7.4 Describe a WSN application for each of the following categories: time-driven, eventdriven, and query-driven.
(译)为以下每一种类型描述一个WSN应用程序:时间驱动、事件驱动和查询驱动。
时间驱动型传感器网络适用于传输速率固定,通过对无线节点设置固定的时间实现周期性的监测采集数据,并通过经常性的启动接收器和传感器来监测基础环境,最后实现数据上传到基站。常规能源下时间驱动EH-WSN的最佳路由
事件驱动:只有当突发事件发生后才会开启收发器采集数据,并将数据发送到 基站,而平常节点的收发器大部分时间处于休眠状态,只需周期性采集少量数据。能量高效的事件驱动型大规模农业监测
查询驱动:地下无线传感器节点的查询驱动路由协议,检测和跟踪使用常规钻探和采矿工具未注意到的全面事件
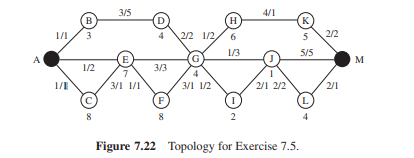
7.5 For the network topology shown in Figure 7.22, identify the optimal routes for source A to sink M according to the following criteria (describe how you compute the cost for the optimal route). The numbers X/Y along each link indicate the latency (X) and energy cost (Y) for transmitting a single packet over the link. The number Z under each node indicates the node’s remaining energy capacity.
(a) Minimum number of hops
(b) Minimum energy consumed per packet
© Maximum average energy capacity (eliminate hops that would result in a higher average but unnecessarily add to the route length!)
(d) Maximum minimum energy capacity
(e) Shortest latency
(译)对于图7.22所示的网络拓扑,根据以下标准确定从源A到接收M的最佳路由(描述如何计算最佳路由的成本)。每个链路上的数字X/Y表示在链路上传输单个数据包的延迟(X)和能量消耗(Y)。每个节点下的数字Z表示节点的剩余能量容量。
(a)最小跳数 答:A-E-G-J-M 4跳(3个中继节点)。
(b)每包的最低能源消耗 答:A-E-F-G-H-K-M. 最低能量消耗为:2+1+1+2+1+2=9.
©最大平均能量容量(消除会导致更高平均但不必要地增加路径长度的跳数!)
答: A-E-G-H-K-M (7+4+6+5)/4 = 5.5.
(d)最大最小能源容量 答:最大最小路径相同A-E-G-H-K-M。
最小能源容量:4
(e)最短的延迟 答:A-E-G-J-L-M 总延迟是9.
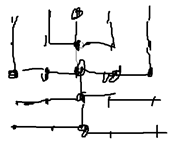
7.6 A WSN is modeled as a 5 × 5 grid as shown in Figure 7.23, with the base station placed at the center of the network (left topology) or at the bottom left corner (right topology). Assume that each node can communicate with only its immediate neighbors on the grid and that packet transmission or forwarding over a link costs exactly one unit of energy (packet reception and processing costs are neglected).
(译)WSN建模为如图7.23所示的5×5网格,基站位于网络的中心(左拓扑)或左下角(右拓扑)。假设每个节点只能与网格上的近邻进行通信,并且数据包传输或在链路上转发的成本正好是一个单位的能量(忽略了数据包接收和处理的成本)。
(a) For both topologies, find an energy optimal graph of routes, that is, the energy cost for each packet traveling through the network is a minimum.
(译)(a)对于两种拓扑结构,找出路由的能量最优图,即通过网络的每个数据包的能量消耗最小。
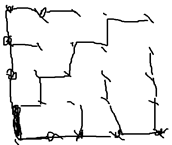
(b) Consider the graphs shown in Figure 7.24. What is the average and total load in the network, when the per-node load is defined as the number of routes a node has to service (including its own)? Do not include the base station in your calculations.
(译)(b)考虑图7.24所示的图表。当每个节点的负载被定义为一个节点必须服务的路由数(包括它自己)时,网络的平均和总负载是多少?不要在计算中包括基站。
括它自己)时,网络的平均和总负载是多少?不要在计算中包括基站。
总负载:66 平均负载:2.75

总负载:68 平均负载:2.83(坐标3.1的2应该是3)
© What is the lifetime of the network topologies in Figure 7.24 when during every second, each node generates and transmits its own packet and forwards all packets received during the previous second? Assume that each node has an initial energy budget of 100. Each transmission costs 1 unit of energy (there is no cost for reception, etc.). Consider the lifetime of a network to have expired once the first node depletes its energy budget. Compare the results and derive design principles for the network topology to optimize the lifetime of the network with respect to placement of the base station and the construction of routing trees.
(译)©图7.24中的网络拓扑的生命周期是什么,在每一秒钟,每个节点产生和传输它自己的数据包,并转发在前一秒钟收到的所有数据包?假设每个节点的初始能量预算为100。每个传输花费1单位的能量(没有接收费用等)。考虑当第一个节点耗尽其能量预算时,网络的生命周期已过。比较结果并推导出网络拓扑结构的设计原则,以优化基站的布置和路由树的构造。
答:生命周期可以理解为,一个网络的发展








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 3275
3275











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








