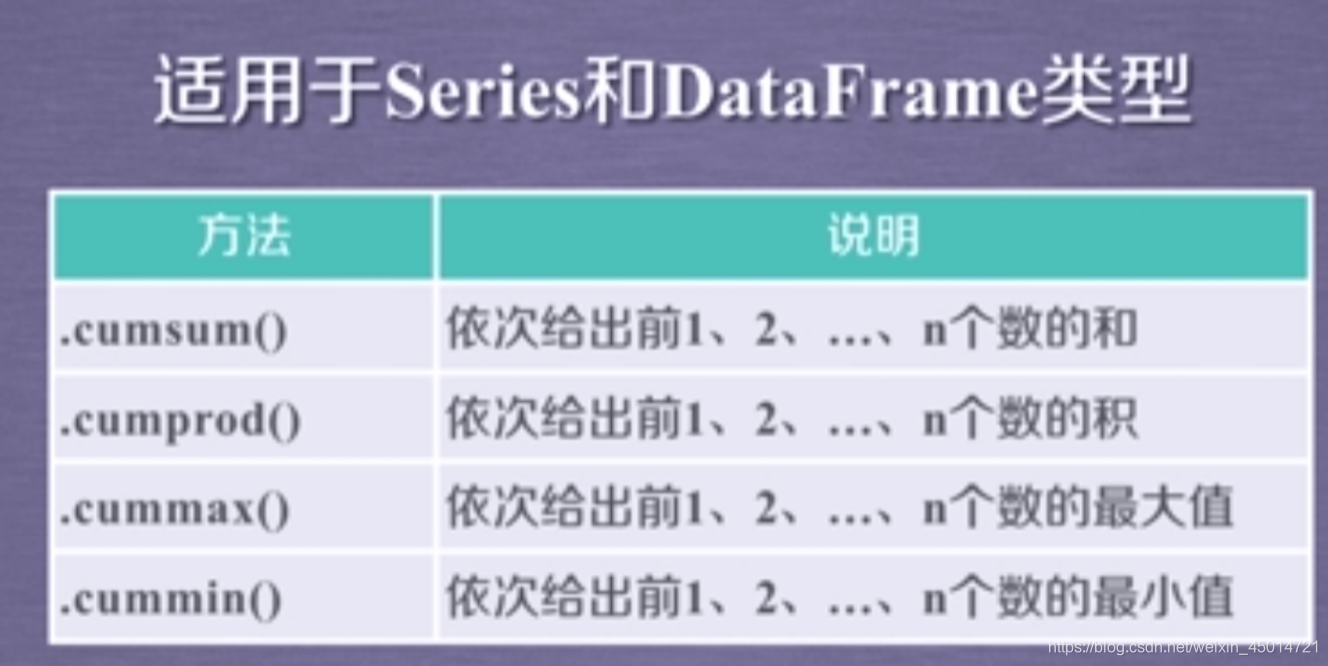
③数据的累计统计分析



5.pandas读取文件
①csv文件
import pandas as pd
# read csv file directly from a URL and save the results
data = pd.read_csv('text.csv', index_col=0)
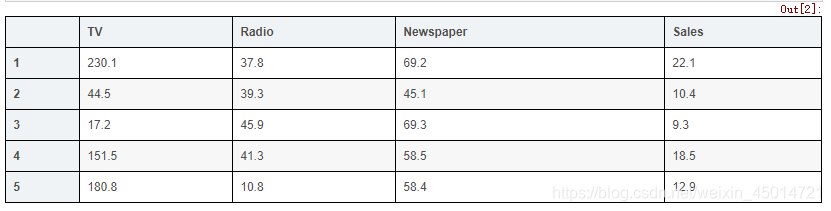
# display the first 5 rows
data.head()
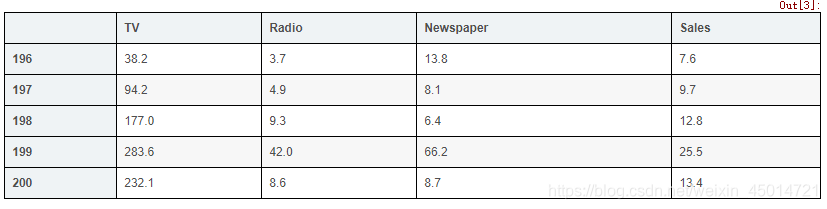
# display the last 5 rows
data.tail()
# check the shape of the DataFrame(rows, colums)
data.shape
输出:(200, 4)
#200行数据,四列特征值
②txt文件如下:
这些数据表示的是每个城市的(x,y)坐标。(中间是用空格分开的)

import pandas as pd #引入pandas包
citys=pd.read_table('./1.txt',sep='\t',header=None) #读入txt文件,分隔符为\t;若不写head=None,则会把第一行当成列名,读取时会没了第一行数据
print(citys)
打印结果:

可以看到全部数据就只有一列了,因为分割符为制表符,而制表符存在于txt文件每行的末尾。
接着把第一列的名字改成x,并添加一列,名字为y,y这一列的数值全是None:
citys.columns=['x']
citys['y']=None
print(citys)

最后把 x列中的数据,以空格为分割符,分给y一个数:
for i in range(len(citys)): #遍历每一行
coordinate = citys['x'][i].split() #分开第i行,x列的数据。split()默认是以空格等符号来分割,返回一个列表
citys['x'][i]=coordinate[0] #分割形成的列表第一个数据给x列
citys['y'][i]=coordinate[1] #分割形成的列表第二个数据给y列
print(citys)
可以看到,已经给txt的数据打上了x和y的标志了。























 4万+
4万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










