Swagger
学习目标
- 了解Swagger的概念及作用
- 掌握在项目中集成Swagger自动生成API文档
基于SpringBoot 2.3.12.RELEASE 版本
Swagger简介
前后端分离
Vue + SrpingBoot
后端时代:前端只用管理静态页面: html ==> 模板引擎 JSP ⇒ 后端是主力
前后端分离时代:
-
后端:后端控制层,服务层,数据访问层 [后端团队]
-
前端:前端控制层,视图层 [前端团队]
- 伪造后端数据,json。已经存在了,不需要后端,前端工程依旧能跑起来
-
前后端如何交互? ==> API
-
前后端相对独立,松耦合;
-
前后端甚至可以部署在不同的服务器上;
产生一个问题:
- 前后端集成联调,前端人员和后端人员无法做到,即使协商,尽早解决,最终导致问题集中爆发
解决方案:
- 首先指定schema[计划的提纲],实时更新最新API,降低集成的风险;
- 早些年:指定Word计划文档;
- 前后端分离:
- 前端测试后端接口:早期:postman
- 后端提供接口,需要实时更新最新的消息及改动!
Swagger
- 号称世界上最流行的Api框架;
- RestFul Api 文档在线自动生成工具 => Api文档与Api定义同步更新
- 直接运行,可以在线测试工具
- 支持多种语言 (如:Java,PHP等)
- 官网:https://swagger.io/
在项目中使用Swagger ,需要springfox;
- swagger2
- ui
新建一个Springboot项目
1.加入swagger依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
2.编写helloworld
package com.lh.swagger.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello world";
}
}
3.配置Swagger - config
package com.lh.swagger.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2 // 开启Swagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
}
4.测试:主启动加入:@EnableSwagger2:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
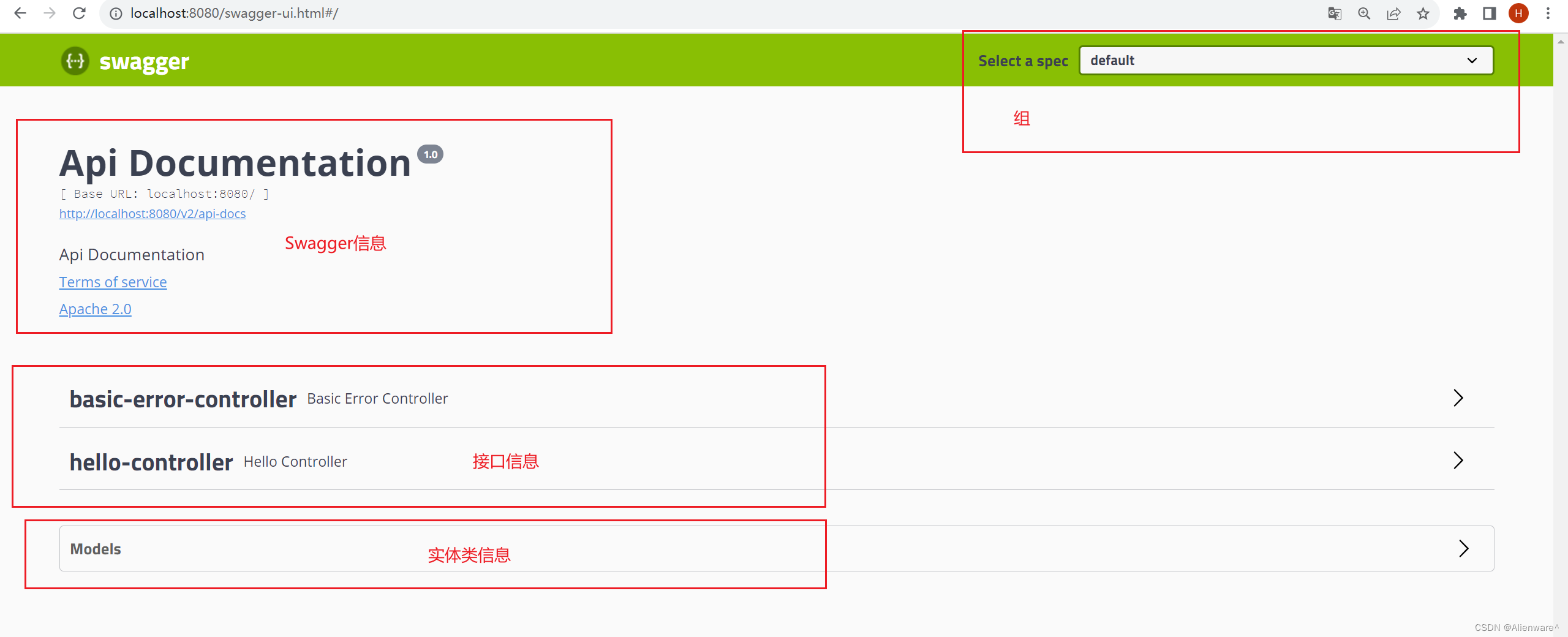
配置Swagger
Swagger 的bean的实例 :Docket;
package com.lh.swagger.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.service.VendorExtension;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2 // 开启Swagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
//配置Swagger 的 Docket的bean实例
@Bean
public Docket docket(){
//替换成自己的ApiInfo
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
//配置Swagger信息 = apiInfo (自定义)
private ApiInfo apiInfo(){
//作者信息
String name = "栾昊";
//指向的url
String url = "https://www.baidu.com/";
//邮箱(收件人)
String email = "luanh_0521@163.com";
Contact contact = new Contact(name,url, email);
//返回内容
return new ApiInfo(
"栾昊的 Swagger API文档",
"亦如美酒尘封多年",
"1.0",
//服务条款网址
"https://gitee.com/",
contact,
"Apache 2.0",
"http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0",
new ArrayList<>());
}
页面:
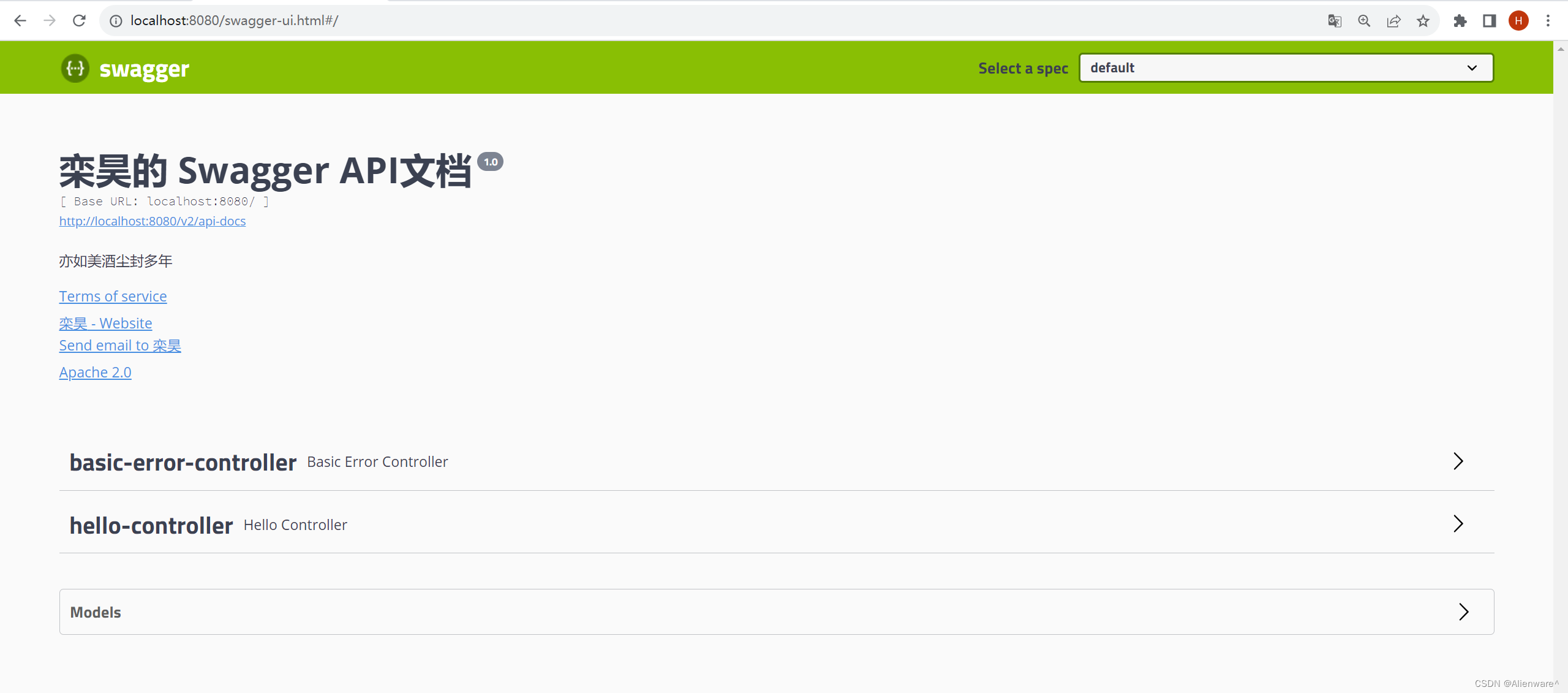
Swagger配置:
//配置Swagger 的 Docket的bean实例
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
//替换成自己的ApiInfo
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口
.select()
//RequestHandlerSelectors,配置要扫描接口的方式
// basePackage:指定要扫描的包
// any:扫描全部
// none:都不扫描
// withClassAnnotation 扫描类上的注解
//withMethodAnnotation 扫描方法上的注解
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.lh.swagger.controller"))
//过滤什么路径
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/swagger/**"))
.build();
}
配置Swagger开关
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
//替换成自己的ApiInfo
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
//不设置为主启动,这样启动就不会启动swagger
.enable(false)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.lh.swagger.controller"))
//过滤什么路径
//.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/swagger/**"))
.build();
}
我只希望我的Swagger在生产环境中使用,在发布时候不使用
- 判断是不是生产环境 flag = false
- 注入enable(flag)

//配置Swagger 的 Docket的bean实例
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment) {
//设置显示的Swagger环境,只显示dev
Profiles profiles = Profiles.of("dev");
//通过 environment.acceptsProfiles 是否处在自己设置的环境中
boolean flag = environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles);
//替换成自己的ApiInfo
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
//设置自己的环境
.enable(flag)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.lh.swagger.controller"))
//过滤什么路径
//.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/swagger/**"))
.build();
}
配置API分组
根据API文档的分组:
.groupName("栾昊")
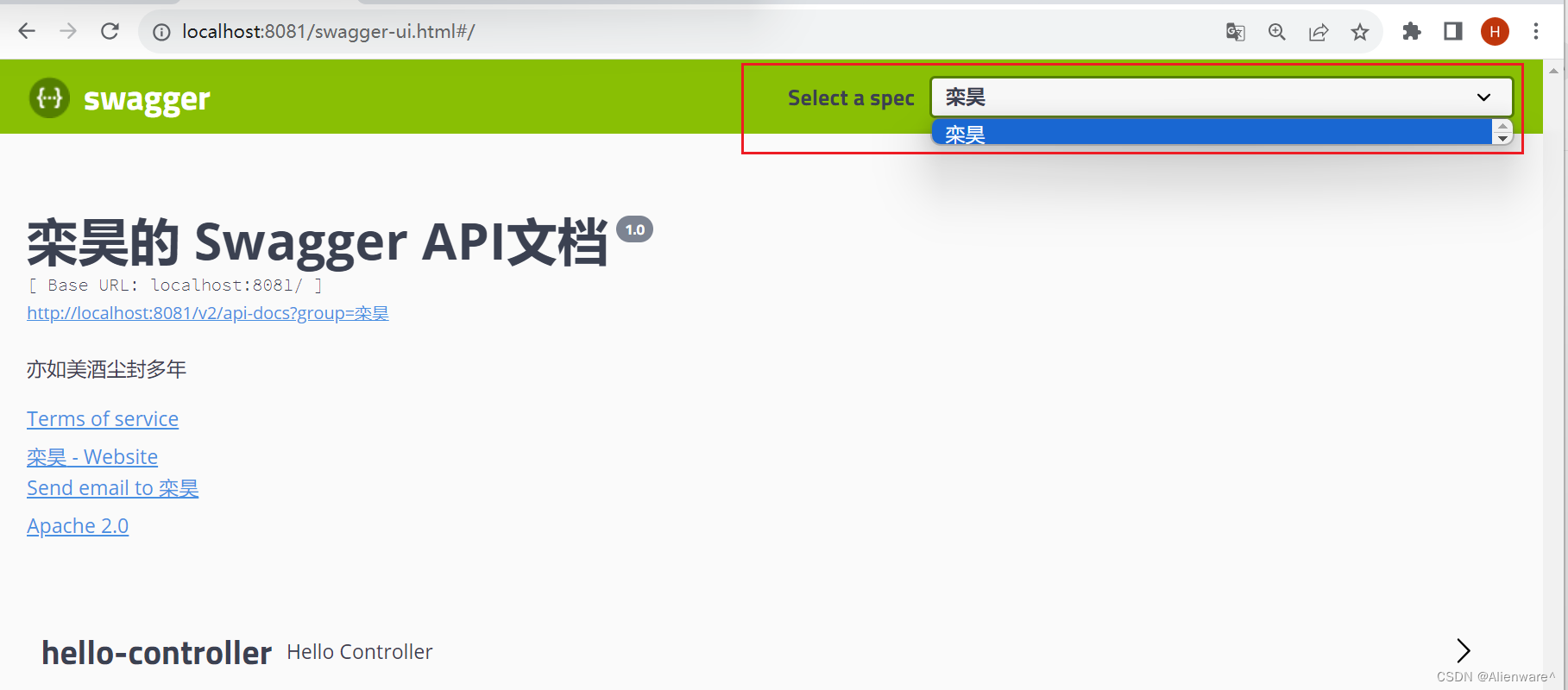
问题:如何配置多个环境?
方式:多个Docket配置多个组
@Bean
public Docket docket1(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("A");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("B");
}
实体类配置
package com.lh.swagger.pojo;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
//文档注释
@ApiModel("用户实体类")
//@Api(注释)
public class User {
//实体类字段必须用public 显示,不然不会出现字段
//字段注释
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
public String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
public String password;
}
controller层配置
package com.lh.swagger.controller;
import com.lh.swagger.pojo.User;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@Api(description = "hello控制层") //整个类的注释
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello world";
}
//只要我们的接口中返回值出现实体类,他就会被扫描到Swagger中
@PostMapping("/user")
public User user(){
return new User();
}
@ApiOperation("hello控制类") //在方法上加该注释
@GetMapping("/hello2")
//@ApiParam("用户名") 在参数上加注释
public String hello(@ApiParam("用户名") String username){
return "hello world" + username;
}
@ApiOperation("post-hello控制类") //在方法上加该注释
@GetMapping("/postHello")
//@ApiParam("用户名") 在参数上加注释
public User postHello(@ApiParam("用户名") User user){
return user;
}
}
页面:
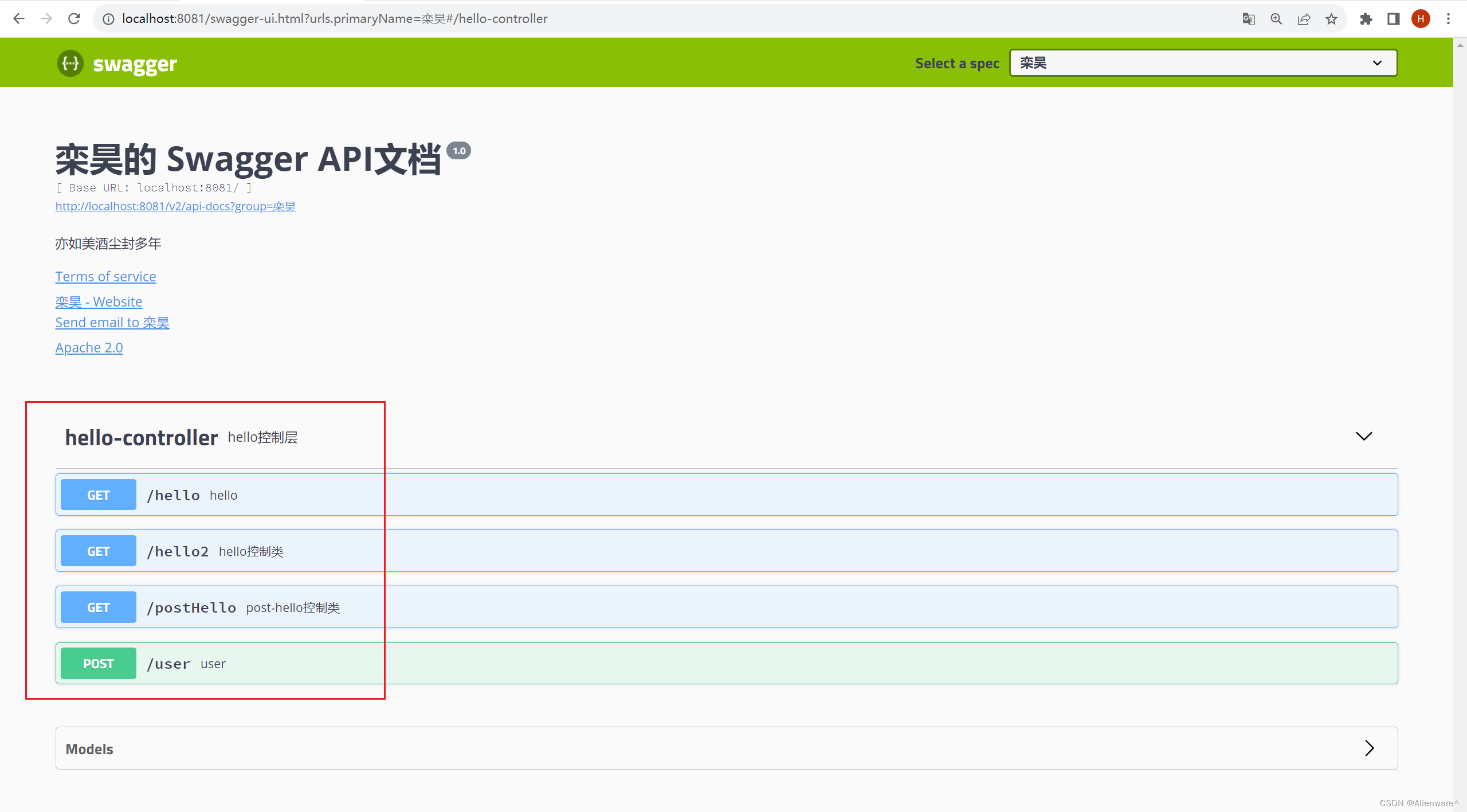
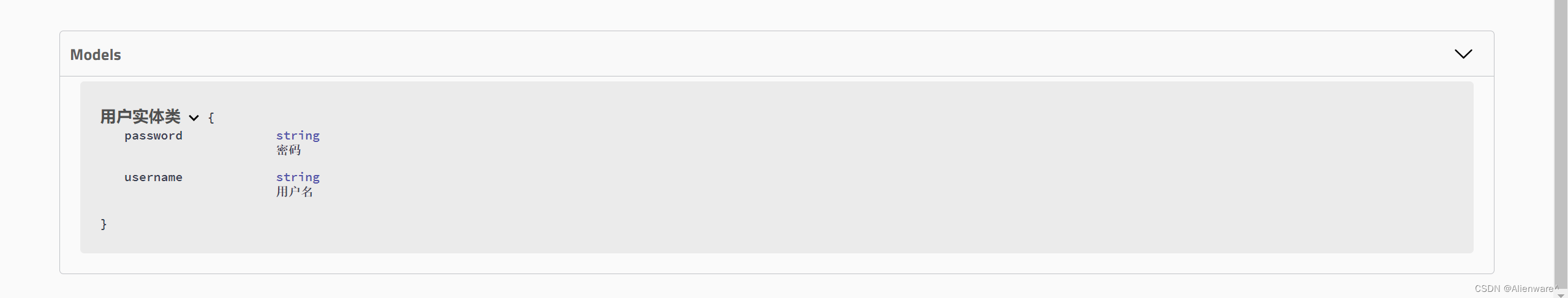
注:并不是因为@ApiModel这个注解让实体显示在这里了,而是只要出现在接口方法的返回值上的实体都会显示在这里,而@ApiModel和@ApiModelProperty这两个注解只是为实体添加注释的。
@ApiModel为类添加注释
@ApiModelProperty为类属性添加注释
总结:
- 我们可以通过Swagger给一些比较难理解的属性或者接口,增加注释信息
- 接口文档实时更新
- 可以在线测试
常用注解
Swagger的所有注解定义在io.swagger.annotations包下
下面列一些经常用到的,未列举出来的可以另行查阅说明:
| Swagger注解 | 简单说明 |
|---|---|
| @Api(tags = “xxx模块说明”) | 作用在模块类上 |
| @ApiOperation(“xxx接口说明”) | 作用在接口方法上 |
| @ApiModel(“xxxPOJO说明”) | 作用在模型类上:如VO、BO |
| @ApiModelProperty(value = “xxx属性说明”,hidden = true) | 作用在类方法和属性上,hidden设置为true可以隐藏该属性 |
| @ApiParam(“xxx参数说明”) | 作用在参数、方法和字段上,类似@ApiModelProperty |
注意点 :在正式发布的时候,关闭Swagger! ! 处于安全考虑,而且节省运行的内存;






















 3280
3280











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








