例题
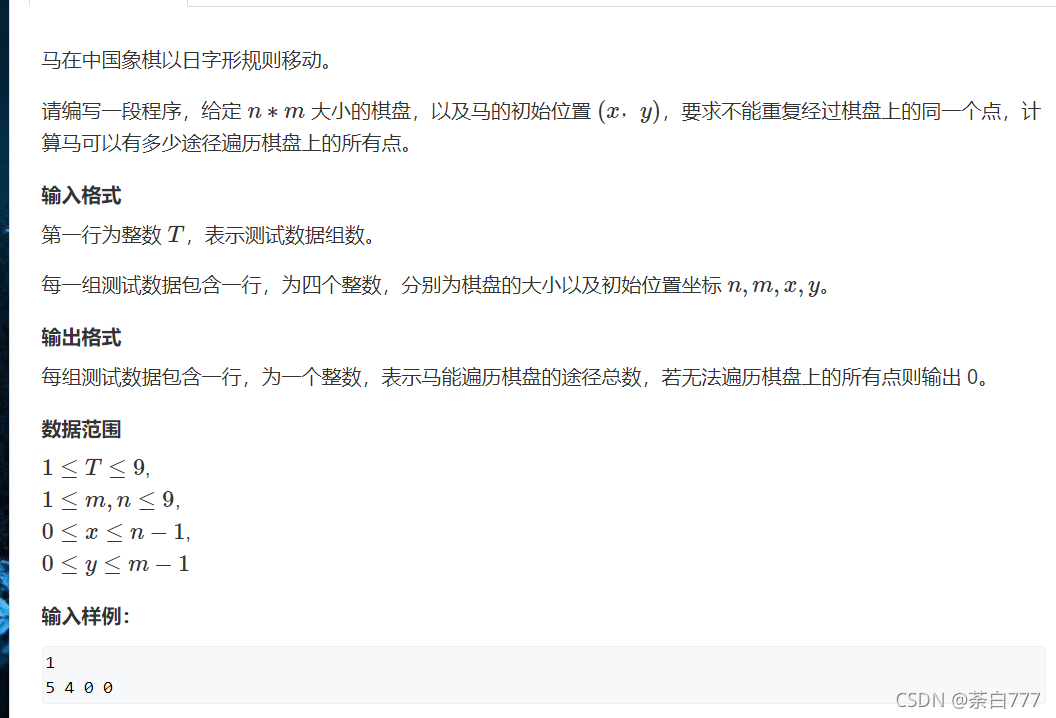
马走日
题面
思路
这题问的是方案数,因此我们需要回溯;
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e1 + 10;
int dx[] = {-2,-1,2,1,2,1,-1,-2};
int dy[] = {1,2,1,2,-1,-2,-2,-1};
int n,m,sx,sy,ans;
bool vis[N][N];
void dfs(int x,int y,int cnt){
if(cnt == n*m){
++ans;
return;
}
for(int i=0,xx,yy;i<8;++i){
xx = x + dx[i];
yy = y + dy[i];
if(xx < 1 || xx > n || yy < 1 || yy > m) continue;
if(vis[xx][yy]) continue;
vis[xx][yy] = 1;
dfs(xx,yy,cnt+1);
vis[xx][yy] = 0;
}
}
void solve(){
memset(vis,0,sizeof vis);
cin >> n >> m >> sx >> sy;
ans = 0;
++sx,++sy;
vis[sx][sy] = 1;
dfs(sx,sy,1);
cout << ans << '\n';
}
int main(){
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
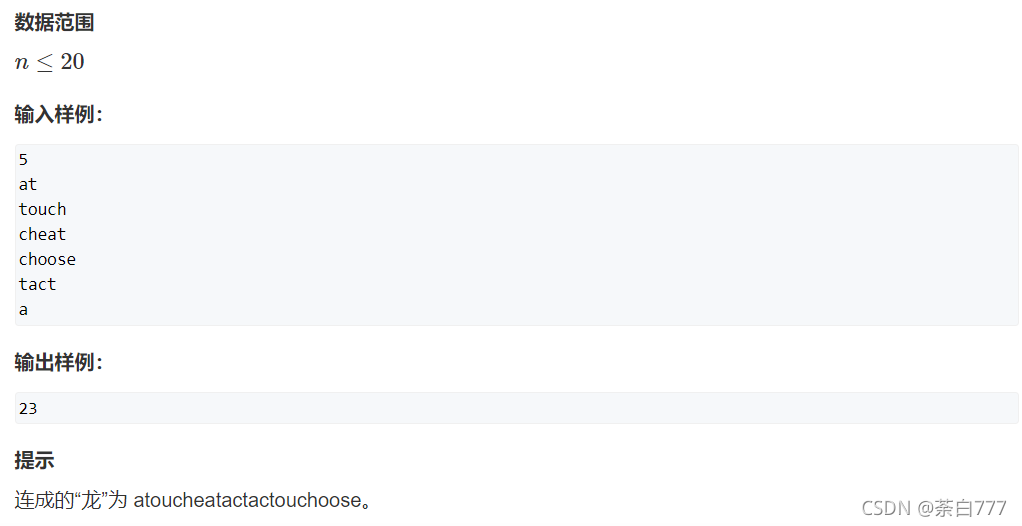
单词接龙
题面
思路
先预处理出任意两个字符串之间的最小覆盖是多少(因为我们想要龙尽可能的长)
随后暴力dfs即可;
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2e1 + 10;
string words[N];
int G[N][N];//G(i,j) 表示单词i后面接j的最小覆盖
int used[N],ans,n;
//"龙"是什么,最后接的谁
void dfs(string tot,int back){
ans = max(ans,(int)tot.size());
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
if(G[back][i] && used[i] < 2){
++used[i];
dfs(tot + words[i].substr(G[back][i]),i);
--used[i];
}
}
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) cin >> words[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j){
string &u = words[i],&v = words[j];
//不能是子集
for(int len=1;len<min(u.size(),v.size());++len){
//后缀匹配前缀
if(u.substr(u.size() - len,len) == v.substr(0,len)){
G[i][j] = len;
break; // 取最小重合
}
}
}
char start;
cin >> start;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
if(words[i][0] == start){
//一开始都是0次
++used[i];
dfs(words[i],i);
--used[i];
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
int main(){
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
分成互质组
题面
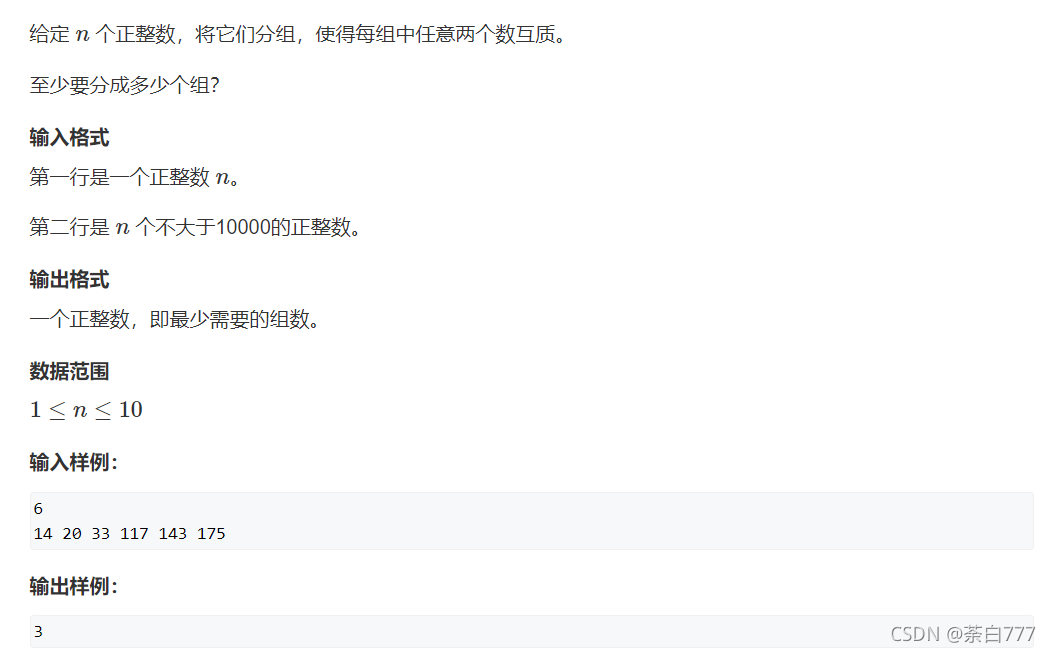
思路
对于每个数来说,有两种选择;
- 放入某一个已存在的组中
- 新开一个组
我们只需要将这两种情况枚举完,最后取一个min即可;
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e1 + 10;
int n,group; // 组数
vector<int> G[N];
int a[N],ans = 1e9;
int gcd(int x,int y){
return y ? gcd(y,x%y) : x;
}
bool check(int x,vector<int>& _group){ //x能否插入group中
for(int i=0;i<_group.size();++i){
if(gcd(x,_group[i]) > 1){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void dfs(int now){ //now代表是第几个数
if(group >= ans) return; //剪枝
if(now == n + 1){
ans = group;
}
for(int i=1;i<=group;++i){
if(check(a[now],G[i])){
G[i].push_back(a[now]);
dfs(now + 1);
G[i].pop_back();
}
}
G[++group].push_back(a[now]);
dfs(now + 1);
G[group--].pop_back();
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) cin >> a[i];
dfs(1);
cout << ans << '\n';
}
int main(){
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}























 98
98











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








