准备材料:

背景:Spring中的Bean
bean是对象,一个或者多个不限定
bean由Spring中一个叫IoC的东西管理
我们的应用程序由一个个bean构成
总而言之:Spring中的loC中可以含有多个Bean,并且Bean是loC中的单元结构
目前认识的Bean可以辅助创建类对象,在Spring loc容器中设置好Bean后,后期的开发中可以有利于开发者的代码规范整齐
下面简单的说明Bean中的几个属性:
一、lazy-init属性:
其对应的值有 true 和 false(default其实就是false),其作用在于是否在获得loC容器时加载其中每个Bean中的对象。
实验一:当将lazy-init设置成default(false)时;
--application.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="userInfo" class="club.shaoyu.vo.UserInfo"></bean>
</beans>
--UserInfo
public UserInfo() {
System.out.println("构造方法");
}
--Test
package club.shaoyu.test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
}
} 结果: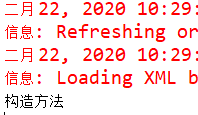
实验二:lazy-init设置成true
--application.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="userInfo" class="club.shaoyu.vo.UserInfo" lazy-init="true" ></bean>
</beans>
--UserInfo
public UserInfo() {
System.out.println("构造方法");
}
--Test
package club.shaoyu.test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
}
}结果:无
通过两个实验的对比可以看出:lazy-init设置成true时,其中的只有在获取Bean时才会创建相应的对象(读者可自己测试),设置成false时当获取loC容器时便可以创建全部的Bean对象
二、scope属性
其对应的值有prototype、request、session、singleton四种,其值得作用在于bean的作用时间问题
实验一:singleton
singleton意味着从bean请求实例化对象开始,该对象一直存在于loC容器中(不被删除),并且之后的调用相同bean都会是第一次调用的对象-资源共享(scope默认属性)
--application.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="userInfo" class="club.shaoyu.vo.UserInfo" scope="singleton"></bean>
</beans>
--Test
package club.shaoyu.test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext application =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Object object=application.getBean("userInfo");
System.out.println(object);
object=application.getBean("userInfo");
System.out.println(object);
application.close();//关闭容器loc
}
}
--UserInfo
public UserInfo() {
System.out.println("构造方法");
} 结果: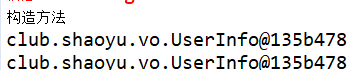
实验二:prototype
当scope的属性被赋予了该值时;每一次从loC中获取bean值,都会重新创建一次bean的实例化对象
--application.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="userInfo" class="club.shaoyu.vo.UserInfo" scope="prototype"></bean>
</beans>
--Test
package club.shaoyu.test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext application =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Object object=application.getBean("userInfo");
System.out.println(object);
object=application.getBean("userInfo");
System.out.println(object);
application.close();//关闭容器loc
}
}
--UserInfo
public UserInfo() {
System.out.println("构造方法");
} 结果: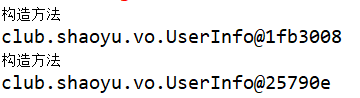
session和request则以此类推,我们可以简单的归结为当更换一次session或者是每向服务器发送一次请求便重新创建一次实例化对象
二、Bean的生命周期
Bean的生命周期就是在loC容器中从开始到结束其这一阶段过程中一共经历了什么。
--application.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="userInfo" class="club.shaoyu.vo.UserInfo" scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="name" value="Tom"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
--UserInfo
package club.shaoyu.vo;
public class UserInfo {
static {
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
{
System.out.println("非静态代码块");
}
String name;
public String getName() {
System.out.println("getter");
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("setter");
this.name = name;
}
public UserInfo() {
System.out.println("构造方法");
}
public void init() {
System.out.println("初始化");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("数据销毁");
}
}
--Test
package club.shaoyu.test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext application =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Object object=application.getBean("userInfo");
application.close();//关闭容器loc
}
}
结果:
这里需要注意的是:property标签可以为bean中的实例化方法赋值
只有当scope的值为singleton时,此时将loC容器关闭时,才会执行最终destroy-method,否则不可以






















 671
671











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








