一、调用写法
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> users = mapper.selectAllUser(new Random().nextInt());
我们正常的调用时是通过SqlSession获取我们的Mapper接口,然后去调用我们的方法。我们可以直接调用sqlSession帮我们封装的CRUD
二、原生写法
List<User> users=sqlSession.selectList("com.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.selectAllUser");//原生写法
这种写法是直接可以调用sqlSession的方法传递我们的Maopper接口全类名+自己写好的方法名就可以了。为什么可以这样用?我们进入源码分析
三、源码分析
1.代理类的invoke方法
我们知道执行我们的Mapper中的方法就是在执行我们代理类的invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
我们可以看一下,在代理类中其实是走我们的execute方法
2.invoke方法源码
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
/**
* 先判断是UPDATE、DELETE、INSERT还是SELECT
*/
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == command.getType()) {
/**
* 根据方法返回值不同去执行不同的代码
*/
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
} else if (SqlCommandType.FLUSH == command.getType()) {
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
} else {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
以上的代码其实很简单,就分两步,都已经备注到了代码中,这里就不再说一遍了!
我们以返回值为一个的分析,其他的类似
3.sqlSession.selectOne();
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
点进来发现走的其实是selectList()方法、然后如果查询出来一条的话返回list.get(0); 否则返回我们都很熟悉的错误:Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found
那么我们继续看selectList()
4.selectList()
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//MappedStatement 是对我们SQL语句的封装 那下边的代码就很简单了 就是获取我们SQL语句
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//调用Query方法去查询
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
我们可以先Debug看一下MapperStatement里边

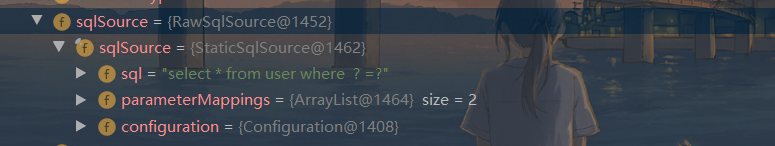
可以清楚的看到MappedStatement的sqlSource里边封装的就是我们的SQL语句,其他信息是与我们Mapper接口对应的还有标记等等
然后去调用我们的query 去查询 query中存在缓存机制我们下期重点分析query方法
那么大致的Executor流程到这已经都清楚了八!






















 590
590











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








