Topics:
- Activity-selection problem
- Elements of the greedy strategy
- Huffman coding
Greedy Method
For many optimization problem, Dynamic
Programming is overkill. A greedy algorithm always make the choice that looks best at every step. That is, it makes local optimal solution in the hope that this choice will lead to a globally optimal one.(有些问题使用动态规划求最优解有些大材小用了,而且也比较麻烦,低效)
Activity-Selection Problem
问题描述:

即就是对于两个活动ai和aj满足[si,fi)和[sj,fj)不重叠,则称他们是兼容的。我们的目标是寻找最大兼容的活动集。
Solution:
- Sort activities by finish times (let a1, a2,…,an denote sorted sequence)
- Pick first activity a1
- Remove all activities with start time before finish time of a1
- Recursively solve problem on remaining activities
Activity Selection

(mutually compatible:相互兼容的)


子问题:构造一个在ai结束后开始,在aj开始前结束的最大兼容集合。令sij表示在ai结束后开始,且
在aj开始前结束的所有活动的集合。
Property(性质) of Sij

性质1:

Optimal Substructure

最优解包含ak,所以获得两个子问题,寻找Sik中的兼容活动和Skj中的兼容活动。令Aik=Aij∩Sik和Akj=Aij∩Skj,所以就有Aij=Aik ∪{ak} ∪ Akj。
A recursive solution
Define c[i,j] as the number of activities in a maximum-size subset of mutually compatible activities. Then:
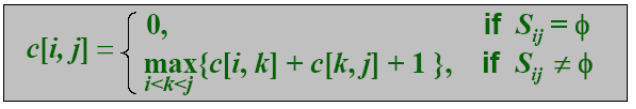
这里我们很容易想到用自底向上的动态规划,但是还有一种更为简化的贪心算法。
Greedy choice property(贪心选择性质)
定理16.1:

am在Sij的某个最大兼容活动子集中。

(disjoint:不相交的)

由此可见,我们可以反复选择最早结束的活动,保留与此活动兼容的活动。重复这一过程,直至不再有剩余活动。贪心算法通常都是这样自顶向下的设计:做出一个选择,然后求解剩下的那个子问题,而不是自底向上地求解出很多子问题,然后再作出选择。
A recursive greedy algorithm

数组s和f表示活动的开始和结束时间,i指出要求解的子问题Si,以及问题的规模j。
int a[50],x=1;
void RECURSIVE_ACTIVITY_SELECTION(int s[],int f[],int i,int j)//O(n lgn)
{
int m=i+1;
while(m<=j&&s[m]<f[i])
m++;
if(m<=j)
{
a[x++]=m+1;
RECURSIVE_ACTIVITY_SELECTION(s,f,m,j);
}
}
An iterative greedy algorithm

int a[50],x=1;
void ITERATIVE_ACTIVITY_SELECTION(int s[],int f[],int i,int j)//Θ(n)
{
for(int m=1;m<=j;m++)
{
if(s[m]>=f[i])
{
a[x++]=m+1;
i=m;
}
}
}
何时使用贪心算法?
How can one tell if a greedy algorithm will solve a particular optimization problem. There is no way in general. If we can demonstrate the following properties, then it is probable to use greedy algorithm:
- Greedy-choice property
- Optimal substructure (the same with that of dynamic programming)
Review

- 将最优化问题转化成这样的形式:对其做出一次选择后,只剩下一个子问题需要求解。
- 证明做出贪心选择后,原问题总是存在最优解,即贪心选择总是安全的。
- 证明做出贪心选择后,剩余的子问题满足性质:其最优解与贪心选择组合即可得到原问题的最优解,这样就得到了最优子结构。
Elements of Greedy Strategy

Greedy-choice property(贪心选择性质)
我们可以通过做出局部最优(贪心)选择来构造全局最优。换句话说,当进行选择时,我们直接做出在当前问题中看来最优的选择,而不必考虑子问题的解。
Optimal substructure(最优子结构)
将子问题的最优解与贪心选择组合在一起就能生成原问题的最优解。
Knapsack Problem(背包问题)
0-1背包问题与分数背包问题:

Optimal Substructure

0/1 Knapsack Example

Fractional Knapsack

void GREEDY_KNAPSACK(double p[],double w[],int W,int n,double x[])//p:价格数组;w重量数组;W:背包容量;n:问题规模;x:结果数组
{
int c=W,i=0;//背包剩余容量
for(;i<n;i++)
{
if(w[i]<c)
{
x[i]=1;
c=c-w[i];
}
else
break;
}
if(i<n)
x[i]=c/w[i];
}
Optimal Substructure (0/1 sack)


表达式如下:
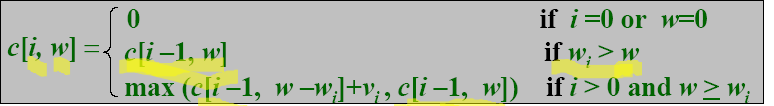

int c[50][50];
void DYNAMIC_PROGRAMMING_FOR_01_KNAPSACK(int v[],int w[],int n,int W)//v:价值数组;w:重量数组;n:问题规模;W:容量。
{
for(int x=0;x<=W;x++)
c[0][x]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
c[i][0]=0;
for(int x=1;x<=W;x++)
{
if(w[i]<=x)
{
if(v[i]+c[i-1][x-w[i]]>c[i-1][x])
c[i][x]=v[i]+c[i-1][x-w[i]];
else
c[i][x]=c[i-1][x];
}
else
c[i][x]=c[i-1][x];
}
}
}

Huffman codes

Example of Data Compression


Example of Huffman codes


Algorithm of Huffman Coding






















 556
556











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








