Abstract
动机:dense boundary and bounding box annotations(密集的边界和目标框标注,这里的边界我认为是与文本相关的视频序列,目标框标注我认为是每一帧图像上的目标框);因此,我们提出了weakly-supervised setting;如果能够捕获video and language分解的结构,video-language component之间的虚假连接可以被避免。
新的框架:WINNER for hierarchical video-text understanding(分层的视频文本理解)
具体做法:(1)language decomposition tree in a bottom-up manner (用一种自底向上的方式构建了一种语言分解树);(2)利用structural attention mechanism(结构化的注意力机制)和top-down的特征回传机制来建立一个multi-model decomposition tree,允许对非结构化的视频进行分层理解;(3)A hierarchical contrastive learning objective(分层对比学习目标函数,学习样本内和样本间视频-文本分解结构之间的多层次相关性和区别,实现video-language分解结构之间的对齐)。
1. Introduction
国内外研究现状:
(1)第一类:fully exploit the fine-grained spatial-temporal annotations(充分利用细粒度的时空标注)
缺点:需要大量的标注成本——弱监督——massive video-language data without spatial-temporal annotations are easily accessible but without exploitation(没有时空标注的大量视觉语言数据很容易获取,但是没有被利用);

(2)第二类:hierarchical video-language understanding
主要挑战:
(i)视频数据的无结构特性:inferring the decomposed structure of continuous spatial-temporal visual data(推理连续的时空视觉数据的分解结构比较难);
(ii)hierarchical alignment requires simultaneously learning video-text correspondence and distinguishment at different hierarchies(分层对齐需要同时学习在不同层级video-text的相关性和区别)。
本文具体做法:
主要贡献:
(1)hierarchical video language decomposition and alignment(分层的视频语言分解和对齐);
(2)encapsulates the structural attention(结构化的注意力机制) and top-down backtracking(top-down的反向跟踪) for multi-modal hierarchical understanding。
2. Related Work
2.1. Spatio-temporal Video Grounding
2.2. Weakly-supervised learning
3. Method
3.1. Model Overview


3.2. Cross-model Hierarchical Understanding
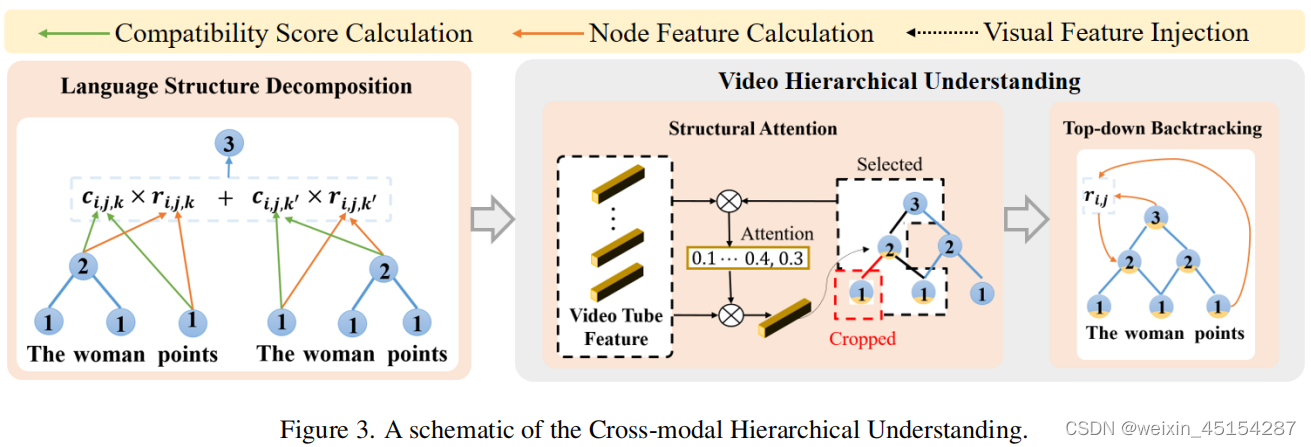
Language Structure Decomposition:
build the language decomposition tree in a bottom-up manner by merging adjacent nodes(通过融合相邻节点的特征,采用bottom-up的方式来建立语言分解树);每个节点都有一个特征和compatibility score(兼容得分,该节点与其他节点融合的可能性);
公式1和2:将短语(i,j)分成两部分(i,k)和(k,j),特征融合公式:

公式3和4:切分后的特征重新进行组合:

Structure-guided Video Hierarchical Understanding:
step-1:extracting multi-hierarchy visual cues relevant to components in the language decomposition tree(提取和语言分层相关的多分层视觉特征)and further transforming the language tree into a multi-modal one by feature fusion(采用特征融合机制将语言树编程一个多模态分层树), powered by the structural attention mechanism(主要采用注意力机制)。
具体做法:找到某一节点的相关节点(包括父节点和子节点);计算语言节点和视频节点的相关性,具体公式为:
![]()
得到平均注意力值:
![]()
一些节点(比如the可能包含不太有用的值)可能干扰多模态特征的对齐,因此首先judge一个node是否为一个interfering node,即首先计算该节点的相关度和平均相关度值的相似性:

并根据阈值进行筛选,得到新的attention value:

提取视觉特征,并加入该节点(语言)特征,得到新的语言特征:
![]()
![]()
step-2:recursively updating the multi-modal node representations through top-down feature backtracking(采用top-down的特征回传方式,循环地更新多模态节点表示), ensuring the hierarchical semantic consistency of the multi-modal decomposition tree(确保多模态分解树的分层一致性)。
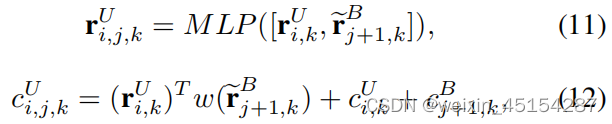
用跟新后的节点来重构输入序列(自监督学习)
3.3. Decomposition Structure Alignment
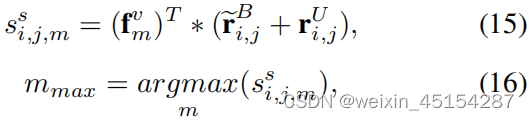
训练过程:
![]()
对于不配对的video-text对。计算最小特征相似度:
![]()
对于短语,我们需要考虑其是如何存在在句子中的:
![]()
与单词类似,分别最大化和最小化相似度值:

总损失:

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








