9.1 树与二叉树
二叉树的存储
struct node {
typename data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
};新建节点
node* newNode(int v) {
node* Node = new node;
Node->data = v;
Node->lchild = Node->rchild = NULL;
return Node;
}二叉树的查找
void search(node* root, int x, int newdata) {
if (root == NULL)
return ;
if (root->data == x) {
root->data = newdata;
}
search(root->lchild, x, newdata);
search(root->rchild, x, newdata);
};9.2 二叉树的遍历
9.2.1 先序遍历
递归
void PreOrder(node T){ //先序递归遍历二叉树
if(T == NULL){
return ;
}
cout<<T->data<<" ";
PreOrder(T->lchild );
PreOrder(T->rchild );
}非递归
void fPreOrder(node root){ //非递归先序遍历二叉树
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
Tnode p = root;
stack<node> s;
while (!s.empty() || p) {
while(p){ //一直往左走 , 先序遍历
cout<<p->data<<' ' ;
s.push(p);
p=p->lchild ;
}
//已经走到最左儿子
if(!s.empty() ){
p = s.top() ;//弹出父节点
s.pop() ;
p = p->rchild ; //然后去父节点的右儿子先序遍历
}
}
}9.2.2 中序遍历
递归
void InOrder(node T) {
if(T == NULL){
return ;
}
InOrder(T->lchild);
cout<<T->data<<" ";
InOrder(T->rchild);
}非递归
void fInOrder(node root) { //非递归中序遍历二叉树
if(root == NULL)
return ;
Tnode p = root;
stack<node> s;
while (!s.empty() || p) {
while(p) {
s.push(p);
p=p->lchild ;
}
if(!s.empty()) {
p=s.top();
s.pop();
cout<<p->data<<' ' ;
p=p->rchild ;
}
}
}
9.2.3 后序遍历
递归
void InOrder(node T) {
if(T == NULL){
return ;
}
InOrder(T->lchild);
InOrder(T->rchild);
cout<<T->data<<" ";
}非递归
9.2.4 层序遍历
struct node {
int data;
int layer;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
};void LayerOrder(node* root) {
queue<node*> q;
root->layer = 1;//根节点层号为1
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
node* now = q.front();
q.pop();
cout<<now->data<<" ";
if (now->lchild != NULL) {
now->lchild-layer = now_layer + 1;
q.push(now->lchild);
}
if (now->rchild != NULL) {
now->rchild->layer = now_layer + 1;
q.push(now->rchild);
}
}
}9.2.5 给定先序遍历和中序遍历求重建二叉树

//当前先序序列区间为[preL,preR], 中序序列区间为[inL, inR],返回根节点的地址
node* create(int preL, int preR, int inL, int inR) {
if(preL > preR)
return NULL;
node* root = new node;//存放二叉树的根节点
root->data = pre[preL];
int k;
for(k = inL; k <= inR; k++) {
if (in[k] == pre[preL]) {
break;
}
}
int numLeft = k - inL;//左子树节点的个数
root->lchild = create(preL + 1, preL + numLeft, inL, k - 1);
root->rchild = creat(preL + numLeft + 1, preR, k + 1, inR);
return root;
}【PAT A1020】 Tree Traversals
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. Given the postorder and inorder traversal sequences, you are supposed to output the level order traversal sequence of the corresponding binary tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the postorder sequence and the third line gives the inorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line the level order traversal sequence of the corresponding binary tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
7
2 3 1 5 7 6 4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
结尾无空行Sample Output:
4 1 6 3 5 7 2
结尾无空行
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 50;
struct node {
int data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
};
int pre[maxn], in[maxn], post[maxn];
int n;//节点数
//当前后序序列区间为[postL,postR], 中序序列区间为[inL, inR],返回根节点的地址
node* create(int postL, int postR, int inL, int inR) {
if(postL > postR)
return NULL;
node* root = new node;//存放二叉树的根节点
root->data = post[postR];
int k;
for(k = inL; k <= inR; k++) {
if (in[k] == post[postR]) {
break;
}
}
int numLeft = k - inL;//左子树节点的个数
root->lchild = create(postL + 1, postL + numLeft - 1, inL, k - 1);
root->rchild = creat(postL + numLeft, postR - 1, k + 1, inR);
return root;
}
void LayerOrder(node* root) {
queue<node*> q;
root->layer = 1;//根节点层号为1
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
node* now = q.front();
q.pop();
cout<<now->data<<" ";
if (now->lchild != NULL) {
q.push(now->lchild);
}
if (now->rchild != NULL) {
q.push(now->rchild);
}
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &post[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++) {
scanf("%d", &in[i]);
}
node* root = create(0,n-1,0,n-1);
LayerOrder(root);
return 0;
}9.2.5 二叉树的静态实现
struct node{
typename data;
int lchild;
int rchild;
} Node[maxn];
9.3 树的遍历
9.3.1 树的静态写法
struct node {
typename data;//数据域
int child[maxn];//指针域,存放所有子节点的下标
} Node[maxn]; //节点数组
由于无法预知子节点的个数,所以child数组的长度只能开到最大。因此可以使用变长数组vector表示
struct node {
typename data;//数据域
vector<node> child;//指针域
} Node[maxn];9.3.2 树的先根遍历
void PreOrder(int root) {
printf("%d ", Node[root].data);
for (int i = 0; i < Node[root].child.size(); i ++) {
PreOrder(Node[root].child[i]);
}
}9.3.3 树的层序遍历
void LayerOrder(int root) {
queue<int> Q;
Q.push(root);
while(!Q.empty()) {
int front = Q.front();
printf("%d ",Node[front].data);
Q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < Node[front].child.size(); i++) {
Q.push(Node[front].child[i]);
}
}
}【PAT A1053】Path of Equal Weight
Given a non-empty tree with root R, and with weight Wi assigned to each tree node Ti. The weight of a path from R to L is defined to be the sum of the weights of all the nodes along the path from R to any leaf node L.
Now given any weighted tree, you are supposed to find all the paths with their weights equal to a given number. For example, let's consider the tree showed in the following figure: for each node, the upper number is the node ID which is a two-digit number, and the lower number is the weight of that node. Suppose that the given number is 24, then there exists 4 different paths which have the same given weight: {10 5 2 7}, {10 4 10}, {10 3 3 6 2} and {10 3 3 6 2}, which correspond to the red edges in the figure.
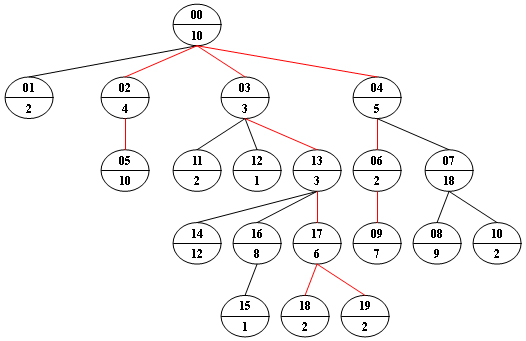
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing 0<N≤100, the number of nodes in a tree, M (<N), the number of non-leaf nodes, and 0<S<230, the given weight number. The next line contains N positive numbers where Wi (<1000) corresponds to the tree node Ti. Then M lines follow, each in the format:
ID K ID[1] ID[2] ... ID[K]where ID is a two-digit number representing a given non-leaf node, K is the number of its children, followed by a sequence of two-digit ID's of its children. For the sake of simplicity, let us fix the root ID to be 00.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print all the paths with weight S in non-increasing order. Each path occupies a line with printed weights from the root to the leaf in order. All the numbers must be separated by a space with no extra space at the end of the line.
Note: sequence {A1,A2,⋯,An} is said to be greater than sequence {B1,B2,⋯,Bm} if there exists 1≤k<min{n,m} such that Ai=Bi for i=1,⋯,k, and Ak+1>Bk+1.
Sample Input:
20 9 24
10 2 4 3 5 10 2 18 9 7 2 2 1 3 12 1 8 6 2 2
00 4 01 02 03 04
02 1 05
04 2 06 07
03 3 11 12 13
06 1 09
07 2 08 10
16 1 15
13 3 14 16 17
17 2 18 19
结尾无空行Sample Output:
10 5 2 7
10 4 10
10 3 3 6 2
10 3 3 6 2
结尾无空行题意:就是给定一个target,求从根节点到叶节点的路径,路径上所有节点的权重和等于target。有的话输出多条,按照权重从大到小输出。



#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100;
struct node {
int weight;
vector<int> child;
} Node[MAXN];
bool cmp(int a, int b) {
return Node[a].weight > Node[b].weight;
}
int n, m, S;
int path[MAXN];//路径
//当前访问节点为index,numNode为当前路径path上的节点的个数(层数)
void DFS(int index, int numNode, int sum) {
if(sum > S) return;
if(sum == S) {
if(Node[index].child.size() != 0) return;
for(int i = 0; i < numNode; i ++) {
printf("%d", Node[path[i]].weigth);
if(i < numNode - 1) printf(" ");
else printf("\n");
}
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < Node[index].child.size(); i++) {
int child = Node[index].child[i];
path[numNode] = child;
DFS(child, numNode + 1, sum + Node[child].weight);//递归进入下一层
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &S);
for (int i = 0; i <n; i ++) {
scanf("%d", &Node[i].weight);
}
int id, k, child;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &id, &k);
Node[id].child.push_back(child);
}
sort(Node[i].child.begin(), Node[id].child.end(),cmp);
}
path[0] = 0;
DFS(0,1,Node[0].weight);
return 0;
}
9.4 二叉查找树
9.4.2 二叉查找树的基本操作
1.查找操作
void search(node* root, int x) {
if (root == NULL) return;
if (x == root->data){
printf("查找成功");
} else if (x < root->data) {
search(root->lchild, x);
} else {
search(root->rchild, x);
}
}
2.插入操作
void insert(node* &root, int x) {
if (root == NULL) {
root = newNode(x);
return;
}
if (x == root->data) {
return;
} else if (x < root->data) {
insert(root->lchild, x);
} else {
insert(root->rchild, x);
}
}
3.二叉树的建立
node* Create(int data[], int n) {
node* root = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
insert(root, data[i]);
}
return root;
}4. 二叉树的删除
把以二叉查找树中比节点权重小的最大节点称为该节点的前驱,而把比权重大的最小节点称为该节点的后继。
//寻找以root为根节点的树中的最大权值节点
node* findMax(node* root) {
while (root->rchild != NULL) {
root = root->rchild;
}
return root;
}
//寻找以root为根节点的树中的最小权值节点
node* findMax(node* root) {
while (root->lchild != NULL) {
root = root->lchild;
}
return root;
} 

![]()
void deleteNode(node* &root, int x) {
if (root == NULL) return;
if (root->data == x) {
if(root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL) {
root = NULL;
} else if(root->lchild != NULL){
node* pre = findMax(root->lchild);
root->data = pre->data;
deleteNode(root->lchild,pre->data);
} else {
node* next = findMin(root->rchild);
root->data = next->data;
deleteNode(root->rchild, next->data);
}
} else if(root->data > x) P
deleteNode(root->lchild, x);
} else {
deleteNode(root->rchild, x);
}
}
【PAT A1043】Is it a Binary Search Tree
9.5 平衡二叉树
9.5.1.平衡二叉树的定义
struct node {
int v, height;//v为节点权重,height为当前子树高度
node* lchild, *rchild;
};node* newNode(int v) {
node* Node = new node;
Node->height = 1;
Node->v = v;
Node->lchild = Node->rchild = NULL;
return Node;
}int getHeight(node* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return root->height;
}
int getBalanceFactor(node* root) {
return getHeight(root->lchild) - getHeight(root->rchild);
}
void updateHeight(node* root) {
root->height = max(getHeight(root->lchild),getHeight(root->rchild)) + 1;
}9.5.2 平衡二叉树的基本操作
1.查找操作
同二叉查找树
2.插入操作
左旋

void L(node* &root) {
node* temp = root->rchild;
root->rchild = temp.lchild;
temp->lchild = root;
updateHeight(root);
updataHeight(temp);
root = temp;
}右旋

void R(node* &root) {
node* temp = root->lchild;
root->lchild = temp->rchild;
temp->rchild = root;
updateHeight(root);
updateHeight(temp);
root = temp;
} 




void insert(node* &root, int v) {
if(root == NULL) {
root = newNode(v);
return;
}
if(v < root->v) {
insert(root->lchild);
updateHeight(root);
if(getBalanceFactor(root) == 2) {
if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild == 1) { //LL型
R(root);
} else if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild) == -1) {//LR型
L(root->lchild);
R(root);
}
}
} else {
insert(root->rchild, v);
updateHeight(root);
if(getBalanceFactor(root) == -2) {
if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild == -1) { //RR型
L(root);
} else if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild) == 1) {//LR型
R(root->Rchild);
L(root);
}
}
}
}
9.6 并查集
9.6.1 并查集的定义
并查集的实现:其实就是一个数组:int father[N]
father[i]表示元素i的父节点,父节点本身也是这个集合内的元素。如果father[i] = i表示元素i是集合的根节点。对同一个集合来说,只存在一个根节点,且将其作为所属集合的标识。
9.6.2 并查集的基本操作
//1.初始化
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
father[i] = i;
}
//2.查找
int findFather(int x) {
while(x != father[x]) {
x = father[x];
}
return x;
}
//3.合并
void Union(int a, int b) {
int faA = findFather(a);
int faB = findFather(b);
if (faA != faB) {
father[faA] = faB;
}
}9.6.3 路径压缩

路径压缩相当于把当前查询路径上所有节点的父亲都直接指向根节点。
int findFather(int x) {
int a = x;
while (x != father[x]) {
x = father[x];
}
while(a != father[a]) {
int z = a;
a = father[a];
father[z] = x;
}
return x;
}
//递归xief
int findFather(int v) {
if(v == father[v]) {
return v;
} else {
int F = findFather[father[v]);
father[v] = F;
return F;
}
}
9.7 堆
9.7.1 堆的定义与基本操作
使用数组来表示堆,并且数组第i号位的节点的左孩子就是2i号位,而右孩子则是(2i+1)号位。
const int maxn = 100;
int heap[maxn],n=10;//对heap数组在[low, high]范围内进行向下调整
void downAdjust(int low, int high) {
int i = low, j = 2 * i;//i为欲调整节点,j为其左孩子
while (j <= high) {
if(j + 1 <= high && heap[j + 1] > heap[j]) {
j = j + 1;
}
if(heap[j] > heap[i]) {//以最大堆为例
swap(heap[i], heap[j]);
i = j;
j = i * 2;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
//建堆
void createHeap() {
for (int i = n / 2; i >= 1; i--) {
downAdjust(i,n);
}
}
//删除堆顶元素
void deleteTop() {
heap[1] = heap[n--];
downAdjust(1, n);
}
//对heap数组在[low, high]范围内进行向上调整
void upAdjust(int low, int high) {
int i = high, j = i / 2;
while (j >= low) {
if(heap[j] < heap[i]) {
swap(heap[i], heap[j]);
i = j;
j = i / 2;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
//添加元素
void insert(int x) {
heap[++n] = x;
upAdjust(1,n);
}9.7.2 堆排序
void heapSort() {
createHeap();
for (int i = n; i > 1; i--) {
swap(heap[i], heap[1]);
downAdjust(1, i-1);
}
}9.8 哈夫曼树
9.8.1 哈夫曼树

#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
priority_queue<long long, vector<long long>, greater<long long>> q;
int main() {
int n;
long long temp, x, y, ans = 0;
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
scanf("%lld",&temp);
q.push(temp);
}
while(q.size() > 1) {
x = q.top();
q.pop();
y = q.top();
q.pop();
q.push(x + y);
ans += x + y;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}9.8.2 哈夫曼编码
此部分留给有兴趣的读者自行实现。
























 139
139











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








