区块链基础知识及发展
前置知识
①区块链要解决的问题

- 在物理世界中,我们通过人面对面直接进行
价值传递(商品购买等)- 在互联网世界中,我们通过我们信赖的
第三方作为中间人来进行价值传递(但是这种方式存在一个弊端,就是过于中心化,一旦中间人被攻击或者出现其他意外,我们的钱或者说财富就会损失)
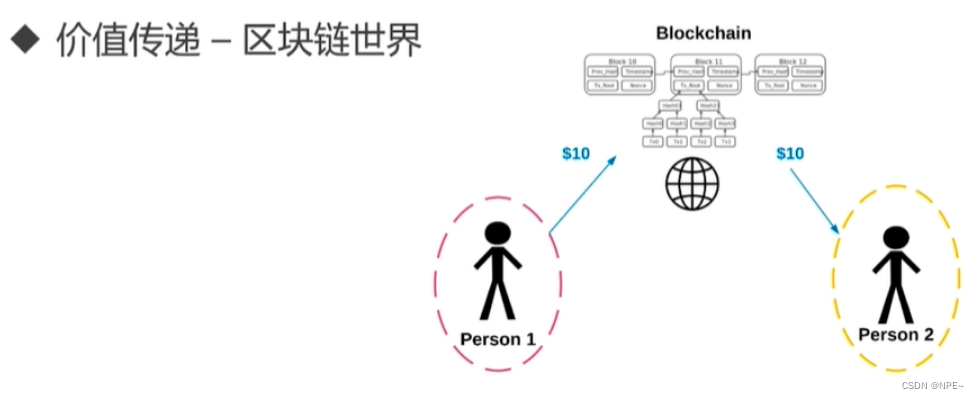
在区块链的世界,是一个去中心化的世界,它依赖区块链中的其他区块来进行记账功能
②区块链的6层
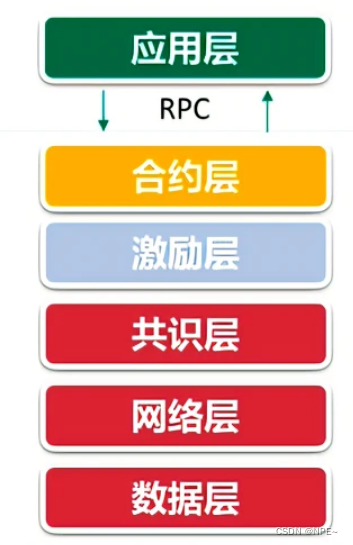
- 应用层:可编程货币、可编程金融、可编程社会
- 应用层则封装了区块链的各种应用场景和案例。
- 合约层:脚本代码、算法机制、智能合约
- 合约层主要封装各类脚本、算法和智能合约,是区块链可编程特性的基础。
- 激励层:发行机制、分配机制
- 激励层将经济因素集成到区块链技术体系中来,主要包括经济激励的发行机制和分配机制等。
- 共识层:PoW(proof of work 工作量证明)、PoS(权益证明机制)、DPoS(股份授权证明机制)…
- 共识层主要封装网络节点的各类共识算法,目前比较知名的有POW工作量证明机制、权益证明机制POS、股份授权证明机制DPOS等。
- 网络层:P2P网络、传播机制、验证机制
- 网络层包括分布式组网机制、数据传播机制和数据验证机制等,P2P组网技术早期应用在BT这类P2P下载软件中,这就意味着区块链具有自动组网功能。
- 数据层:数据区块、链式结构、时间戳、哈希函数、Merkle树、非对称加密
- 数据层封装了底层数据区块以及相关的数据加密和时间戳等基础数据和基本算法,这是整个区块链技术中最底层的数据结构。

注意:数据层、网络层、共识层是构建区块链技术的必要元素,缺一不可,而激励层、合约层和应用层不是每个区块链应用的必要因素。
1 比特币(电子货币)
- 比特币是一种去中心化的数字货币,由一些计算机程序生成,没有中央银行或其他中央机构控制。比特币的交易是通过区块链技术实现的,这是一种去中心化的数据库,记录了所有比特币交易的历史记录。
- 比特币的用途包括支付、投资和存储价值。比特币的发展历程可以追溯到2008年,当时一个名为Satoshi Nakamoto(中本聪)的人发布了一篇名为《比特币:一种点对点的电子现金系统》的论文,描述了比特币的基本原理。
- 现在,比特币已经成为全球最受欢迎的数字货币之一,被广泛用于各种用途,包括购买商品和服务、投资和交易。
2 以太坊(分布式计算平台-执行智能合约)
- 以太坊是一个分布式计算平台和操作系统,允许开发者在其上构建去中心化的应用程序。以太坊的核心是以太坊虚拟机(EVM),它是一种基于区块链技术的虚拟机,可以执行智能合约。
- 以太坊的用途包括构建去中心化的应用程序、发行代币和进行智能合约。以太坊的发展历程可以追溯到2013年,当时Vitalik Buterin发布了一篇名为《以太坊白皮书》的论文,描述了以太坊的基本原理。
- 现在,以太坊已经成为全球最受欢迎的分布式计算平台之一,被广泛用于各种用途,包括去中心化应用程序、代币发行和智能合约。
3 智能合约(程序)
本质上,智能合约就是一段代码,开发者将代码公开,让所有人都可以知道核心源代码。比如:我们开发了一个抽奖系统,那么我们就需要将执行抽奖逻辑的代码公开,并且受到其他所有人的监督,如果违反我们之前源代码的逻辑将被惩罚,因此保证了公平性。
- 智能合约是一种基于区块链技术的自动化合约,可以在没有第三方的情况下执行交易。智能合约是在区块链上编写的代码,可以自动执行合同条款,并在满足特定条件时触发交易。
- 智能合约的用途包括自动化交易、数字身份验证和去中心化应用程序。智能合约的发展历程可以追溯到1994年,当时Nick Szabo提出了“智能合约”的概念。
- 现在,智能合约已经成为区块链技术的核心组成部分之一,被广泛用于各种用途,包括自动化交易、数字身份验证和去中心化应用程序。
4 常见网站
- Binance:全球最大的比特币和加密货币交易平台之一,提供交易、存储和管理加密货币的服务。
- Coinbase:美国最大的比特币和加密货币交易平台之一,提供交易、存储和管理加密货币的服务。
- Kraken:欧洲最大的比特币和加密货币交易平台之一,提供交易、存储和管理加密货币的服务。
- Huobi:全球领先的数字资产交易平台之一,提供交易、存储和管理加密货币的服务。
- Bitfinex:全球最大的比特币和加密货币交易平台之一,提供交易、存储和管理加密货币的服务。
5 实战(自己构建一个区块链)
项目地址:https://gitee.com/Zifasdfa/blockchain-demo
5.1 Block
package core
import (
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/hex"
"time"
)
// Block : define Block struct
type Block struct {
Index int64 //区块编号
Timestamp int64 //区块时间戳
PreBlockHash string //上一个区块的hash值
Hash string //当前区块hash值
Data string //区块数据
}
// calculateHash: calculate hash(index + timestamp + preBlockHash + data)
func calculateHash(b Block) string {
blockData := string(b.Index) + string(b.Timestamp) + b.PreBlockHash + b.Data
//hash step
hashInBytes := sha256.Sum256([]byte(blockData))
return hex.EncodeToString(hashInBytes[:])
}
// GenerateNewBlock : Generate new block
func GenerateNewBlock(preBlock Block, data string) Block {
newBlock := Block{}
newBlock.Index = preBlock.Index + 1
newBlock.PreBlockHash = preBlock.Hash
newBlock.Timestamp = time.Now().Unix()
newBlock.Data = data
//the block hash contains the data , so we should calculate the hash in the end
newBlock.Hash = calculateHash(newBlock)
return newBlock
}
// GenerateGenesisBlock first block int blockchain world
func GenerateGenesisBlock() Block {
//the first block's preBlock is not exist, so the index is -1 and the hash is empty str
preBlock := Block{}
preBlock.Index = -1
preBlock.Hash = ""
return GenerateNewBlock(preBlock, "Genesis Block")
}
5.2 BlockChain
package core
import (
"fmt"
"log"
)
type Blockchain struct {
Blocks []*Block
}
func NewBlockchain() *Blockchain {
//build the head block
genesisBlock := GenerateGenesisBlock()
blockChain := Blockchain{}
blockChain.AppendBlock(&genesisBlock)
return &blockChain
}
// SendData : record the data
func (bc *Blockchain) SendData(data string) {
preBlock := bc.Blocks[len(bc.Blocks)-1]
newBlock := GenerateNewBlock(*preBlock, data)
bc.AppendBlock(&newBlock)
}
// AppendBlock : add a new block
func (bc *Blockchain) AppendBlock(newBlock *Block) {
if len(bc.Blocks) == 0 {
bc.Blocks = append(bc.Blocks, newBlock)
return
}
//the newBlock should be added in the end of BlockChain
if isValid(*newBlock, *bc.Blocks[len(bc.Blocks)-1]) {
bc.Blocks = append(bc.Blocks, newBlock)
} else {
log.Fatal("invalid block")
}
}
// judge the block if valid
func isValid(newBlock Block, oldBlock Block) bool {
//fmt.Println("newBlock=", newBlock)
//fmt.Printf("Index: %d\n", newBlock.Index)
//fmt.Printf("Pre.Hash: %s\n", newBlock.PreBlockHash)
//fmt.Printf("Curr.Hash: %s\n", newBlock.Hash)
//fmt.Printf("Data: %s\n", newBlock.Data)
//fmt.Printf("Timestamp: %d\n", newBlock.Timestamp)
//fmt.Println("=================")
fmt.Println("oldBlock=", oldBlock)
//fmt.Printf("Index: %d\n", oldBlock.Index)
//fmt.Printf("Pre.Hash: %s\n", oldBlock.PreBlockHash)
//fmt.Printf("Curr.Hash: %s\n", oldBlock.Hash)
//fmt.Printf("Data: %s\n", oldBlock.Data)
//fmt.Printf("Timestamp: %d\n", oldBlock.Timestamp)
//index is err
if newBlock.Index-1 != oldBlock.Index {
//fmt.Printf("newBlock.Index-1 != oldBlock.Index, newBlock.Index-1:%v, oldBlock.Index:%v\n", newBlock.Index-1, oldBlock.Index)
return false
}
if newBlock.PreBlockHash != oldBlock.Hash {
//fmt.Printf("newBlock.PreBlockHash != oldBlock.Hash, newBlock.PreBlockHash:%v, oldBlock.Hash:%v\n", newBlock.PreBlockHash, oldBlock.Hash)
return false
}
if calculateHash(newBlock) != newBlock.Hash {
//fmt.Printf("calculateHash(newBlock) != newBlock.Hash, calculateHash(newBlock):%v, newBlock.Hash:%v\n", calculateHash(newBlock), newBlock.Hash)
return false
}
return true
}
func (bc *Blockchain) Print() {
for _, block := range bc.Blocks {
fmt.Printf("Index: %d\n", block.Index)
fmt.Printf("Pre.Hash: %v\n", block.PreBlockHash)
fmt.Printf("Curr.Hash: %v\n", block.Hash)
fmt.Printf("Data: %s\n", block.Data)
fmt.Printf("Timestamp: %d\n", block.Timestamp)
}
}
5.3 本地测试
package main
import (
"go_code/blockchain/core"
)
func main() {
bc := core.NewBlockchain()
bc.SendData("Send 1 BTC to Jack")
bc.SendData("Send 1 EOS to Mary")
bc.Print()
}
5.4 发布
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"go_code/blockchain/core"
"io"
"net/http"
)
// exposure the blockchain to the internet
var blockchain *core.Blockchain
func run() {
//get the blockchain info
http.HandleFunc("/blockchain/get", blockchainGetHandler)
//add the block(write the data)
http.HandleFunc("/blockchain/write", blockchainWriteHandler)
http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8888", nil)
}
func blockchainGetHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
bytes, err := json.Marshal(blockchain)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
io.WriteString(w, string(bytes))
}
func blockchainWriteHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
blockData := r.URL.Query().Get("data")
blockchain.SendData(blockData)
blockchainGetHandler(w, r)
}
func main() {
blockchain = core.NewBlockchain()
//start the serve
run()
}
- 测试
①首先在浏览器上输入URL访问我们的区块链
URL:
http://localhost:8888/blockchain/get
结果:

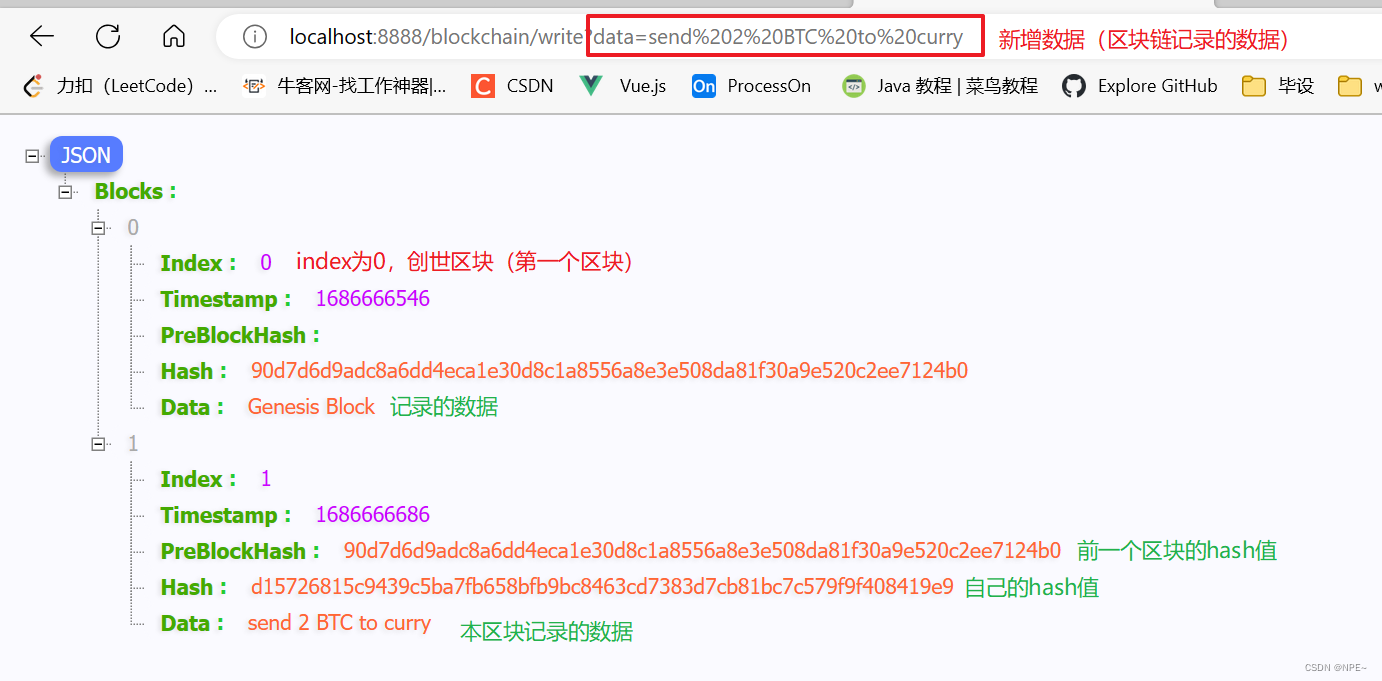
②新增区块,记录数据
在URL上执行:
http://localhost:8888/blockchain/write?data=send%202%20BTC%20to%20curry





















 615
615











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








