1.数据来源:
https://github.com/alexgkendall/SegNet-Tutorial
2.网络参数选择
输入尺寸:512*512
Epoch:100
损失函数:CEloss
pytorch实现segnet:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# from collections import OrderedDict
#Encoder模块
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Encoder,self).__init__()
#前13层是VGG16的前13层,分为5个stage
#因为在下采样时要保存最大池化层的索引, 方便起见, 池化层不写在stage中
self.stage_1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.stage_2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.stage_3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.stage_4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.stage_5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
)
def forward(self, x):
#用来保存各层的池化索引
pool_indices = []
x = x.float()
x = self.stage_1(x)
#pool_indice_1保留了第一个池化层的索引
x, pool_indice_1 = nn.MaxPool2d( 2, stride=2, return_indices=True)(x)
pool_indices.append(pool_indice_1)
x = self.stage_2(x)
x, pool_indice_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2, return_indices=True)(x)
pool_indices.append(pool_indice_2)
x = self.stage_3(x)
x, pool_indice_3 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2, return_indices=True)(x)
pool_indices.append(pool_indice_3)
x = self.stage_4(x)
x, pool_indice_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2, return_indices=True)(x)
pool_indices.append(pool_indice_4)
x = self.stage_5(x)
x, pool_indice_5 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2, return_indices=True)(x)
pool_indices.append(pool_indice_5)
return x, pool_indices
#SegNet网络, Encoder-Decoder
class SegNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super(SegNet, self).__init__()
#加载Encoder
self.encoder = Encoder()
#上采样 从下往上, 1->2->3->4->5
self.upsample_1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.upsample_2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.upsample_3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.upsample_4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(128, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.upsample_5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, num_classes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
)
def forward(self, x):
x, pool_indices = self.encoder(x)
#池化索引上采样
x = nn.MaxUnpool2d(2, 2, padding=0)(x, pool_indices[4])
x = self.upsample_1(x)
x = nn.MaxUnpool2d(2, 2, padding=0)(x, pool_indices[3])
x = self.upsample_2(x)
x = nn.MaxUnpool2d(2, 2, padding=0)(x, pool_indices[2])
x = self.upsample_3(x)
x = nn.MaxUnpool2d(2, 2, padding=0)(x, pool_indices[1])
x = self.upsample_4(x)
x = nn.MaxUnpool2d(2, 2, padding=0)(x, pool_indices[0])
x = self.upsample_5(x)
return x
3.网络结果:
各类iou指标:

预测结果:


4.总结:
预测会出现许多噪点,效果不太好,上述指标是在val上的结果,论文上指标好像是50几左右,整体来说还是unet比较扛一点,
用resnet_unet的miou都达到66%miou,
Biformer_tiny版本的unet更达到了72.4%的Miou。(参数量比rensnet_unet少一倍)

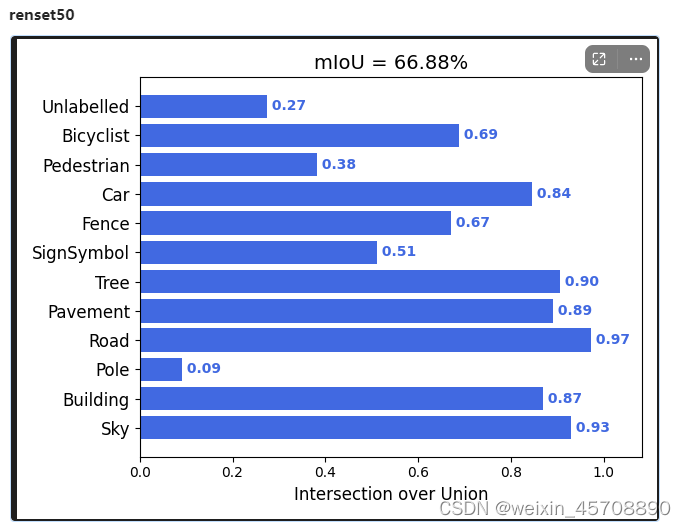







 文章介绍了使用Pytorch实现SegNet和Unet语义分割模型的过程,包括网络参数选择、编码器-解码器结构以及训练细节。在512*512的输入尺寸下,经过100个epoch的训练,SegNet的预测结果存在较多噪点,性能逊于Unet。ResNet-Unet和Biformer_tiny版本的Unet表现出更高的IoU指标,分别为66%和72.4%,显示了更好的分割效果。
文章介绍了使用Pytorch实现SegNet和Unet语义分割模型的过程,包括网络参数选择、编码器-解码器结构以及训练细节。在512*512的输入尺寸下,经过100个epoch的训练,SegNet的预测结果存在较多噪点,性能逊于Unet。ResNet-Unet和Biformer_tiny版本的Unet表现出更高的IoU指标,分别为66%和72.4%,显示了更好的分割效果。
 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44791964/article/details/108866828
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44791964/article/details/108866828















 6127
6127

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








